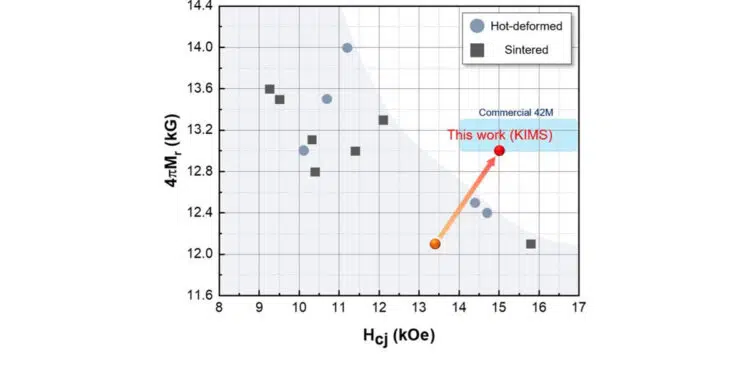
KIMS Korea Institute of Materials Science research team developed rare-earth-reduced permanent magnet that can achieve the commercial magnet (grade 42) level of performance while reducing the amount of neodymium (Nd), expensive rare earth, by about 30%.
A research team led by Dr. Lee Jeong Gu and Dr. Kim Tae Hun of the Department of Magnetic Materials in the Powder Materials Division at the Korea Institute of Materials Science, a government-funded research institute under the Ministry of Science and ICT, succeeded in developing rare-earth-reduced permanent magnet. The technology has a significant value as it achieved the commercial magnet-level of performance, which is currently used in the industry, even though it reduces the amount of high-priced rare earth.
Neodymium (Nd) is expensive and unstably supplied, but it has been inevitably used, as it is essential for manufacturing rare earth permanent magnets. In order to develop a neodymium (Nd) reduced permanent magnet, the content of cerium (Ce), an inexpensive element, has to be increased, instead of reducing the content of neodymium (Nd). Until now, with the increased content of cerium (Ce), it was not able to prevent the deterioration of the magnetic properties. The research team focused on clarifying the cause and mechanism of the deterioration of the magnetic properties caused by the increased cerium (Ce) content, and they successfully solve the problem of rare-earth-reduced permanent magnets by controlling atomic-scale microstructure.
The researchers discovered that unnecessary magnetic particles were formed in the existing manufacturing process, which are the cause of the deterioration of the magnet’s microstructure and magnetic properties. They improved the microstructure of magnets and enhance magnetic properties to prevent the formation of unnecessary magnetic particles by suppressing their atomic diffusion of them.
The research team applied the melt-spinning method and the hot-deformation method, which have very fast cooling velocity compared to the conventional process, to the manufacturing process of rare-earth-reduced precursors and permanent magnets, respectively. As a result, they succeeded in optimizing the microstructure of the magnet by suppressing the formation of unnecessary magnetic particles. In addition, they were able to simultaneously improve the residual magnetism and coercive force, which are the main properties of permanent magnets. As the residual magnetism and coercive force are in a trade-off relationship, the technology that improves both main properties is very useful and valuable.
The domestic market of the rare earth permanent magnets for high-efficiency motors is worth 186 billion won per year in 2021, but Korea depends on imports of the material. In the context of China’s weaponization of rare earth, Japan’s export restrictions on materials, and global carbon neutrality, localization of rare earth permanent magnet material is a must for Korea. When this technology is commercialized, it can be used in high value-added industries such as electric vehicles, drones, flying cars, and electric ships that require high-efficiency motors.
Dr. Kim Tae-hoon, a senior researcher at KIMS, who led the research team, said, “When the technology is commercialized, it will simultaneously solve the resource problems and material, parts, and equipment issues of the domestic rare earth permanent magnet material market. This is only the beginning. With further research in the future, we will spare no effort to lead the development of the domestic rare earth permanent magnet industry.”
This research was supported by the material technology development project of magnetic powder with performance modified composite magnetic structure, a fundamental research project of KIMS and funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT. In addition, on March 17th, the research outcome was published in Scripta Materialia, one of the world’s top 5 academic journals in the field of metal materials (The first author, Gayoung Kim, Ph.D. student, Title: High-performance Ce-substituted) (Nd0.7Ce0.3)-Fe-B hot-deformed magnets fabricated from amorphous melt-spun powders).