Kemet blog article describes EMI challenges and how to address it by EMI-Suppression capacitors.
One of the most enduring trends in the electronics industry is miniaturization. Advances in semiconductor technology, such as the implementation of wide-bandgap (WBG) MOSFET and diode devices, emphasize reducing the size of electronic components while significantly improving performance. Smartphones, wearables, and tablets are just a few examples of the numerous devices that utilize the latest semiconductor technologies. However, reliability remains a concern when components and devices downsize and become more compact.
Miniaturization is not only intended for mobile devices. The utilization of WBG semiconductor components in power conversion systems allows for smaller footprints and greater efficiency with lower energy losses during the energy conversion. Other key advantages include reducing audible noise and the miniaturization of passive components (all with the benefit of PCB real estate reduction).
However, due to the ever-increasing number of electronic components integrated into smaller geometries, miniaturized devices have become increasingly susceptible to electrical noise or interference. While the use of higher frequencies in WBG devices helps to minimize audible noise, it produces more high-frequency emissions and requires more complex designs to meet emission requirements by regulatory agencies. For these reasons, EMI suppression capacitors play a crucial role in the electronics industry, with the need for more miniaturized solutions under critical electrical and environmental applications.
Reliability Challenges Due to Miniaturization of Semiconductor Devices
Two significant concerns come from the miniaturization of power devices with high voltages and higher frequencies: more inductive noise and greater heat losses. These challenges can have a significant effect on the reliability and performance of electronic devices.
Along with miniaturization, many of these devices face the challenge of operating within severe environmental conditions throughout their extended lifespan. Specific examples include:
- Electric and hybrid vehicles expected to withstand higher temperatures and extreme thermal shock cycles.
- Miniaturized solar micro-inverters and smart energy meters with expected lifetimes of up to 25 years without servicing, in different field environments.
- Data and communication systems with less and less space to work with (and, therefore, higher power density per square foot requirements) to improve the efficiency of the electronic infrastructure.
Challenges of Metallized Polypropylene Film Technology in EMI Suppression Applications
In the latest EMI suppression film technology developments, manufacturers are achieving excellent protection of film elements by utilizing new materials and improving the capacitor manufacturing processes. In this way, products can withstand severe operating conditions that would otherwise lower their reliability and performance. However, enhancing the reliability levels under high temperature, humidity, and bias (THB) conditions in miniaturized capacitors can be particularly challenging.
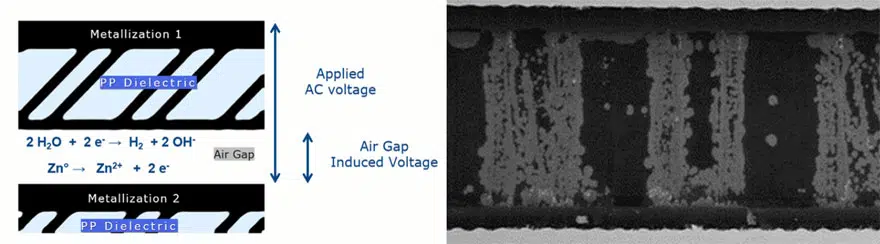
Metallized polypropylene film technology (MKP) is currently the mainstay of EMI suppression capacitor solutions due to its excellent high voltage per micron and ultra-low, stable DF capabilities. Perhaps most importantly, it also has the best self-healing properties compared to other film dielectric technologies. However, combining high temperature and humidity conditions often has a drastic effect on MKP material when an AC or DC voltage is applied, resulting in accelerated degradation and potentially catastrophic failures of the capacitors. The reason for this is the phenomena of electrochemical corrosion in the zinc metallization.
Stress Testing to Ascertain Reliability
A well-accepted accelerated life test standard for active and passive components in the electronic industry is the Temperature-Humidity-Bias (THB) test, with levels of 85°C and 85% relative humidity under AC or DC bias conditions. For many years, designers in various industries (including automotive, energy, consumer, and industrial) have used this test to ascertain the reliability of their final products for up to 25 years of operation under severe climatic conditions. More recently, the THB test has been recognized as an IEC standard for EMI suppression film capacitors.
The table below shows the different Temperature-Humidity-Bias (THB) testing conditions per IEC Standard:
| Grade | Test Condition A | Test Condition B |
|---|---|---|
| I | 40°C / 93% RH 21 days | 85°C / 85% RH 168 hours |
| II | 40°C / 93% RH 56 days | 85°C / 85% RH 500 hours |
| III | 60°C / 93% RH 56 days | 85°C / 85% RH 1,000 hours |
| Requirement | |
|---|---|
| Capacitance | |ΔC| ≤ 10% |
| Dissipation Factor | 0.024 for CN ≤ 1 μF 0.015 for CN > 1 μF |
| Insulation Resistance | > 50% of the applicable limits |
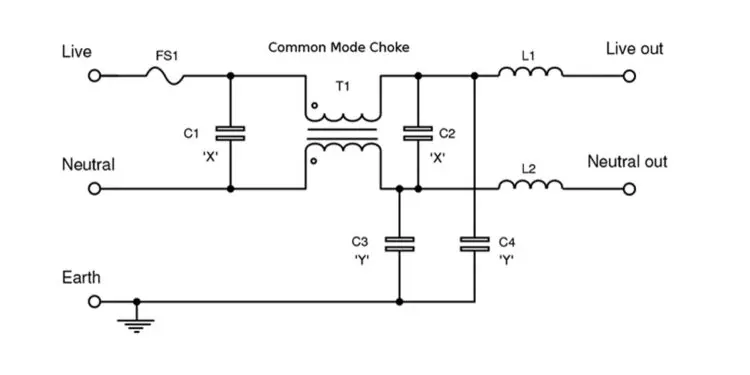
Designers needing to ensure that their products pass the THB evaluation and emission certification have encountered several challenges; for instance, it can be difficult to obtain the required technology and include multiple EMI suppression capacitors into already component-dense circuits. There are also higher power requirements within a limited board space to take into consideration. See below examples of circuit designs with a limited footprint surface for EMI suppression capacitors, X2 and Y2.
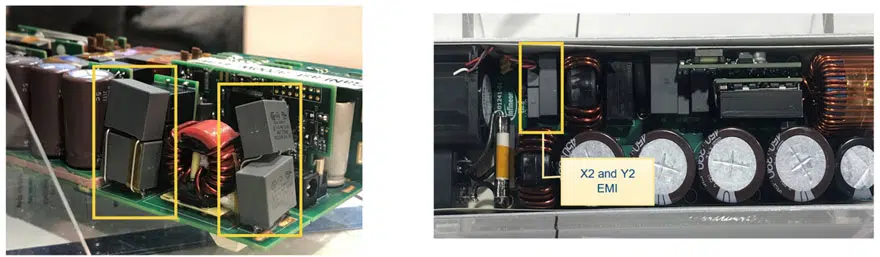
Miniaturizing Safety Capacitor Constructions: Challenges and Solutions
Some of the constraints of EMI suppression capacitors correlate to the film quality and protection surrounding it. The amount and type of resin used, the epoxy filling the surrounding of the capacitor element, and the material and thickness of the radial box encapsulating them all play vital roles in a product’s reliability. Moreover, there is a mechanical challenge in manufacturing capacitors with smaller capacitance values; lower capacitances require less film and metallization material, making the product more susceptible to damage due to humidity.
KEMET’s Solution: The R52 Miniaturized X2 Suppression Capacitor
KEMET’s R&D team has studied and experimented with unique solutions to address the challenges of designing EMI suppression capacitors that meet THB test requirements without sacrificing miniaturization and reliability. The first KEMET harsh environment solution was the F862, X2 series based on an enhanced MKP technology that met the AEC-Q200 qualification for automotive applications. The F863, X2, followed a few years later, providing a more compact and cost-driven solution for a consumer-oriented market.
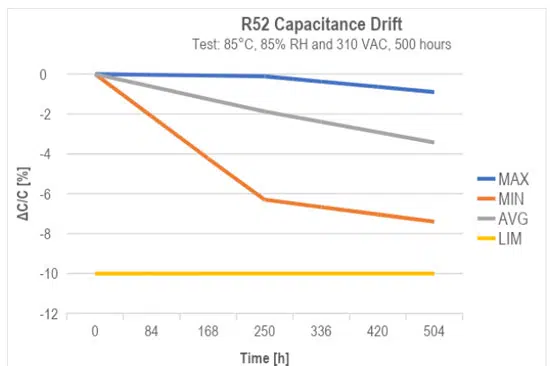
The latest EMI suppression solution from KEMET is its new R52, X2 capacitor with harsh environment capabilities, exceeding previous solutions and passing the latest IEC-60384-14 humidity robustness test with a Class IIB classification. It achieved 500 hours during an accelerated life test under 85°C and 85% relative humidity at rated voltage. See the image below for the maximum, average, and minimum capacitance drift for the R52 family.
The R52 series successfully passes stringent tests while also providing a solution for space-constrained applications. The table below shows a comparison of KEMET’s R52 technology with those of three competitors’ EMI solutions using one particular part number, a capacitance of 0.47 µF, and 15 mm lead spacing. On average, the R52 physical volume is 60% smaller than any other X2 solution with the same range of capacitance values in the market.
| Competitor X2 310 VAC | B x H x L (mm x mm x mm) | % In Volume vs. KEMET R52 X2 C: 0.47 µF, (9 x 12.5 x 18) |
|---|---|---|
| A | 11 x 19 x 17.5 | +81% |
| B | 11 x 18.5 x 18 | +81% |
| C | 13.5 x 22.5 x 18 | +170% |
The high capacitance and current capabilities of KEMET’s R52 allow it to function as an excellent EMI suppression solution both across and in series with the mains on high energy density designs requiring a high level of filtering capability on a broad spectrum of frequencies. A good example is in variable frequency drives and EV fast-charging systems where designers prefer to utilize high-capacitance, certified EMI suppression capacitors together with AC and DC filtering solutions to mitigate harmonic content on the output of the drives and converters. The R52 is also suited for use in capacitive power supplies and power line communication systems.
KEMET’s R52 EMI suppression capacitor is a first-to-market solution that provides an optimal balance of miniaturization and reliability in automotive, industrial, consumer, and energy applications. This product offers an ultra-high capacitance in a compact package for more board savings and lower application costs for engineers. Extensively tested for high reliability in harsh environments, KEMET’s R52 meets THB test requirements and passes the IEC-60384-14 humidity robustness test with a Class IIB classification. The R52 also meets AEC-Q200 qualification.