Source: University of Missoury news
MU researchers developed a magnetic material that employs a unique structure – a “honeycomb” lattice that exhibits distinctive electronic properties and are working to commercialize it.
COLUMBIA, Mo. – Among the chief complaints for smartphone, laptop and other battery-operated electronics users is that the battery life is too short and—in some cases—that the devices generate heat. Now, a group of physicists led by Deepak K. Singh, associate professor of physics and astronomy at the University of Missouri, has developed a device material that can address both issues. The team has applied for a patent for a magnetic material that employs a unique structure—a “honeycomb” lattice that exhibits distinctive electronic properties.
“Semiconductor diodes and amplifiers, which often are made of silicon or germanium, are key elements in modern electronic devices,” said Singh, who also serves as the principal investigator of the Magnetism and Superconductivity Research Laboratory at MU. “A diode normally conducts current and voltage through the device along only one biasing direction, but when the voltage is reversed, the current stops. This switching process costs significant energy due to dissipation, or the depletion of the power source, thus affecting battery life. By substituting the semiconductor with a magnetic system, we believed we could create an energetically effective device that consumes much less power with enhanced functionalities.”
Singh’s team developed a two-dimensional, nanostructured material created by depositing a magnetic alloy, or permalloy, on the honeycomb structured template of a silicon surface. The new material conducts unidirectional current, or currents that only flow one way. The material also has significantly less dissipative power compared to a semiconducting diode, which is normally included in electronic devices.
The magnetic diode paves the way for new magnetic transistors and amplifiers that dissipate very little power, thus increasing the efficiency of the power source. This could mean that designers could increase the life of batteries by more than a hundred-fold. Less dissipative power in computer processors could also reduce the heat generated in laptop or desktop CPUs.
“Although more works need to be done to develop the end product, the device could mean that a normal 5-hour charge could increase to more than a 500-hour charge,” Singh said. “The device could also act as an ‘on/off switch’ for other periphery components such as closed-circuit cameras or radio frequency attenuators, which reduces power flowing through a device. We have applied for a U.S. patent and have begun the process of incorporating a spin-off company to help us take the device to market.”
The proposed startup company associated with this research, highlights the university’s impact on the state’s economic development efforts, including commercialization of research conducted at Mizzou, workforce development and job growth, quality of life improvements for residents, and attracting corporations and businesses to the state. Companies commercializing MU technologies have secured hundreds of millions of dollars in investments and grants to advance their commercialization efforts. In 2017, the Office of Technology Management and Industry Relations reported that 31 U.S. patents were issued to members of the MU community.
The studies, “Magnetic Diode Behavior at Room Temperature in 2D Honeycombs” and “Spin Solid versus Magnetic Charge Ordered State in Artificial Honeycomb Lattice of Connected Elements,” were published in Advanced Electronic Materials and Advanced Science, respectively. The U.S. Department of Energy, Office of Basic Energy Sciences (DE-SC0014461) provided funding for this research. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the funding agencies.
featured image:
Honeycomb Structure
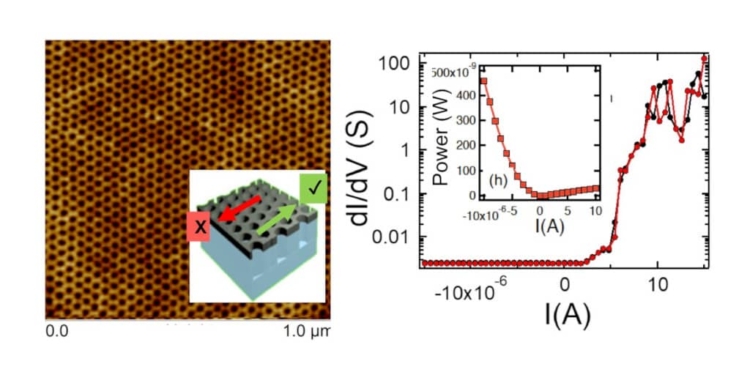
The left shows the atomic force micrograph, exhibiting honeycomb structure pattern behind a magnetic device. Inset shows the schematic of current flow direction. On the right: electrical data reveals diode-type behavior of current flowing in one direction. Inset shows that the dissipative power is of the order of nano-watt in the current flowing direction, which is at least three orders of magnitude smaller than the semiconductor diode. Credit: Deepak Singh