Researchers from KIT, Germany published their study on supercapacitor performance: “Impact of the Channel Length in Nanoporous Electric Double-Layer Capacitors on the Charge Transport Explored by Metal–Organic Framework Films” in ACS Physical Chemistry Journal.
This study explores the impact of channel length in nanoporous electric double-layer supercapacitors (EDLCs) using metal-organic framework (MOF) films.
Cu3(HHTP)2 films of varying thicknesses were deposited on substrates and used as working electrodes in EDLCs with aqueous KCl and pure ionic liquid electrolytes.
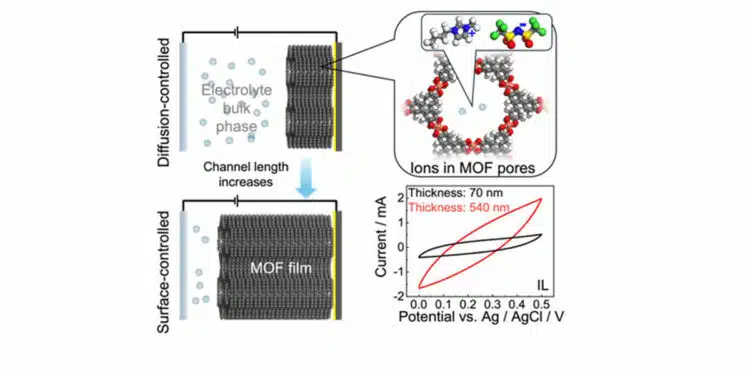
The study found that the scan-rate-dependent capacitance is proportional to the MOF film thickness, indicating accessible pore space.
Cu3(HHTP)2 SURMOF films were synthesized using a layer-by-layer dipping method on gold-coated silicon wafers. The films exhibited a dense, continuous morphology with a linear growth rate, with thickness increasing with the number of synthesis cycles. Electrochemical analysis showed nearly rectangular CV curves in KCl electrolyte, indicating excellent capacitive performance, while IL electrolyte exhibited spindle-shaped curves, reflecting a deviation from ideal double-layer capacitance.
The capacitance of MOF electrodes in KCl and IL electrolytes is proportional to film thickness, indicating homogeneous material. Analysis of scan rate-dependent capacitance reveals that the entire pore space is accessible to KCl ions, while IL ions are partially blocked. The capacitance per MOF surface area is constant for KCl but decreases for IL due to larger ionic sizes and kinetic effects.
The study synthesized 2D-cMOF Cu3(HHTP)2 films with varying thicknesses and evaluated their performance as working electrodes in EDLCs. The b-values, determined from the Randles–Sevcik equation, increased with film thickness, indicating a transition from diffusion-controlled to surface-controlled current behavior. The analysis of total capacitance showed that film thickness impacts capacitance, depending on the electrolyte, with highly mobile electrolytes like KCl benefiting from thicker films while less mobile electrolytes like IL require shorter channel lengths for optimal performance.
A review of supercapacitors with graphene/graphyne electrodes and various ionic liquids is presented. The study compares the performance of these supercapacitors using molecular dynamics simulations. The findings highlight the potential of graphene/graphyne electrodes in enhancing supercapacitor performance.
Key Points
Here are the key points extracted from the article:
- Objective:
- The study explores the impact of pore channel length (i.e., film thickness) in nanoporous electrodes on the performance of electric double-layer capacitors (EDLCs).
- Materials Used:
- Two-dimensional conductive metal–organic frameworks (MOFs), specifically Cu₃(HHTP)₂, were synthesized with precisely controlled thickness.
- Electrolytes Studied:
- Aqueous potassium chloride (KCl) solution.
- Pure ionic liquid (IL), [BMIM]⁺[TFSI]⁻.
- Key Findings:
- For KCl: Ion transport is primarily surface-controlled, even for thick films, leading to efficient charge kinetics. Capacitance per surface area remains constant irrespective of film thickness.
- For IL: Ion transport is diffusion-limited, and thicker films significantly decrease capacitance due to higher transport resistance.
- Channel length influences capacitance differently based on the electrolyte’s mobility.
- Methodologies:
- Cyclic voltammetry (CV) experiments were conducted to analyze ion transport and charge kinetics.
- Techniques such as Trasatti and Dunn’s methods were applied for capacitance evaluation.
- Applications:
- Insights aid in designing high-performance energy storage devices by balancing film thickness and electrolyte properties.
Conclusions
In summary, we synthesized 2D-cMOF Cu3(HHTP)2 films with varying thicknesses and evaluated their performance as working electrodes in EDLCs. By using two types of electrolytes, aqueous KCl and pure IL [BMIM]+[TFSI]−, we systematically investigated the impact of the channel length of the pores on the EDLC capacitance and the ion transport kinetics within the MOF electrodes. The CV data are analyzed by various methods, including those introduced by Trasatti and Dunn.
The determined b-value from the Randles–Sevcik equation increases with film thickness, indicating a transition from diffusion-controlled to surface-controlled current behavior, highlighting the growing influence of surface processes in thicker films. The analysis of the total capacitance shows that, while the entire pore space seems to be accessible by the ions of the electrolyte, the film thickness (i.e., the channel length) can have a dramatic impact on the capacitance, depending on the electrolyte.
For highly mobile aqueous KCl solution, the capacitance per specific MOF surface area is not affected by the film thickness; thus, thicker films result in larger capacitances normalized to the substrate area. On the other hand, using IL as the electrolyte shows a strong diffusion transport limitation, which results in decreasing performance with increasing channel length. This study provides valuable insights into the design and optimization of electrodes made of 2D c-MOF and also other materials for energy storage applications.
In future studies, the effect of the pore structure and functionality along with electrolyte optimization needs to be explored in combination with the effect of the channel length. This will allow us to develop the ideal material for high-performance supercapacitors and other energy storage technologies.
Read the full article here: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsphyschemau.4c00104