OAK RIDGE, researchers at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory, the University of Tennessee and Texas A&M University demonstrated bio-inspired devices – memristors, memcapacitors and meminductors that accelerate routes to neuromorphic, or brain-like, computing.
Results published in Nature Communications report the first example of a lipid-based “memcapacitor,” a charge storage component with memory that processes information much like synapses do in the brain. Their discovery could support the emergence of computing networks modeled on biology for a sensory approach to machine learning.
“Our goal is to develop materials and computing elements that work like biological synapses and neurons—with vast interconnectivity and flexibility—to enable autonomous systems that operate differently than current computing devices and offer new functionality and learning capabilities,” said Joseph Najem, a recent postdoctoral researcher at ORNL’s Center for Nanophase Materials Sciences, a DOE Office of Science User Facility, and current assistant professor of mechanical engineering at Penn State.
The novel approach uses soft materials to mimic biomembranes and simulate the way nerve cells communicate with one another.
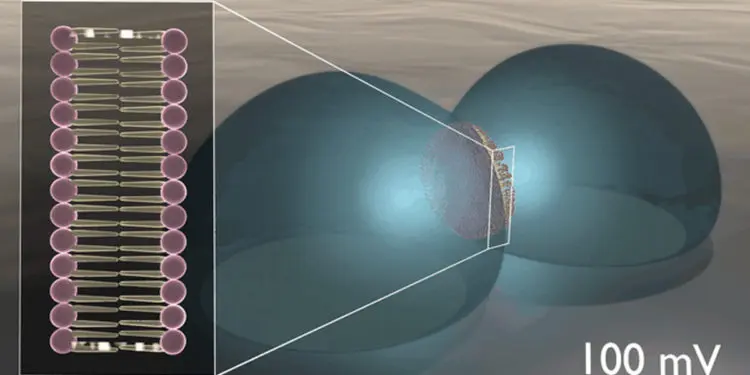
The team designed an artificial cell membrane, formed at the interface of two lipid-coated water droplets in oil, to explore the material’s dynamic, electrophysiological properties. At applied voltages, charges build up on both sides of the membrane as stored energy, analogous to the way capacitors work in traditional electric circuits.
But unlike regular capacitors, the memcapacitor can “remember” a previously applied voltage and—literally—shape how information is processed. The synthetic membranes change surface area and thickness depending on electrical activity. These shapeshifting membranes could be tuned as adaptive filters for specific biophysical and biochemical signals.
“The novel functionality opens avenues for nondigital signal processing and machine learning modeled on nature,” said ORNL’s Pat Collier, a CNMS staff research scientist.
A distinct feature of all digital computers is the separation of processing and memory. Information is transferred back and forth from the hard drive and the central processor, creating an inherent bottleneck in the architecture no matter how small or fast the hardware can be.
Neuromorphic computing, modeled on the nervous system, employs architectures that are fundamentally different in that memory and signal processing are co-located in memory elements—memristors, memcapacitors and meminductors.
These “memelements” make up the synaptic hardware of systems that mimic natural information processing, learning and memory.
Systems designed with memelements offer advantages in scalability and low power consumption, but the real goal is to carve out an alternative path to artificial intelligence, said Collier.
Tapping into biology could enable new computing possibilities, especially in the area of “edge computing,” such as wearable and embedded technologies that are not connected to a cloud but instead make on-the-fly decisions based on sensory input and past experience.
Biological sensing has evolved over billions of years into a highly sensitive system with receptors in cell membranes that are able to pick out a single molecule of a specific odor or taste. “This is not something we can match digitally,” Collier said.
Digital computation is built around digital information, the binary language of ones and zeros coursing through electronic circuits. It can emulate the human brain, but its solid-state components do not compute sensory data the way a brain does.
“The brain computes sensory information pushed through synapses in a neural network that is reconfigurable and shaped by learning,” said Collier. “Incorporating biology—using biomembranes that sense bioelectrochemical information—is key to developing the functionality of neuromorphic computing.”
While numerous solid-state versions of memelements have been demonstrated, the team’s biomimetic elements represent new opportunities for potential “spiking” neural networks that can compute natural data in natural ways.
Spiking neural networks are intended to simulate the way neurons spike with electrical potential and, if the signal is strong enough, pass it on to their neighbors through synapses, carving out learning pathways that are pruned over time for efficiency.
A bio-inspired version with analog data processing is a distant aim. Current early-stage research focuses on developing the components of bio-circuitry.
“We started with the basics, a memristor that can weigh information via conductance to determine if a spike is strong enough to be broadcast through a network of synapses connecting neurons,” said Collier. “Our memcapacitor goes further in that it can actually store energy as an electric charge in the membrane, enabling the complex ‘integrate and fire’ activity of neurons needed to achieve dense networks capable of brain-like computation.”
The team’s next steps are to explore new biomaterials and study simple networks to achieve more complex brain-like functionalities with memelements.
The journal article is published as “Dynamical nonlinear memory capacitance in biomimetic membranes.” The research was conducted in part at the CNMS.
featured image: Researchers at ORNL’s Center for Nanophase Materials Sciences demonstrated first samples of capacitance in lipid-based biomimetic membranes. Credit: Michelle Lehman / Oak Ridge National Research Laboratory U.S. Dept. of Energy