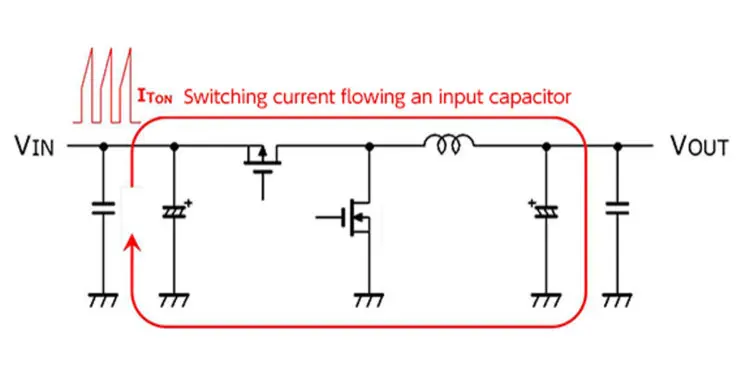
Continuous ripple current, power rating, transient/pulse capabilities etc. are the key parameters to consider for a proper capacitor selection in electric circuit design.
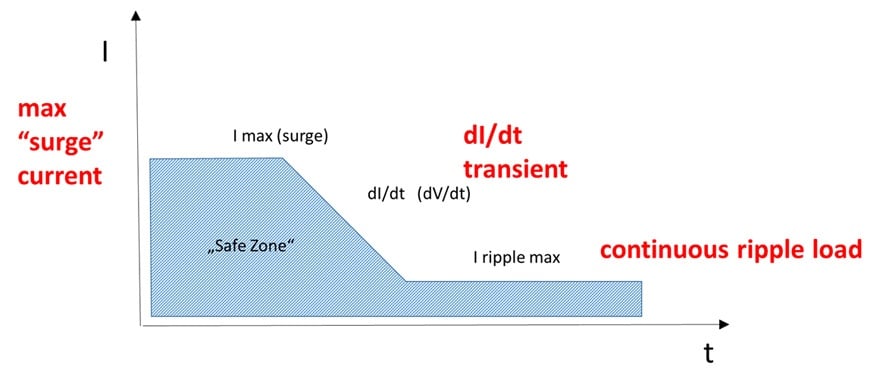
Capacitors are naturally limited by its capability to handle/dissipate ripple current and pulse energy load. The limitation may be significantly different by each capacitor technology, dielectric type, its losses (and its characteristics), but also to a specific construction of the product type individual series. In general, the impact of inrush and ripple current can be divided to three time zones:
- high current immediate surge spike
- transient load dI/dt (dV/dt)
- continuous ripple current/voltage load
The key differentiator is the time domain – how long the current is flowing through the capacitor and how / how quickly / the component can handle / dissipate the heat. See the following figure illustrating general model of the ripple/inrush current load as function of time.
Capacitor ripple current calculation principles and details are explained also in the following article:
Ripple Current and its Effects on the Performance of Capacitors
High Current Surge Spikes & Transient
The high immediate current spike is a typical short time ‘micro-seconds’ load zone during power switch ON/OFF of a high power, low impedance source circuit. In low impedance circuits, the current spikes can easily reach tenth or hundreds of amperes and it can present an overload risk to the capacitor. Typical example would be a hot plug-in of a low ESR, high capacitance, capacitor directly to automotive 12V battery terminations.
During the “current spike”, high current is flowing through the lowest impedance parts of the capacitor and as this a “high frequency” ripple load type, the current path will flow first mainly through a “surface skin effect“ area of conductive materials. The capacitor dielectric may be then subjected to immediate high electrostatic mechanical pressure force once the electric field on electrodes is created. Depending on duration of the surge spike, Joule heat is generated that has to be absorbed by the capacitor. This is indeed more relevant to the dI/dt transient discussed in the next chapter, but the initial spike may generate some “pre-conditioning” stage of the capacitor and a total energy to be dissipated by the capacitor during the power on sequence has to be considered.
The maximum allowable capacitor’s current shall be specified by manufacturer, however in some cases, the internal resistance of the capacitor is high enough not to allow any dangerous current to flow through the capacitor structure and thus ripple current specification of the part is specified only. It means the capacitor technology is not sensitive to power on load as for example conventional aluminium electrolytic “high ESR” capacitors.
A good circuit design practice is to use soft start circuits, where applicable, to limit the power ON/OFF current load that eliminates most of the immediate current surge load and of course improve overall the hardware design robustness and reliability.
Some capacitor constructions such as tantalum MnO2 capacitors are sensitive to the maximum surge current. Manufacturers and standards (ESA) specify its surge current limits.
Note: “voltage spike” is another phenomenon, however, during voltage spike, the maximum available current can be limited. Typical example of a voltage spike is a low impedance switching between inductor and capacitor that is used in high voltage start-up systems. The risk here is the capacitor electric breakdown when the induced voltage exceeds its breakdown voltage. Sufficient design margin, protective diode or other circuit protection measures may be good idea to implement for robust design of such circuits. In some cases, dangerous “unwanted” low impedance switching can be caused by broken connector/jumper or PCB crack under a vibration conditions – as a tip for uneven capacitor failure identification.
Transient Load dI/dt
In the next transient time domain – approximately in miliseconds to hundrends of milliseconds about range – the current move from the skin surface to the bulk of materials / lower conductive sites of the capacitors and heating of its real resistive elements begin. This Joule heat has to be dissipated by the construction and not to cause any thermal damage to its structure.
This zone is a “usual” operating transient load zone for the capacitors, as most of the power management systems will use soft-start circuits and “shift” the power switch peak from the very short duration of very high current spike (tenth and hundred of amps in microseconds) to this range of typically units of Amps within tenth to hundreds of milliseconds range.
dI/dt (dV/dt) transient power source capability is the key parameter for high power, high voltage circuits using film or ceramic capacitors, thus attention shall be paid for the correct design respecting capacitor manufacturers’ recommendation.
The maximum allowed ripple current and transient load may be very specific to the capacitor type. Some capacitor technologies may define ripple current and maximum surge current only, while dI/dt is considered to be covered by its “maximum surge current limitation”. Thus manufacturer datasheets and technical notes should be followed for details.
Continuous Ripple Current Load
In longer time stamp, after all the transient events are over, the capacitor can be loaded up to its maximum specified continuous ripple current limit. The value is based on the capacitor’s ability to continuously dissipate the heat generated on its resistive elements. These values as a function of ambient operating temperature are usually part of the catalogue or detailed capacitor datasheets.
Continuous ripple current capacitor specification remarks
The maximum allowable ripple current is based on the capacitor’s power dissipation capability (as function of construction and case size) and expressed by maximum “self-heating” during the operation under ripple current load condition. The maximum “safe” self-heating value that the capacitor can dissipate continuously without thermal impact to its specified function and reliability can be for example by 10°C. It has to be also noted that the maximum temperature ranking of the part shall not be exceeded. So in our case, if the capacitor’s temperature range is up to 125°C, the 10°C increment, caused by the ripple current self-heating, limits its operation up to 115°C maximum. In often case, the maximum ripple current values at higher ambient temperatures are derated and its values at elevated temperatures can be found directly in the manufacturers’ datasheets.
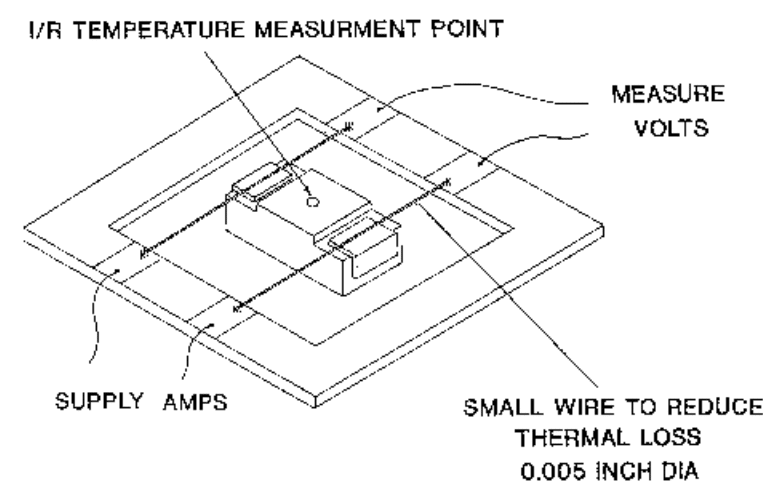
In real circuit, the capacitor dissipation capabilities are influenced by more factors such as PCB layout, thermal convection, hardware packaging etc. Therefore, capacitor power dissipation ratio and calculated ripple current load has to be defined at some reference point – “open-air” conditions: Capacitors are connected by sharp termination pins, to minimize thermal conduction, and self-heating temperature under ripple load is monitored by infra-red camera; see example picture on right.
In practical applications, thermal conduction of PCB through terminations are providing much better cooling compare to referenced “open-air” and thus the ripple current rating of the component soldered on PCB is much better compare to the specified catalogue values. In a good thermally balanced PCB the ripple current load can be by rule of thumb up to twice higher compare to its catalogue values. Nevertheless, it is always best to check the self-heating of the part in its worst case load scenario is not exceeding the power dissipation capability of the capacitor type.
Construction of High Power Transient Capacitor Types
There are more ways how capacitor construction can specifically address requirements for higher ripple current and transient load robustness. Such “high power, surge, transient” robust products may be available under a specific series of the capacitor technology.
Here we note two examples of transient pulse ruggedized capacitor designs:
Thicker electrode leads in multilayer capacitor design can be done by reinforced metallization of the electrodes – see figure below on left. This construction will lower resistivity of the electrodes as well as increase its power capability in the transient short time domain when surface skin effect takes place.
This technique is used mostly by organic film capacitors.
Thicker dielectric layer on surface of tantalum capacitor anode – see figure below on right.
Tantalum capacitors are made from a fine sintered tantalum powder and dielectric is then formed elecro-chemically on the tantalum surface. A technology called “shell formation” has been developed by manufacturers to form a thicker dielectric layer on outer surface of the anode that is closest to the cathode system – and thus first hit by surge current.
This technology provides higher power ratings and surge robustness against power spikes.


Simulations and Modelling
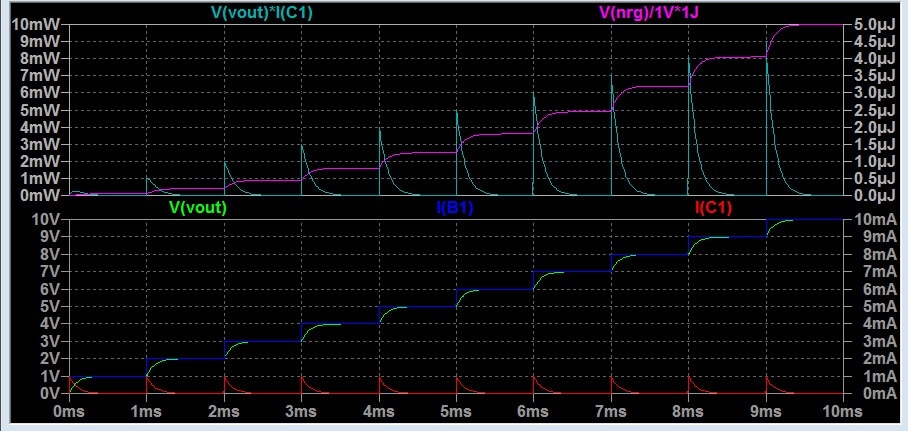
Transient, power ON/OFF simulation and ripple current computer modelling are today a standard tool for electronic design and verification. Use of correct capacitor models may significantly impact relevance and fidelity of PSpice modelling and thus detect potential circuit issues already in the design stage.
Many times, simulation of passive components is not considered as critical parts of PSpice circuit simulation. However, general PSpice software built-in passive components libraries may offer only ideal components model that do not respect its electrical parameters behavior with frequency, temperature or voltage.
Often to see, PSpice simple capacitor equivalent circuit simulations are made from an ideal capacitor, resistor in series in value representing ESR, parallel resistor as DCL and series inductance as ESL MAY NOT be able to realistically simulate the circuit function especially in the transient zone including potential spikes and ripple current load estimations.
Leading manufacturers and PSpice software companies are offering today libraries of passive components including S-parameters of each capacitor part type that can be imported into the simulation to achieve high fidelity of modelling.
Further read:
- Ripple Current and its Effects on the Performance of Capacitors
- Capacitor Ripple Current Testing: A Design Consideration
- Examining the Influence of ESR and Ripple Current on Selecting the Suitable Capacitor
- Why Low ESR Matters in Capacitor Design