Researchers from China published its article “Giant energy storage density with ultrahigh efficiency in multilayer ceramic capacitors via interlaminar strain engineering” published in Nature Communications Journal.
This research introduces a new method for improving the energy storage capabilities of multilayer ceramic capacitors (MLCCs). The core innovation involves a heterogeneous layer structure, where different antiferroelectric (AFE) materials are laminated together.
This “interlaminar strain engineering” leverages the electrostrictive effect to control domain size and polarization behavior within the materials, leading to significantly enhanced energy storage density and efficiency compared to conventional MLCC designs. The resulting MLCCs exhibit a combination of high energy storage density, ultrahigh energy efficiency, and excellent stability across various temperatures and frequencies.
Key Concepts and Findings:
- The Problem: Dielectric capacitors, particularly MLCCs, are essential for modern electronics due to their fast charge-discharge capabilities. However, their relatively low energy storage density limits device miniaturization. Simply increasing polarization in ferroelectric materials often leads to high energy loss (hysteresis) and overheating, making it impractical.
- The Solution: Interlaminar Strain Engineering
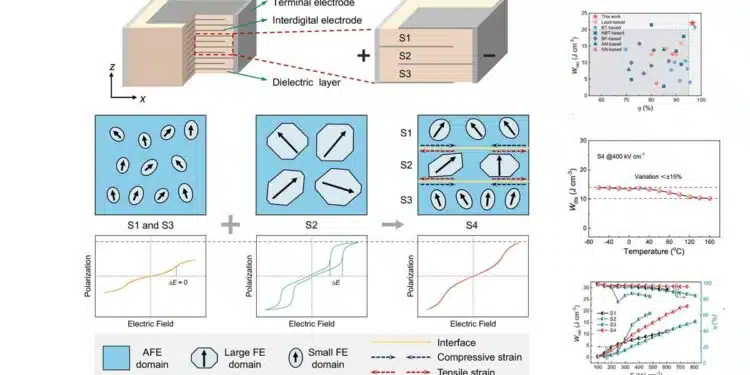
- The researchers designed MLCCs with alternating layers of three different AFE materials: PBLZST (S1), PBLZS (S2), and PCLZS (S3). These materials have complementary properties regarding polarization, hysteresis, and breakdown strength.
- The key is that each AFE material layer responds differently to applied electric fields, resulting in strain.
- The in-plane tensile strain decreased the domain size of S2 to depress its hysteresis while the in-plane compressive strain increases the polarization of S1 and S3
- This architecture allows for optimizing the overall energy storage performance.
- How It Works:
- When an electric field is applied, each layer experiences a different strain due to the electrostrictive effect. This interlaminar strain modifies the domain structure and polarization behavior of each material.
- Specifically, the in-plane tensile strain in S2 reduces the domain size and thus its hysteresis, while the in-plane compressive strain in S1 and S3 increases their polarization.
- The researchers used phase-field simulations to model and understand these strain-induced effects on domain evolution and polarization.
- Key Results:
- The novel MLCC (S4) achieves an exceptional recoverable energy density of 22.0 J/cm3 with an ultrahigh energy efficiency of 96.1%.
- This is the highest reported energy density for MLCCs with efficiency exceeding 95%.
- The MLCC demonstrates excellent temperature stability (meeting X8R industrial standards), frequency stability, and cycling stability (antifatigue).
- Charge-discharge measurements confirm its fast discharge capability and high discharge energy density.
Key Points:
- Problem: Low energy density in MLCCs limits miniaturization; high polarization often linked to high energy loss (hysteresis).
- Solution: Heterogeneous layer structure with interlaminar strain engineering.
- Materials: Three AFE compositions: (Pb0.9Ba0.04La0.04)(Zr0.65Sn0.3Ti0.05)O3 (S1), (Pb0.95Ba0.02La0.02)(Zr0.6Sn0.4)O3 (S2), and (Pb0.92Ca0.06La0.02)(Zr0.6Sn0.4)0.995O3 (S3).
- Mechanism: Electrostrictive effect generates interlaminar strain; tensile strain reduces hysteresis in one layer (S2), compressive strain enhances polarization in others (S1, S3).
- Key Result: High energy density (22.0 J/cm3) AND ultrahigh efficiency (96.1%) achieved simultaneously.
- Stabilities: Excellent temperature, frequency, and cycling stability demonstrated.
- Importance: Near-zero energy loss (ultrahigh efficiency) is crucial for practical MLCC applications to prevent overheating.
- Characterization: SEM, EDS, XRD, TEM, STEM, PFM, Dielectric measurements, Phase-field simulations, Charge-discharge testing
Conclusion:
This work provides a new design strategy for MLCCs that overcomes the trade-off between high energy density and low energy loss. The interlaminar strain engineering approach offers a promising pathway for developing high-performance capacitors for advanced power electronic systems.
Read the full paper:
Yang, Y., Xu, K., Yang, B. et al. Giant energy storage density with ultrahigh efficiency in multilayer ceramic capacitors via interlaminar strain engineering. Nat Commun 16, 1300 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-56605-3