This Würth Elektronik webinar dives into the fascinating world of miniaturization of printed circuit boards with embedded active and passive components.
The efficient use of ever smaller housing volumes and tiny surfaces is becoming increasingly important. Embedding technology is the proven solution to these challenges.
Find out more about the advantages and possibilities of embedding technologies using the case study of our physical PCB sample WEembed. Plagiarism protection and improved protection against environmental influences are included free of charge.
In our webinar we will offer you insights into:
- our WE.embed physical PCB sample and what you can learn from it
- the advantages of DEVICE.embedding technology
- the current standards of embedding technology and their application
Technical Article: Advanced Insights into PCB Device Embedding and Miniaturization
Introduction
Welcome to an in-depth exploration of device embedding, miniaturization, and reliability in printed circuit board (PCB) technology. This article captures critical insights from a recent webinar hosted by Andrea Schil featuring Yan Wolf, Head of the Advanced Solutions Center at WE Electronic Circuit Board Technology.
Overview of PCB Device Embedding
Device embedding in PCBs is a transformative technology that enhances miniaturization, functional reliability, and thermal management. The process strategically integrates components within PCB layers, optimizing space and improving performance.
Key Benefits of Device Embedding
- Miniaturization: Embedding components reduces board real estate requirements, enabling compact device designs without compromising functionality.
- Custom Packaging: Create bespoke packages for specific circuitry needs.
- Space Efficiency: Utilize internal PCB layers to add components beyond the surface.
- Performance & Functionality:
- Integrated Shielding: Embedded components benefit from natural EMI shielding using surrounding copper layers.
- Short Signal Paths: Reduced signal travel distances improve speed and reduce power loss.
- Anti-Plagiarism Measures: Concealing components within layers protects against reverse engineering.
- Reliability:
- Environmental Protection: Embedded components are less susceptible to moisture, mechanical stress, and temperature extremes.
- Enhanced Thermal Management: Better heat dissipation through direct copper contact.
Technical Process of Device Embedding
- Inner Layer Preparation:
- Structuring copper layouts.
- Applying solder resist to create solder windows for component placement.
- Surface finishing with modified chemical tin to aid soldering and adhesion.
- Component Assembly:
- Standard SMD processes for component placement.
- Rigorous cleaning protocols to ensure void-free lamination.
- Multilayer Stack-Up and Lamination:
- Use of prepregs with precision cutouts forming virtual cavities.
- High-pressure, vacuum-assisted lamination to encapsulate components seamlessly.
- Finishing Processes:
- Drilling, plating, and final outer layer structuring.
- Comprehensive testing tailored to project specifications (ICT, functional tests).
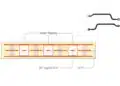
Case Study: PCB Sample “We Embed”
The sample features:
- Six Copper Layers with components embedded on layer 4.
- Component Variety: LEDs, resistors, capacitors, and active ICs in diverse packages (UDFN, TSSOP, QFN).
- Functional Demonstration: A running light circuit accessible via USB power.
Design Considerations and Testing
- Layer Count Flexibility: From minimal configurations to complex multi-layered designs.
- Component Thickness: Custom stack-ups accommodating various component heights.
- Testing Protocols: Defined collaboratively with clients to meet application-specific reliability standards.
Cost Implications
Costs are influenced by:
- Base PCB technology (rigid, flex, HDI).
- BOM specifics and component sourcing.
- Assembly complexity and testing requirements.
Conclusion
Device embedding significantly advances PCB design by enabling compact, high-performance, and reliable electronic solutions. For more information, technical guidelines, and sample requests, visit WE Electronic’s website or reach out to their technical support team.