This paper based on post Samtec’s Cable Management in High‑Data‑Rate Applications offering a cbrief framework for engineers, technicians, and system integrators about the best practices for cable management in high-speed and high-density systems.
In the era of high‑data‑rate (HDR) and high‑speed electronic systems, cable management has evolved from a tidy‑up exercise into a critical engineering discipline. The way cables are routed, bent, twisted, labeled, and secured can have a measurable effect on signal integrity, thermal performance, and long‑term reliability.
1. Introduction
As data rates climb into the tens and hundreds of gigabits per second, the physical layer becomes increasingly sensitive to mechanical handling. A poorly routed cable can introduce impedance discontinuities, skew, and crosstalk, while also restricting airflow and creating serviceability headaches. In high‑density environments such as AI accelerators, hyperscale data centers, and advanced test systems, the stakes are even higher: downtime is costly, and rework is disruptive.
Cable management, therefore, is not just about aesthetics. It is about preserving the electrical and mechanical integrity of the interconnect over the system’s operational life. This requires a disciplined approach that considers bend radius, twist control, strain relief, slack allocation, labeling, and structured routing — all while anticipating future maintenance and upgrades.
2. Bend and Twist: The Mechanics of Signal Integrity
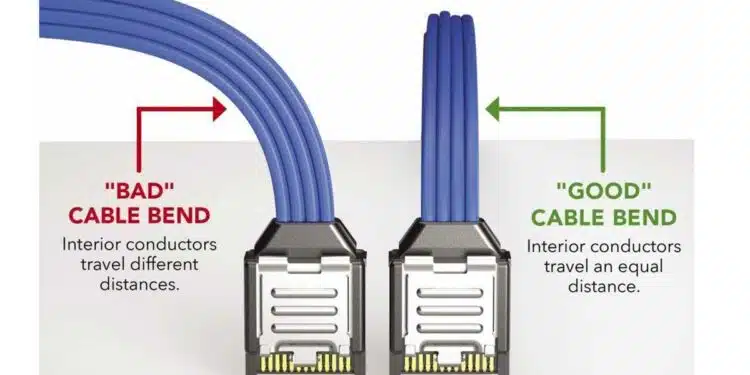
One of the most overlooked aspects of cable management is the geometry of bends and twists. Samtec’s guidance highlights a subtle but critical distinction between a “good” bend and a “bad” bend. In a good bend, the conductors inside the cable remain at consistent lengths, preserving timing alignment. In a bad bend — often caused by bending along the connector’s length — the inner and outer conductors travel different distances, introducing skew and degrading high‑speed performance.
The recommended practice is to first bend the cable in the optimal direction, then apply a controlled 90‑degree twist along the connector length. This twist should not be forced; instead, it should follow the cable’s natural lay, which is easier to achieve when cables are loosely bundled rather than tightly bound. Over‑tight bundling not only resists proper twisting but also increases mechanical stress and can deform the dielectric, altering impedance.
3. Stress Relief at Cable Exits
The point where a cable exits a connector is a mechanical weak spot. Sharp bends here can transfer stress directly to the termination, leading to intermittent faults or outright failure. Allowing cables to splay outward before routing them into a bend distributes mechanical load more evenly. This technique also enables tighter bend radii without exceeding the cable’s minimum bend specification, which is especially important for twinax and coax assemblies used in HDR applications.
4. Slack Management: Balancing Flexibility and Order
Slack is both a necessity and a liability. Too little slack, and cables may be strained during servicing or thermal expansion; too much, and they form loops that obstruct airflow and create clutter. The goal is to provide just enough slack to allow for connector mating/demating and minor re‑routing, while keeping the overall path taut and predictable. Horizontal and vertical cable managers, Velcro straps (preferred over zip ties for reusability and reduced compression), and modular routing panels can help maintain this balance.
5. Identification and Documentation
In complex systems, the time spent tracing an unmarked cable can dwarf the time spent replacing it. Industry standards such as ANSI/TIA‑606 recommend labeling both ends of every cable with durable, legible identifiers. Color coding can further speed identification, especially when differentiating between copper, fiber, and power lines. Beyond physical labels, maintaining an up‑to‑date cable map — ideally in a DCIM (Data Center Infrastructure Management) system or CAD model — ensures that changes are tracked and future work is streamlined.
6. Structured Routing and Pathways
Structured cabling principles apply equally inside a chassis as they do in a data hall. Separating power and data cables reduces electromagnetic interference (EMI) risk, while dedicated trays, raceways, and runways prevent accidental damage. For high‑density racks, it is wise to design pathways with 30–40% spare capacity to accommodate future expansion without re‑routing existing cables. Fiber optic cables, in particular, require careful routing to avoid microbending losses.
7. Thermal and Electrical Performance Considerations
Cable bundles can act as thermal insulators, trapping heat around active components. This is especially problematic in systems with high‑power GPUs, FPGAs, or CPUs, where every degree of cooling margin matters. Over‑bundling can also increase insertion loss by compressing the dielectric. Engineers should route cables to preserve airflow channels and, where possible, use perforated managers or open‑frame trays to promote convection.
From an electrical standpoint, improper bends or excessive mechanical stress can alter the characteristic impedance of high‑speed cables, leading to reflections and jitter. In HDR systems, even small impedance mismatches can cause measurable eye‑diagram closure, reducing link margin.
8. Standards and Compliance
Adhering to established standards ensures consistency and interoperability. ANSI/TIA‑606 provides a framework for labeling and administration, while TIA‑942 outlines best practices for data center cabling infrastructure. For product‑specific handling, always consult the manufacturer’s datasheets for parameters such as static and dynamic bend radius, flex life, and mating cycles.
9. Summary and Conclusion
- Consistent conductor lengths: Good bends keep all conductors on equal-length paths; bad bends force different path lengths and add skew.
- Bend plane vs connector plane: Good bends occur after the exit, in a single plane; bad bends “wrap” along the connector length.
- Bend-then-twist sequencing: Bend first, then apply a controlled 90° twist along the cable’s axis—not at the exit or through the connector.
- Stress relief at exits: Allow cable fan-out before routing; do not force tight turns immediately at the termination.
- Minimum bend radius: Honor datasheet values; when unspecified, use conservative planning like ≥10×OD for copper and fiber-safe radii for optics.
- Bundle pressure: Use low-compression ties (hook-and-loop), avoid over-tightening that deforms dielectric or jacket.
Cable management in high‑speed and high‑density environments is a convergence of mechanical engineering, electrical design, and operational foresight. By applying disciplined bend and twist techniques, relieving stress at exits, managing slack intelligently, labeling rigorously, and routing with structure, engineers can safeguard performance and reliability while simplifying maintenance. As data rates continue to climb, these practices will only grow in importance — transforming cable management from an afterthought into a core design consideration.