source: Science Daily news
October 25, 2016, Vienna University of Technology. How can you produce a magnet with exactly the right magnetic field? A research team now has a solution: for the first time, they have created magnets with a 3D printer.
Today, manufacturing strong magnets is no problem from a technical perspective. It is, however, difficult to produce a permanent magnet with a magnetic field of a specific pre-determined shape. That is, until now, thanks to the new solution devised at TU Wien: for the first time ever, permanent magnets can be produced using a 3D printer. This allows magnets to be produced in complex forms and precisely customised magnetic fields, required, for example, in magnetic sensors.
Designed on a computer
“The strength of a magnetic field is not the only factor,” says Dieter Süss, Head of the Christian-Doppler Advanced Magnetic Sensing and Materials laboratory at TU Wien. “We often require special magnetic fields, with field lines arranged in a very specific way — such as a magnetic field that is relatively constant in one direction, but which varies in strength in another direction.”
In order to achieve such requirements, magnets must be produced with a sophisticated geometric form. “A magnet can be designed on a computer, adjusting its shape until all requirements for its magnetic field are met,” explains Christian Huber, a doctoral student in Dieter Süss’ team.
But once you have the desired geometric shape, how do you go about implementing the design? The injection moulding process is one solution, but this requires the creation of a mould, which is time-consuming and expensive, rendering this method barely worthwhile for producing small quantities.
Tiny magnetic particles in the polymer matrix
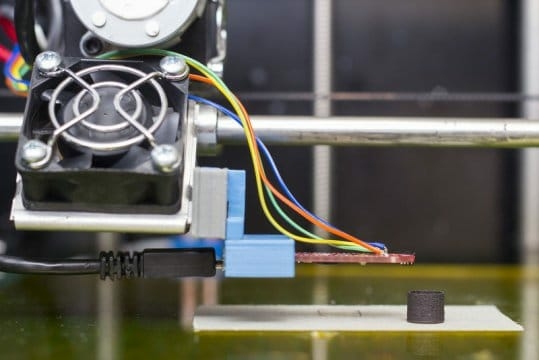
Now, there is a much simpler method: the first-ever 3D printer which can be used to produce magnetic materials, created at TU Wien. 3D printers which generate plastic structures have existed for some time, and the magnet printer functions in much the same way. The difference is that the magnet printer uses specially produced filaments of magnetic micro granulate, which is held together by a polymer binding material. The printer heats the material and applies it point by point in the desired locations using a nozzle. The result is a three-dimensional object composed of roughly 90% magnetic material and 10% plastic.
The end product is not yet magnetic, however, because the granulate is deployed in an unmagnetised state. At the very end of the process, the finished article is exposed to a strong external magnetic field, converting it into a permanent magnet.
“This method allows us to process various magnetic materials, such as the exceptionally strong neodymium iron boron magnets,” explains Dieter Süss. “Magnet designs created using a computer can now be quickly and precisely implemented — at a size ranging from just a few centimetres through to decimetres, with an accuracy of well under a single millimetre.”
A whole world of new possibilities
Not only is this new process fast and cost-effective, it also opens up new possibilities which would be inconceivable with other techniques: you can use different materials within a single magnet to create a smooth transition between strong and weak magnetism, for instance.
“Now we will test the limits of how far we can go — but for now it is certain that 3D printing brings something to magnet design which we could previously only dream of,” declares Dieter Süss.
featured image: A magnetic cup-like shape, created in the 3D-printer. Credit: Image courtesy of Vienna University of Technology