The scientific paper on evaluation of effect of burn-in process on reliability of X7R multilayer ceramic capacitors has been published by Penn State researchers.
Base metal electrode (BME) multilayer ceramic capacitors (MLCCs) continue to advance with higher volumetric capacitance, higher voltage, and higher temperature operational ranges with greater numbers of capacitors being manufactured and integrated into the electronic infrastructure of society. Many of these applications range from aerospace, transport, computation, medical, satellite, military, and the internet of things means the interdependence of these devices require higher reliability at a collective and individual component level.
Thus, determining the lifetime reliability of MLCCs is critical to provide more reliable components, and no weak links to the electrified infrastructure. For some of the more costly systems that support military and satellite systems, the reliability testing is very extensive.
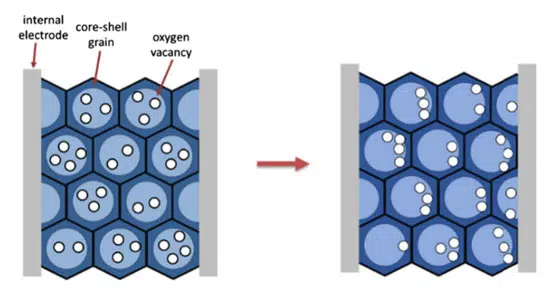
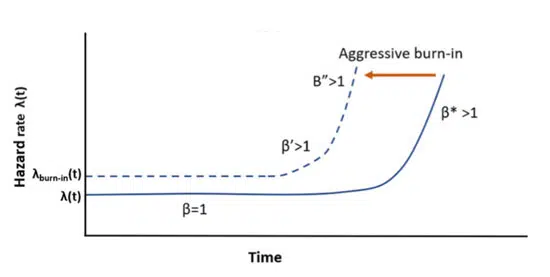
The burn-in test is a screening procedure used to remove components with higher probability of infant mortality failures. In this process, components are exposed to high temperatures and voltages relative to their design. The thermal stimulated depolarization current results revealed that burn-in test caused the intragranular and transgranular migration of oxygen vacancies, which will not be relaxed after the burn-in test.
Time to failure data obtained through in situ highly accelerated lifetime tests demonstrated that not only burn-in tests were ineffective at detecting infant mortality failures, but they also had a negative impact on reliability of BME MLCCs by creating a weak population. The electromigration of oxygen vacancies during burn-in tests shorten the lifetime of MLCC population by reducing the protection effects of double Schottky barriers at the grain boundaries and electrode interfaces.
Experimental
Commercial BME X7R MLCCs (1206 case size, 1 uF, and voltage rating (Vr) of 50 V) were used for this study to investigate the dynamics of oxygen vacancies and the associated space charge distribution during burn-in test.
Burn-in tests were carried out at 125 °C with DC fields of 2xVr for 168h and 4xVr for 21h, referred to as long and short burn-in tests in this study. For burn-in tests, these two extreme voltage conditions were chosen based on the MIL- PRF-32535A standard. After burn-in tests, the MLCCs were cooled to room temperature without maintaining the electric field.
Thermal stimulated depolarization current (TSDC) is a powerful technique for studying the relaxation kinetics of polarizable defects, and it was used to investigate the effect of the short and long burn-in tests on ionic space charge development, both intergranular (ionic charge pile up within individual grains) and transgranular (ionic transportation beyond each grain). After short and long burn-intests, TSDC was performed on screened samples; samples were then heated at a constant heating rate; and the leakage current from depolarization of the relaxing defects was measured.
Results and discussion
A burn-in test can lead to electromigration of oxygen vacancies that accumulate into metastable ionic space charge regions, and these in turn reduces the reliability of MLCCs by compromising the double Schottky barriers at the grain boundaries and electrode interfaces. TSDC measurements confirmed inter-granular and transgranular ionic space charge accumulation after burn-in tests.
These oxygen vacancies electromigration can weaken the protection effect of double Schottky barriers at the grain boundaries and electrode interfaces which eventually reduces MLCCs lifetime. The reduction in MLCCs lifetime was confirmed by comparing the mean time to failure (MTTF) and standard deviation (SD) values of samples before and after burn-in tests. Although the MTTF did not change significantly (dropped up to 18%) after burn-in tests, the SD values increased up to 130percent indicating that the TTF data are spread out, raising concerns about the consistency, predictability, and quality of BME MLCCs for applications requiring higher levels of reliability.
Conclusions
The burn-in test is a screening procedure used to eliminate weak components with a high likelihood of infant mortality and to produce uniform components for applications demanding higher levels of reliability.
We demonstrated that the costly burn-intest may be ineffective in identifying infant mortality failures, and it reduces the reliability and lifetime of BME MLCCs through intragranular and transgranular electromigration of oxygen vacancies which may not relax after the burn-in test.
These oxygen vacancies electromigration creates a weak population of BME MLCCs that may fail much sooner than expected, resulting in a subsystem or system failure.
Read more at: Yousefian, P., Randall, C.A. Determining the effect of burn-in process on reliability of X7R multilayer ceramic capacitors. J Mater Sci (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-022-07623-9