Researchers from Tsinghua University, Beijing, China published their research on supercapacitors separators: “Separator with high ionic conductivity enables electrochemical capacitors to line-filter at high power” in Nature Communications Journal.
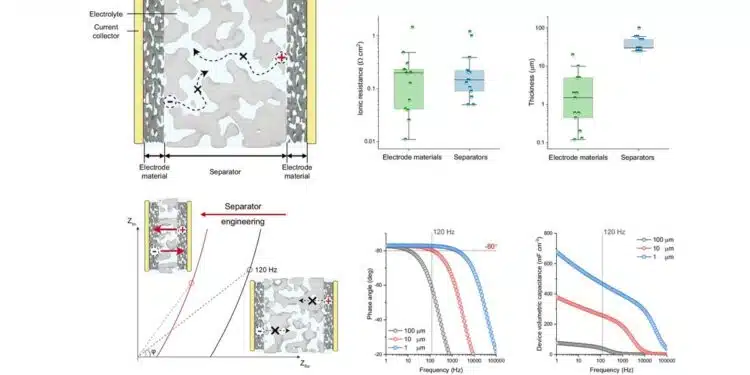
A 3 μm-thick thread-anchor structured separator (TAS) is developed for high-power line filtering supercapacitors – electrochemical capacitors (LFECs). TAS, featuring accelerated ionic transport and reliability, achieves a low ionic resistance of 25 mΩ cm2. With a phase angle of −80° at 120 Hz, the assembled device exhibits an areal capacitance of 6.6 mF cm−2, enabling high-power line filtering with steady ripple suppression and thermal control.
A thread-anchor structure (TAS) separator, composed of carbon nanotubes (CNFs) and graphene oxide (GO), was developed for electrochemical capacitors. TAS exhibits high tensile strength, low ionic resistance, and excellent stability, outperforming commercial separators. TAS-based electrochemical capacitors (TAS-LFECs) demonstrate superior frequency characteristics and capacitance, with a phase angle of -81° and capacitance of 4.8 mF cm-2 at 120 Hz, making them suitable for line filtering applications.
A highly ionic conductive separator with a thread-anchor structure (TAS) was designed for line-filtering electrochemical capacitors. TAS enables low resistance and high capacitance, achieving 240 mF cm−2 without frequency response decay. This allows for high-power line filtering with reasonable ripple suppression, outperforming commercial electrolytic capacitors.
This study details the fabrication and characterization of a novel line-filtering electrochemical capacitor (LFEC) using graphene oxide (GO) and PEDOT:PSS. The LFEC, integrated with a thin-film active separator (TAS), exhibits high areal capacitance and low resistance, making it suitable for AC line filtering. The study also includes theoretical simulations to understand the LFEC’s performance and optimize its design.
This study explores the use of laser-induced self-organization of TiN(x) nano-filament percolated networks for high-performance surface-mountable filter capacitors. The networks exhibit enhanced conductivity and capacitance, making them suitable for AC line filtering applications. The study also investigates the impact of water on the performance of these capacitors, highlighting the importance of understanding water dynamics for optimizing their functionality.
Key Points
- Challenges with Line-Filtering Electrochemical Capacitors (LFECs):
- LFECs have advantages over traditional electrolytic capacitors in line filtering but face limitations in high-frequency capacitance due to excessive ionic resistance.
- Significance of Separators:
- Separators play a crucial role in ion migration and capacitance. Conventional separators contribute significantly to ionic resistance, impacting device performance.
- Innovation – Thread-Anchor Structured Separator (TAS):
- A 3 μm-thick separator with thread-anchor architecture was developed, combining cellulose nanofibers (CNFs) and graphene oxide (GO) nanosheets.
- TAS features accelerated ionic transport and mechanical reliability, achieving a low ionic resistance of 25 mΩ cm².
- Key Electrochemical Achievements:
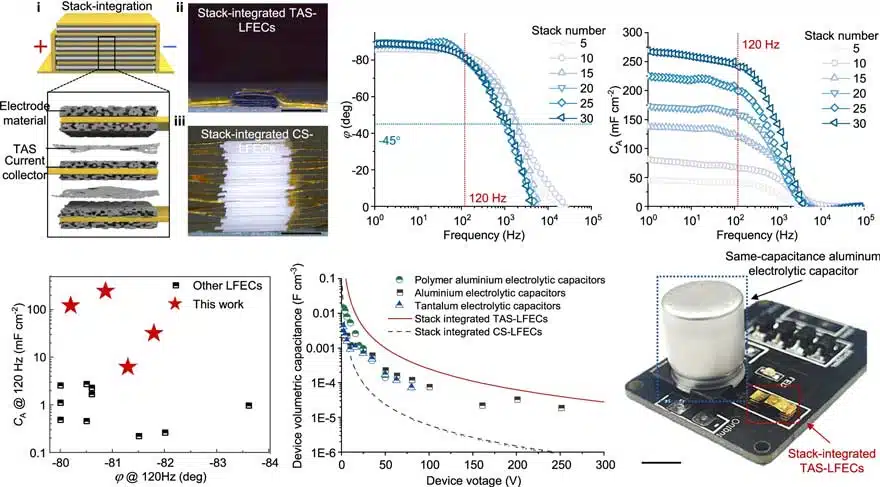
- TAS-enabled LFECs exhibit an areal capacitance of 6.6 mF cm⁻² with a phase angle of −80° at 120 Hz.
- The stack integration of TAS-LFECs in parallel improves capacitance by two orders of magnitude without compromising frequency characteristics.
- Practical High-Power Line Filtering:
- TAS-LFECs demonstrate effective ripple suppression for high-power line filtering, maintaining voltage ripple below 5% even with a load power density of 2.5 W cm⁻².
- Durability and Stability:
- TAS enhances separator integrity, reducing risks of rupture and ensuring stable performance over extended cycles and in acidic electrolytes.
- Broader Implications:
- This development emphasizes the importance of separator engineering for next-generation capacitors, enabling applications in high-power scenarios while reducing the device’s footprint.
Discussion
In this study, we proposed the significance of separators in line-filtering electrochemical capacitors. A highly ionic conductive separator is designed with a unique thread-anchor structure, which ensures both ionic transport and mechanical strength, realizing low resistance of down to 25 mΩ cm2. By employing it in the device, CA reaches 6.6 mF cm−2 with φ = −80° at 120 Hz and could be boosted to 240 mF cm−2 without frequency responses decay by TAS-enabled stack integration in parallel, overcoming the dilemma of thickening electrode materials. On this basis, high-power line filtering is achieved with reasonable ripple suppression. This work arouses a perspective on line-filtering electrochemical capacitors and promotes their practical applications for high-power scenarios.
Read the full original paper: Hu, Y., Li, P., Lai, G. et al. Separator with high ionic conductivity enables electrochemical capacitors to line-filter at high power. Nat Commun 16, 2772 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-58064-2