This article discusses corrosion in electronic systems, contacts and housing, including its development and prevention. The post is based on Würth Elektronik‘s “Reference Guide ABC of Shielding” that can be ordered from WE website here. Published under permission by Würth Elektronik.
Poor connections can cause fluctuating contact resistances and even sporadic interruptions.
These changes are often caused by mechanical vibrations and temperature fluctuations.
Modulations of operating voltages and signals may occur, resulting in noisy signals. Occasional spark overs causing fast transient electrical pulses can also be caused by shocks, vibrations, or climatic influences. Furthermore, all these problems worsen over time. The reason for these phenomena is often corrosion.
Galvanic Corrosion
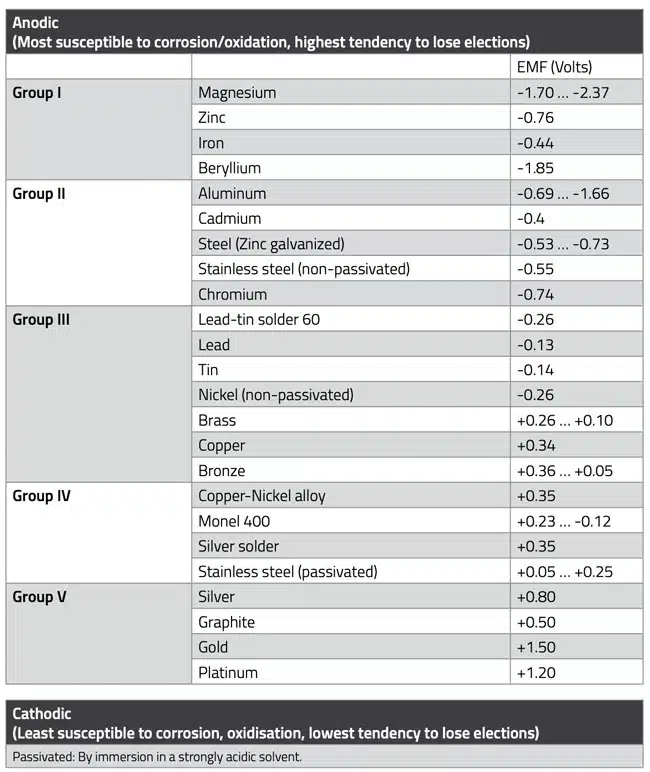
Galvanic corrosion occurs when a voltage cell forms between metal parts, with moisture acting as an electrolyte. The extent of corrosion depends on the relative positions of the metals in the electrochemical series. This series is presented in Table 1. below, where metals with smaller numbers corrode faster than those with higher numbers.
The metals in the electrochemical series are categorized into five groups. When dissimilar metals are combined, it’s advisable to use metals from the same group. However, metals from adjacent groups can be used together if the product is intended for domestic or environmentally uncritical industrial applications.
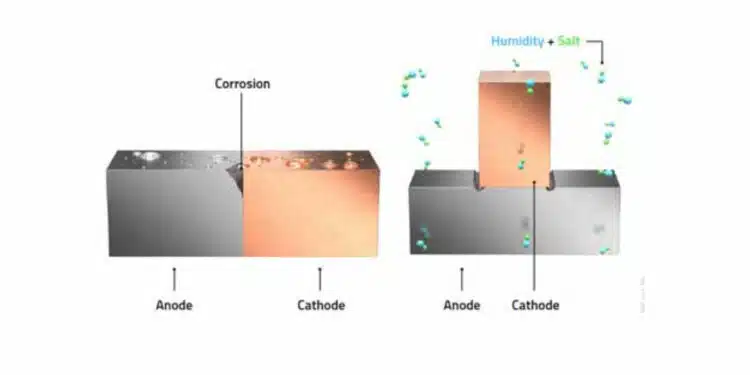
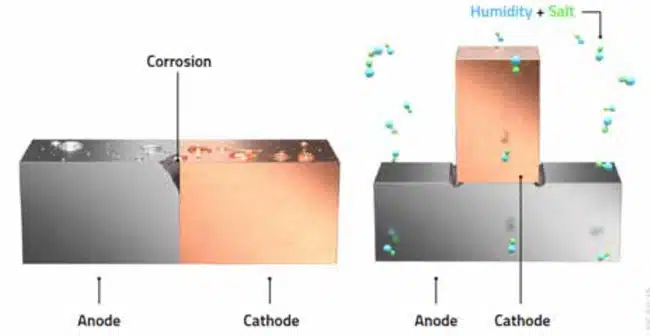
The further the metals in this table are from each other, the greater the voltage generated; if they are equal, no potential difference can occur. Galvanic corrosion causes positive ions to migrate from one metal to another, gradually degrading the anode material. The rate of corrosion depends on humidity and the distance between the metals in the galvanic series. The further apart they are, the faster the ion transfer. The example in Figure 1. illustrates this concept. A common combination of metals is aluminum and copper; in this case, the aluminum is ultimately completely decomposed.
The following four elements are required before a galvanic reaction can occur:
- Cathode material (higher rank in Table 1., e.g., copper)
- Electrolyte (as moisture, e.g., water and salt)
- Anode material (lower rank in Table 1., e.g., aluminum)
- Conductive electrical connection between the anode and cathode
Corrosion Protection
To avoid the adverse effects of corrosion, metals like tin, copper, and nickel are used, as they are close to each other in the electrochemical series and are relatively resistant to corrosion. However, these metals are often not feasible due to cost, manufacturability, and weight. Therefore, aluminum is commonly used.
Stainless steel has also been widely used in industrial applications. When joining metals, it’s crucial to ensure they are close together in the activity series to minimize corrosion. If different metals are required, such as washers, bolts, conductive gaskets, or springs, materials should be selected during design to provide optimal corrosion protection. Würth Elektronik eiSos offers a range of materials to adapt designs to various environmental conditions, including humidity, water exposure, transportation and storage conditions, and operating temperatures.
If sufficient corrosion protection cannot be guaranteed, the smaller mass of the two metal objects should have the higher potential (cathode), as seen in the example of steel washers used with brass structures. If the washer deteriorates, it can be replaced later when corrosion has progressed.
The surface of components can also be electroplated to reduce the electrochemical series difference. Organic electrolytic processes can electrically insulate materials, providing long-term moisture protection against corrosion. However, this method is not suitable for EMC applications since individual housing components lack electrical connections.
Design and construction guidelines for an effective connection of sheet metal components or housing parts are provided below.
- Welds are the preferred method whenever possible due to their durability and low impedance, or “low resistance,” connection. If anti-corrosion protection is provided for the welds, the connection is safeguarded against corrosion in the long run.
- Spot welding can be used in cases where RF-tightness is not necessary. However, there’s a risk of corrosion between the welds in spot-welded seams.
- Fasteners like rivets or self-tapping sheet metal screws exhibit similar behavior to spot welding, leading to corrosion. Additionally, there’s a potential for open gaps between the joints due to material tension.
- For spot connections, such as spot welding, screws, and rivets, spring elements or conductive gaskets should always be used. This ensures a continuous and permanent connection between the two metal parts. It’s crucial to observe the electrochemical voltage series in such cases.
- Soldering should be avoided if mechanical strength is required. In such cases, the solder should be supported by screws or bolts. Similarly, the electrochemical series should be considered, especially when silver-plated components are used and moisture is a concern.
Related articles:
- Electromagnetic Housing Shielding and Its Effectiveness
- Parameters of Shielding Attenuation
- Influence of Shielding Materials on Shielding Effectiveness
- Electromagnetic Emissions Leakage in Enclosures
- Housing EMC Requirements, Issues and Solutions