High-temperature 150°C MLCC ceramic capacitors are required in the powertrain of internal combustion engines, but also in the EV powertrain systems. Samsung Electro-Mechanics released a technical note to address this application field.
Carbon-neutral policies affect all industries. The automotive market will inevitably be impacted as it accelerates towards an electric and eco-friendlier environment. High voltage power converters are essential to EV Powertrain systems as HEV(Hybrid Electric Vehicle)is being developed with a combination of the ICE(Internal Combustion Engine) powertrain.
In this article we will discuss why ICE powertrain operates in a high temperature environment and which part of the EV Powertrain’s thermal management is a key design aspect to consider. Samsung Electro-Mechanics X8L and X8G MLCC guarantee high reliability in an extreme temperature environment.
Power Semiconductor Application(SiC) and High Temperature MLCC Needs
Driving range on electric cars is limited to its battery capacity. What changes would be required to increase range? The answer is simple; we need to improve battery capacity and MPGe (km/kW). However, when the battery capacity increases, charging times also increase which makes it inconvenient for drivers and this needs to be resolved.
Car makers continue to develop and improve fast charging systems to reduce this inconvenience for electric vehicle owners. In order to reduce charging times, there are 2 options. First one is to increase the charging voltage and the second one is to increase the capacity (kW) of an electric vehicle charger (OBC).
The power semiconductor types which you select for the circuit are also an important part to enable an efficient power system. SiC MOSFETs are being widely used with Automotive Powertrain DC/DC converter, which help improve power density by increasing frequency and voltage. High power circuit applications such as OBC and Inverters generate heat, ultimately resulting in thermal management issues.
Coolant systems are designed to solve the thermal issue which is originated by the heat generated by the power semiconductors.
This is why high-temperature 150°C MLCC is required not only in the powertrain of internal combustion engines, but also in the EV powertrain systems.
High Temperature Ambient Powertrain and Electrification
There are also unexpected obstacles in the rapid growth of the EV market, i.e. the battery supply cannot keep up with demand. As a result, global OEMs have seen a shortage of minerals used in batteries and therefore prices have increased.
In parallel, demand for ICE and HEV has stayed consistent and co-exist with BEV(Battery Electric Vehicle) market. So far, the technical development trend of ICE powertrain has been focused on improvements such as driving performance, gas mileage and reduced gas emissions. In order to reduce emissions and improve gas mileage, engine load has to be reduced.
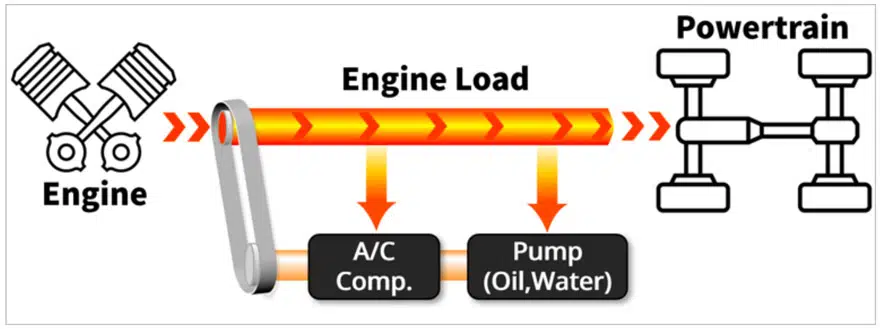
The power of the combustion engine drives the transmission to move a vehicle and additional power is distributed by an axillary belt connection. Engine power is additionally distributed to the alternator, oil pump (steering, transmission, etc.), water pump and A/C compressor.
Ultimately, all of these mechanically driven devices reduce gas mileage, to solve this problem these devices are being replaced with electrical alternatives. Additional electrical components such as an ECU and sensors are required and because they are placed in the engine compartment they are exposed to high temperatures. Overall, an ICE powertrain environment runs at a high temperature.
Typically, an exhaust systems radiates heat in excess of 587°C, engine oil and transmission oil are roughly 148°C, adding to the overall high-temperature environment. Taking this into consideration, OEMs and suppliers provide a mission profile, which represents the temperature load of a vehicle. It is essential to select the appropriate components considering the environmental operating temperature where a product is used.
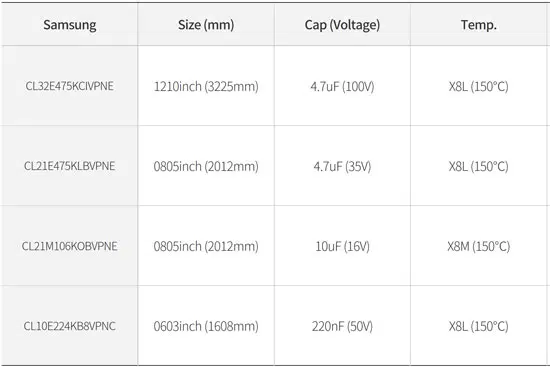
150°C MLCC , Higher MLCC capacitance at high temperature range
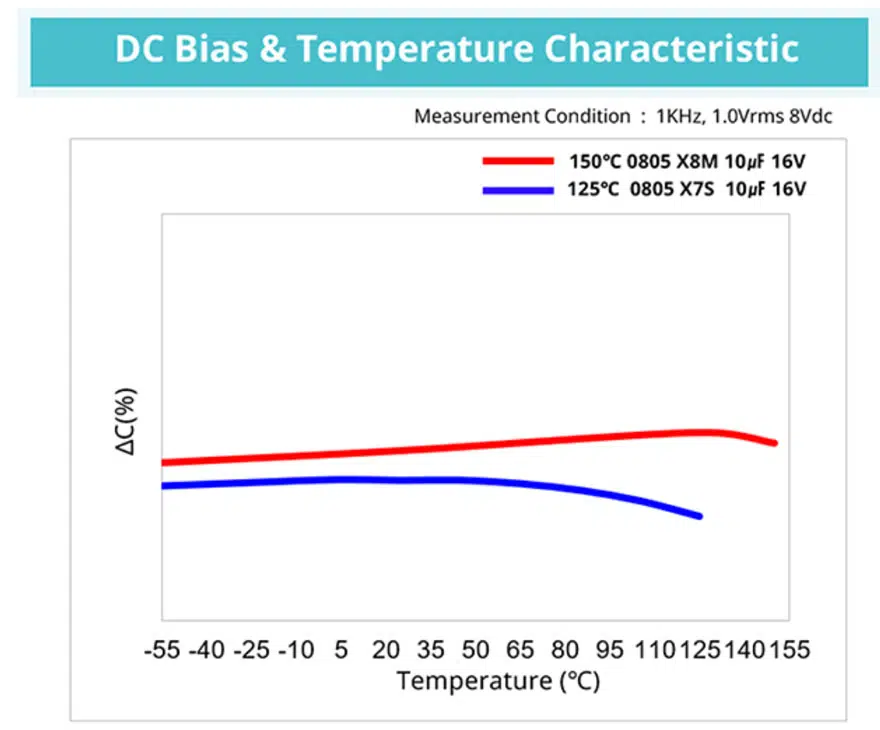
Temperature and voltage are factors that affect lifetime of MLCC. 150°C MLCC not only guarantees reliability at high temperature but also provides a higher MLCC Capacitance. List of available products see below.