Partial vias play a decisive role in the miniaturization of printed circuit boards. Learn more insights in this Würth Elektronik Webinar.
These are buried vias and microvias, which can be combined in different ways. We call microvias placed directly in solder pads “microvia-in-pad”. This saves valuable space, and since microvias are very small blind holes, they can also be integrated into very small solder pads. This is crucial for unbundling miniaturized or complex components such as micro BGAs.
In this webinar, learn more about
- our sample WE.microbga and what you can learn from it
- the current design rules of the MICROVIA.hdi technology and their application
- the routing of a BGA component with pitch 0.4 mm
- the advantages of MICROVIA.hdi technology in terms of signal integrity
- impedance calculations
Advances in HDI PCB Design: A Technical Overview
Introduction
High-Density Interconnect (HDI) technology is revolutionizing the electronic circuit board industry with its ability to support complex designs and high-speed data transmission. This article explores the intricacies of HDI Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs), focusing on the Microvia technology and its applications, as presented in a recent webinar hosted by Andrea Schil and featured expert Andreas Drea from V Electronic Circuit Board Technology.
Understanding HDI PCB Sample
The HDI PCB sample represents a typical industrial board used in automotive, sensor applications, and various machinery. It integrates power lines, memory chips, QFP components, and BGA units. A closer look reveals details hidden beneath the surface, such as specific impedance requirements, runtime matching, and complex stackups.
BGA Components and Routing Techniques
- Standard BGA (0.8 mm pitch): Utilizes through-hole drilling for routing, requiring multiple layers (typically 8-10) to accommodate all connections.
- Microvia BGA (0.4 mm pitch): Employs laser-drilled vias, significantly reducing the number of layers needed and saving space, thus lowering production costs.
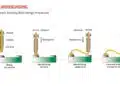
Stackup Configurations
Key features include:
- Buried Vias: Resin-filled for enhanced reliability.
- Staggered & Stacked Microvias: Optimized for different performance requirements.
- Galvanic Processes: Sequential layer additions with meticulous copper plating techniques ensure structural integrity.
Production Insights
Inner Layer Manufacturing
Starting with a copper-clad laminate:
- Photolithography: Defines circuit patterns.
- Etching: Removes excess copper, creating precise trace geometries.
Via Formation and Filling
- Laser Drilling: Achieves high precision for microvias without significant wear.
- Filling Processes: Utilize copper or resin to enhance conductivity and mechanical strength.
Cost Considerations
- Laser Drilling vs. Mechanical Drilling: While laser drilling has higher setup costs, it offers lower variable costs per via, making it cost-effective for high-density designs.
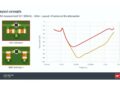
Impedance Control
Impedance is influenced by:
- Line Width and Layer Spacing: Primary factors in determining signal integrity.
- Material Properties: Dielectric constants play a secondary role.
V Electronic offers three levels of impedance services:
- Calculation: During the design phase.
- Manufacturing Control: Ensuring consistency across production.
- On-Panel Testing: Verifying impedance for each production batch.
Design Recommendations
- Utilize Microvias Extensively: Not just in BGA areas but across the board for cost efficiency.
- Optimize Line and Space Parameters: To enhance production yield and reduce costs.
- Early Collaboration: Engage with PCB manufacturers early to mitigate redesign efforts and ensure manufacturability.
Conclusion
Advancements in HDI technology, particularly Microvia and impedance control techniques, offer significant benefits in efficiency, performance, and cost. Early-stage collaboration with PCB manufacturers like V Electronic is crucial for optimizing these advantages in electronic circuit board designs.