This article presents Samsung Electro-Mechanics’ lineup of compact, high-capacitance, low-ESL Multi-Layer Ceramic Capacitors (MLCCs) optimized for modern IVI architectures.
In-Vehicle Infotainment (IVI) systems are evolving beyond basic driving information displays to fully integrated entertainment and connectivity hubs. As high-resolution multi-display setups, V2X communication links, and advanced driver-and-passenger features become standard, processors demand rapid power-noise suppression and stable voltage rails under fast current transients.
Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) and autonomous driving technologies have redefined in-car electronics. IVI platforms now handle up to eight simultaneous high-resolution displays, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, emergency call services, and vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication. These complex tasks require System-on-Chips (SoCs) with high computing throughput and stringent power-integrity demands.
In-Vehicle Infotainment IVI Technology Trends
- Expansion from single driving-status displays to multi-monitor entertainment and passenger interfaces
- Integration of V2X, emergency call, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth networks
- Increasing reliance on real-time driver monitoring and voice-recognition engines
- Greater graphics throughput and low-latency data processing
MLCC Requirements for IVI
As IVI processors scale performance:
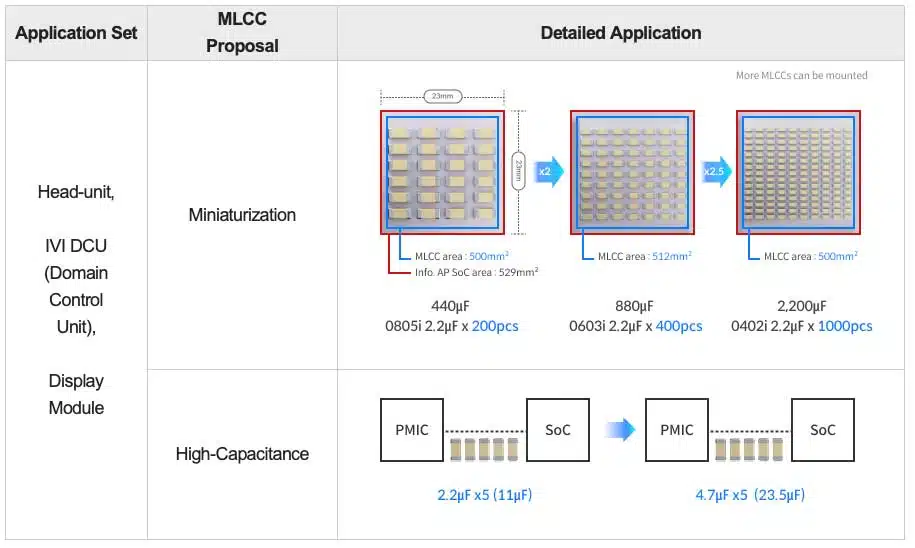
- Miniaturization becomes critical to accommodate more decoupling capacitors in limited PCB real estate.
- High capacitance per footprint ensures stable supply during rapid load changes.
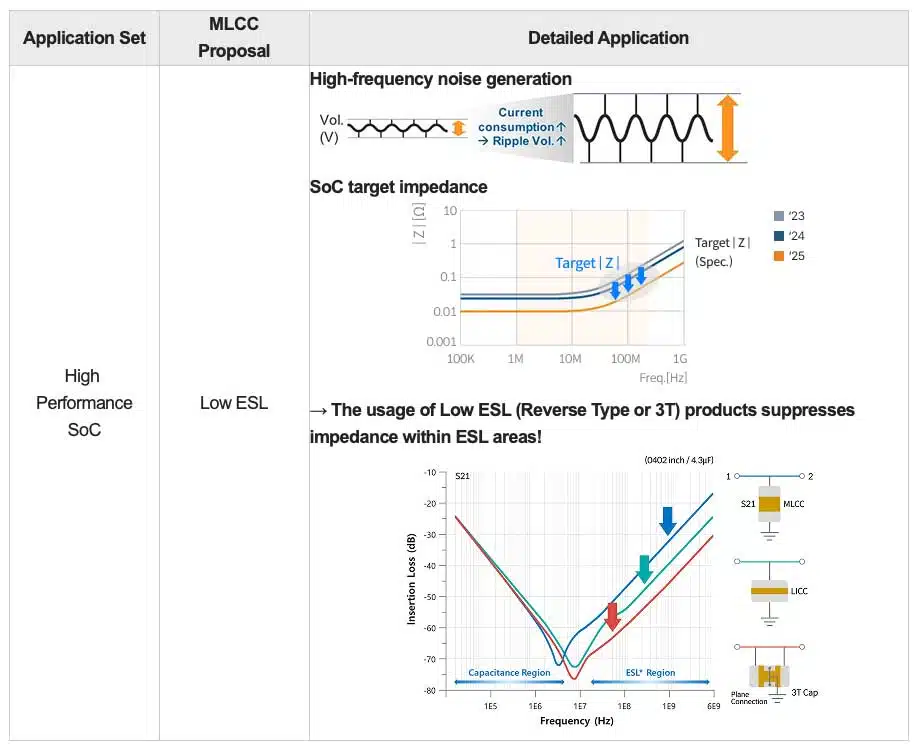
- Low equivalent series inductance (ESL) is essential for suppressing high-frequency noise on SoC power rails.
- Automotive-grade reliability (AEC-Q200) guarantees operation across temperature and vibration extremes.
Proposed MLCC Solutions
Miniaturized, High-Capacitance MLCCs for IVI Head-Units and Displays
Samsung Electro-Mechanics offers three dielectric series tailored for IVI:
| Series | Dielectric | Footprints | Capacitance Range | Voltage Ratings | Production Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X6S | X6S (AEC-Q200) | 0201, 0402 | 1 nF – 100 µF | 10 Vdc – 25 Vdc | Mass Production |
| X5R | X5R (AEC-Q200) | 0201, 0402 | 1 nF – 100 µF | 6.3 Vdc – 35 Vdc | Mass Production |
| C0G | C0G (AEC-Q200) | 0201, 0402 | 10 pF – 33 nF | 50 Vdc – 100 Vdc | Mass Production |
These MLCCs enable tighter power-rail decoupling around CPU cores and GPUs, maintaining low impedance from DC to hundreds of megahertz.
Low-ESL MLCCs for High-Performance SoCs
To address fast switching currents and high-frequency noise, Samsung Electro-Mechanics introduces two low-ESL designs:
| Type | Construction | Footprints | Capacitance | Voltage | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reverse Type | 2-Terminal | 0204 (0.22 mm), 0510 (0.30 mm), 0.53 mm | 47 nF, 1 µF, 2.2 µF | 2.5 V – 50 V | Mass Production & Under Development |
| 3-Terminal | 3-Terminal (3T) | 0402 /1005 (0.50 mm), 0603 /1608 (0.70 mm), 1.35 mm | 4.3 µF, 10 µF, 4.7 µF | 2.5 V – 16 V | Mass Production & Under Development |
These low-ESL MLCCs push the self-resonant frequency higher, sharply reducing impedance in the MHz-to-GHz region and ensuring SoC target-impedance requirements are met.
Technology Highlights
Samsung’s IVI-optimized MLCC portfolio leverages:
- Proprietary fine-particle ceramic dielectrics for maximized volumetric efficiency
- Advanced electrode materials to boost capacitance density
- Ultra-precision wafer stacking to achieve sub-0.2 mm thickness and consistent ESL performance
- Full AEC-Q200 qualification for automotive temperature and mechanical stress resilience
Detailed Product Lineup
| Part Number | Category | Size (inch/mm) | Capacitance | Dielectric | Rated Voltage | Samples & Data Sheet |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CL03C220JB31IN# | Infotainment | 0201 / 0603 | 22 pF | C0G | 50 Vdc | Available |
| CL03A105MOR1IN# | Infotainment | 0201 / 0603 | 1 µF | X5R | 16 Vdc | Available |
| CL03X105MPR1IN# | Infotainment | 0201 / 0603 | 1 µF | X6S | 10 Vdc | Available |
| CL05C102JB51IN# | Infotainment | 0402 / 1005 | 1 nF | C0G | 50 Vdc | Available |
| CL05A475MPQ1IN# | Infotainment | 0402 / 1005 | 4.7 µF | X5R | 10 Vdc | Available |
| CL05X475MQQ1IN# | Infotainment | 0402 / 1005 | 4.7 µF | X6S | 6.3 Vdc | Available |
| CLL5Z225MS21PN# | Low ESL (Reverse) | 0204 / 0510 | 2.2 µF | X7T | 2.5 Vdc | Available |
| CLL5Z105MR41PN# | Low ESL (Reverse) | 0204 / 0510 | 1 µF | X7T | 4 Vdc | Available |
| CL05Z105MR41PT# | Low ESL (3T) | 0402 / 1005 | 1 µF | X7T | 4 Vdc | Available |
Conclusion
Compact, high-capacitance, and low-ESL MLCCs are critical enablers for next-generation IVI systems. Samsung Electro-Mechanics’ proprietary materials and precision stacking technologies deliver automotive-grade components that support multi-display configurations, V2X communication, and high-frequency SoC decoupling.
For inquiries, documentation, or samples, please contact your Samsung Electro-Mechanics representative or submit requests through our product portal.
All listed MLCCs are AEC-Q200 qualified for automotive Infotainment applications.