Nickel underplates in noble metal finishes provide another very important performance benefit that is not related to corrosion. The durability of noble metal finishes during connector mating and unmating is significantly improved by a nickel underplate.
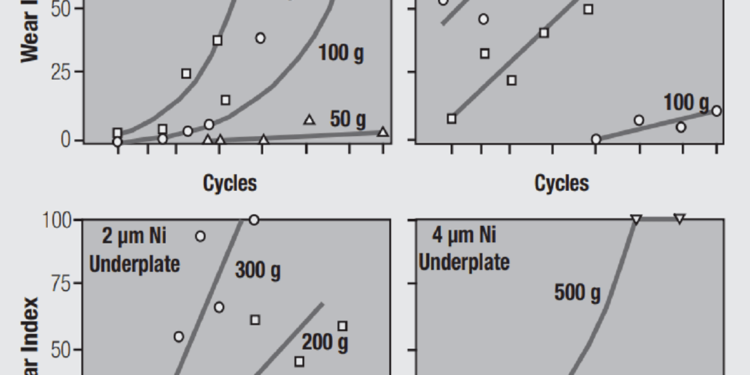
This improvement arises from the hardness of a nickel underplate as compared to that of a gold or palladium contact plating. Hard metals tend to be more wear resistant than softer materials and a nickel underplate increases the composite hardness of a noble metal finish system. This benefit is demonstrated by the data shown in Figure 2.9.
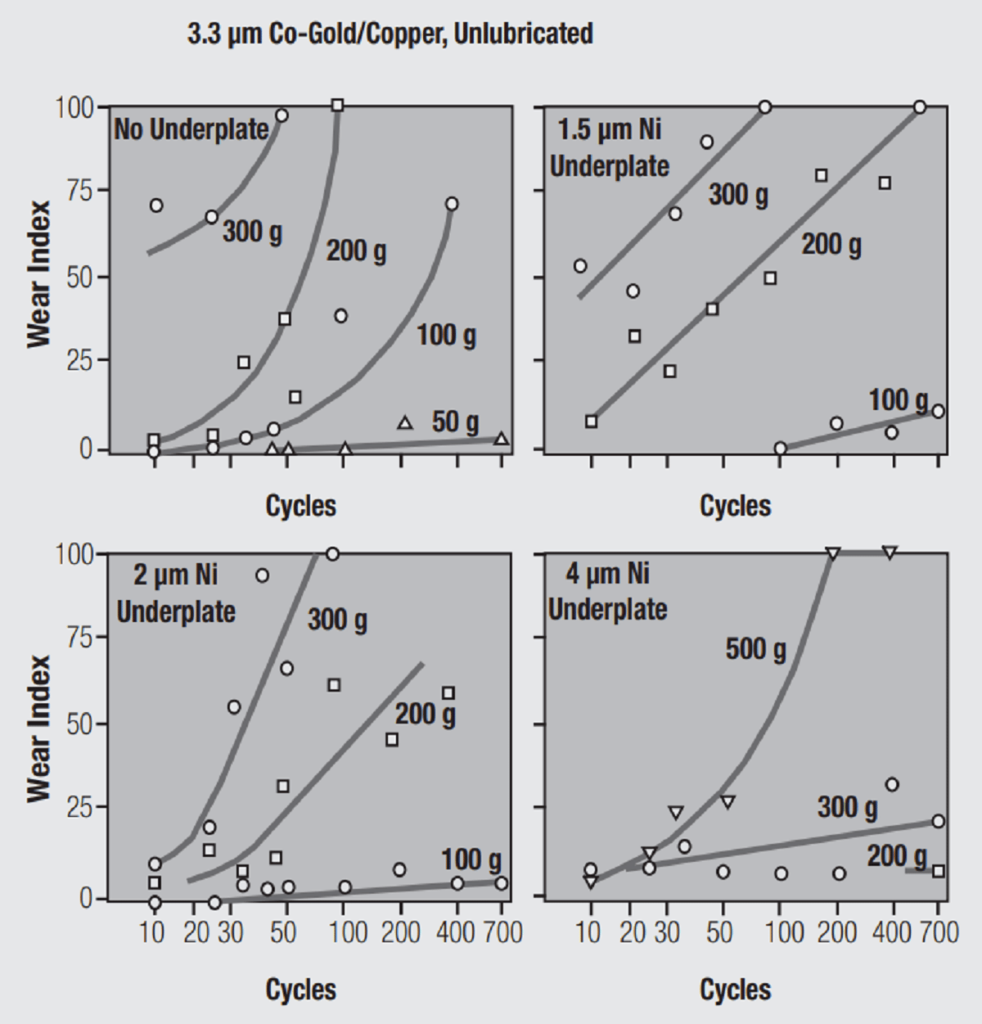
This figure is only one example of an extensive body of work on the durability of noble metal contact finishes carried out at Bell Telephone Laboratories in Murray Hill, New Jersey, USA during the 1970’s. At that time telecom applications were using gold thicknesses in the range of 3 µm (120 microinches) as indicated by the 3.3 µm (130 microinches) thickness in the figure. Note that this example was not intentionally lubricated. Four nickel thicknesses were tested, 0 µm, 1.5 µm (60 microinches), 2 µm (80 microinches) and 4 µm (160 microinches). The data are plotted as Wear Index versus the Number of Passes along the linear mechanically driven wear track. A wear index of 25 means that 25 percent of the length of the wear track showed exposed underplate or base metal, that is, all the gold was worn through in 25% of the track.
Consider the data for 200 gram contact force as a reference for this discussion. With no nickel, the entire wear track, 100 percent wear index, is worn through at about 50 passes. With 1.5 µm (60 microinches) of nickel, a 100 percent wear index occurs at about 600 passes. Extrapolating the data for 2 µm (80 microinches) indicates a wear index of about 85 at about 700 passes. Finally, at 4 µm (160 microinches) of nickel the wear index at 700 passes is about 20. Clearly, as the nickel thickness, and the composite hardness of the finish, increases the wear rate decreases significantly. As noted previously the 4 µm thickness approaches the upper limit of nickel thickness suitable for connectors.
Summary of Nickel Underplate Benefits
To summarize, a nickel underplate reduces:
• the sensitivity of the finish to porosity by passivating pore sites
• the rate of corrosion migration from exposed base metal edges and pore sites to the contact interface
• the rate of copper diffusion from the contact spring to the finish surface where the copper could react with the application environment
• the wear rate of the finish during mating or fretting cycles
Because of these benefits all noble metal contact finishes should include a nickel underplate with a thickness in the range of 1.25 to 2.5 µm (50 to 100 microinches).