source: Electronics Weekly news
Spectrum’s AWG is helping the University of Tokyo create world’s highest indoor magnetic fields, writes Greg Tate
The International MegaGauss Science Laboratory is part of the Institute for Solid State Physics (ISSP) at the University of Tokyo.
Its objective is to study the physical properties of solid-state materials (such as semiconductors, magnetic materials, metals, insulators, superconducting materials) as they are subjected to ultra-high magnetic fields. The fields are also used for researching new materials and controlling their phase and functionality.
The laboratory’s pulse magnets can currently generate up to 87 Tesla (T) by non-destructive methods, and from 100T up to 760T (the world record for the strongest field generated indoors) by a destructive process.
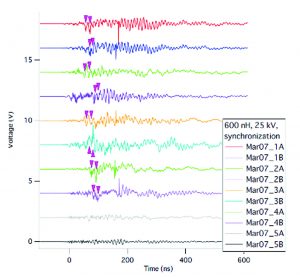
As part of a push to optimise the magnetic fields generated by the laboratory’s MegaGauss machine, it is important to synchronise the trigger events that fire banks of large capacitors.
Ideally, the capacitors all need to be triggered within 10ns of one another, so the laboratory must examine the trigger signals for each capacitor to determine their key characteristics and timing relationships. The MegaGauss machine also requires careful control as physical parameters restrict its firing to just a few shots per day.
To capture and analyse the trigger signals, ISSP required a fully synchronous, 10-channel digitiser system that delivers a single shot sampling rate in excess of 1GS/s. The high sampling rate allows the shape and frequency content of individual trigger pulses to be revealed, while fully synchronous sampling ensures inter‑channel timing measurements can be consistently made with sub‑nanosecond precision.
A further complication is the fact that the MegaGauss machine generates dangerously high magnetic fields that are potentially unsafe and can easily interfere with the measuring instrumentation. Great care needs to be taken to shield both equipment and operators.
The measurement system needs to be located in the laboratory while the operator adjusts and monitors the experiments from the safety of a control room. The digitiser system must be able to operate remotely and be controlled over the laboratory’s network.
Spectrum Instruments’ DN6.221-12 ‘digitizerNetbox’ system met all the technical requirements, offering 12 fully synchronous channels, each sampling at 1.25 GS/s. As it is LXI-compliant the instruments allows full remote-control and data transfer over a G-bit Ethernet connection.
The units also come with SBench 6-Pro software that allows the user to quickly set up the system and start making measurements. The software has an easy-to-use GUI that allows multi-channel waveform display, data analysis and documentation.
Acquired and analysed signals can be stored and exported to other devices, or other software programs, in a number of formats, including MatLab, ASCII, binary and wave (Figure 1).
The Netbox system provides a turnkey solution to multi-channel acquisition. Users can select the desired number of digitiser channels, as well as setting fundamental specifications such as the sampling rate, resolution and on‑board acquisition memory.
The device provides a multi-channel data acquisition system that matches the requirements of ISSP. The system was quickly installed and integrated into the MegaGauss machine so that trigger timing measurements and analysis could be made with improved precision and detail. The laboratory now expects to be able to generate the highest ever indoor magnetic fields later in 2017.
featured image: Large capacitor banks are used to generate the ultra-high magnetic fields of the MegaGauss machine, source: University of Tokyo