Murata’s new Silicon Snubber Capacitor technology offers solutions for high voltage power modules, enabling them to fully harness the benefits of wide band gap technologies by overcoming the issues they may face.
This paper was presented by Tom Choisy, junior product manager Murata Integrated Passive Solutions, Caen, France at the 4th PCNS 10-14th September 2023, Sønderborg, Denmark as paper No.1.1.
Automotive Industry Trends
The world is moving towards a “Greener” society. The collective drive to achieve zero-emissions is already affecting the way that energy is produced and consumed. As of today, more than 70 countries have set net-zero targets, covering 76% of global emissions. This brings new market perspectives and new technological trends.
Wide-Bandgap technologies and SiC major adoption leads the way to new opportunities and new requirements. According to Yole study “Power SiC 2022, Market and Technology Report” the acceleration of EV/HEV remains the primary market driver for SiC, especially in the main inverter : “The total power electronic system market, made up of main inverters, DC/DC, and OBC, will grow to ~$26B by 2027, with the main inverter taking more than 60% market share by 2027.” [1]
- Market problems to be solved:
With the era of Wide-Bandgap devices in power electronics, the new challenges already on the table will be more pronounced such as:
- Higher frequencies
- Higher power densities
- Higher voltage levels
- Better efficiency (lower losses)
- Lower inductance
- Smaller size
- Higher reliability
- Higher temperature stability
- Easy module integration
- Consequences for capacitor requirements:
To meet the new requirements of the automotive power electronics industry, it is essential to develop new capacitor solutions offering:
- High voltage performance
- High reliability
- High temperature stability
- High frequency
- Ultra-low parasitic inductance
- Very small form factor for very close implementation
- Compatibility with advanced packaging.
Advanced components to Improve Power Module Efficiency
The automotive industry is moving towards high voltage (800V) electric vehicles, creating a demand for advanced components meeting the requirements listed above. These requirements are driven by the need to maximize overall efficiency of the car and to increase the lifetime of SiC/GaN transistors.
High frequency and high-density components are essential for efficient power conversion, enabling effective energy transfer between the battery and the motor. They facilitate rapid switching, reducing energy losses and improving overall system efficiency. High voltage capabilities are needed to ensure optimal performance. These components need to be highly reliable since they operate in harsh environments but also as small as possible because of the limited space.
New Silicon RC Snubber technology to Improve Power Module Efficiency
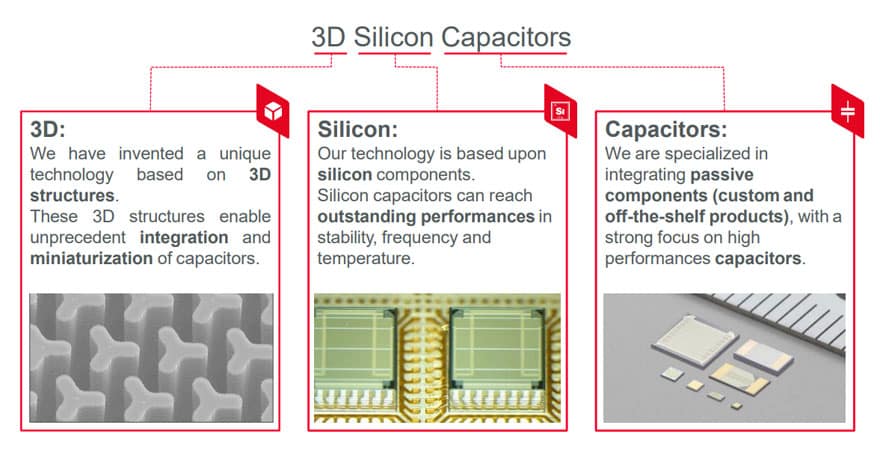
Murata Silicon Capacitors Technology
Murata silicon capacitor technology based on 3D structure brings high performance and miniaturisation together thanks to unique structure and stable SiO2 dielectric features.

Silicon Snubber Capacitors
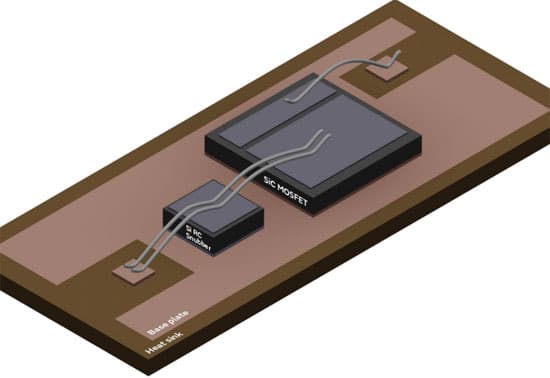
Snubbers are passive components used to address issues linked to rapid switching of power transistors, such as ringing effect. The new innovative technology developed by Murata integrates a resistor and a capacitor inside a single silicon die that reduces the ringing effect caused by the high speed switching of power transistors.
To achieve higher power module efficiency, snubbers need to be placed as close as possible to SiC/GaN transistors. Placing a Silicon Snubber as close as possible to a SiC/GaN will minimize parasitic elements like inductance, which can negatively impact high speed switching performance. By reducing these parasitic effects, Silicon RC Snubbers enable faster and controlled switching, thus improving power conversion efficiency.
Example: R+C Passives inside one die of 3.5 x 3.5mm, with a BV of 1500V, made to fit inside High Voltage Power Modules (SiC 1200V).

Key Features :
- Ultra low ESL (< 20 pH)
- 3D structure allows large capacitance value (high density)
- Low leakage current & Low Loss factor
- High temperature reliability (Up to 200°C)
Key Benefits :
- Ringing suppression
- Maximizes inverter efficiency
- Can be placed near SiC/GaN transistors
- Same assembly method as power transistors
- Reduces EMC interferences
By placing the Si RC Snubber as close as possible to the power transistors, you can limit the ringing effect and fully harness the advantages of SiC as shown in figure below:
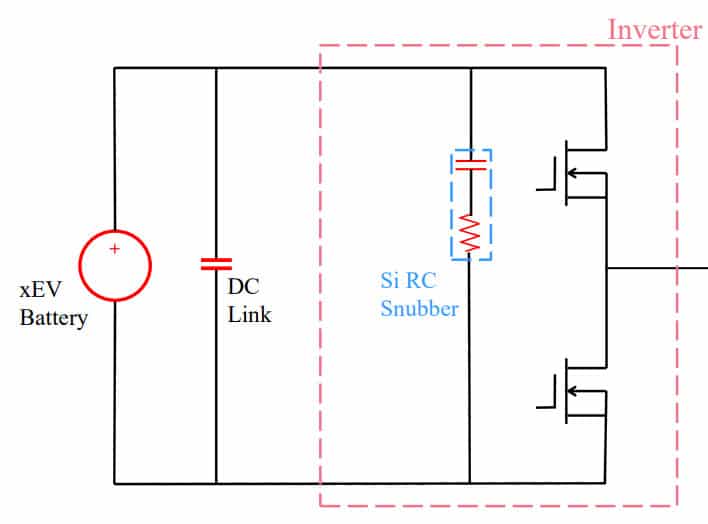
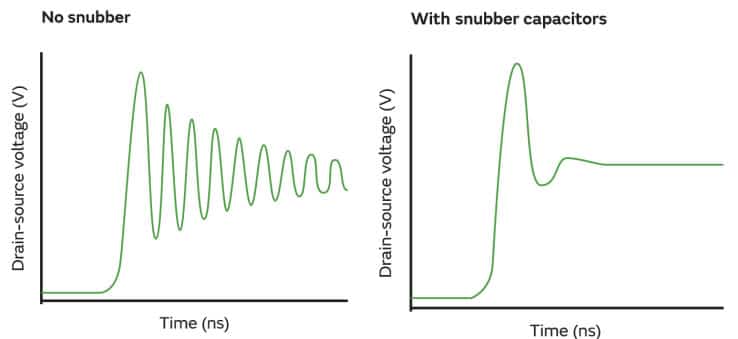
Outcomes:
- Ringing suppression = Higher Inverter Efficiency
- Potential downsizing of the cooling device
- Improved battery autonomy & potential downsizing
- Extended lifetime of SiC transistors
- EMC reduction = downsizing / lower price for EMC filters
- No need for high cost & complex assembly (e.g. double sintering) to gain
inverter efficiency
SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS
The integration of Silicon RC Snubbers as close as possible to SiC/GaN power transistors offers several benefits that have a major impact on the overall performance and efficiency of EVs. By eliminating the ringing effect, RC snubbers increase switching speeds, thus improving the overall efficiency of the module and reducing the need for cooling systems. This reduction in cooling devices will contribute to weight and space savings inside the car but also enhances battery autonomy and driving range.
The compatibility of our Silicon RC Snubber technology with the assembly techniques used for SiC/GaN transistors (wirebonding on the top and sintering on the bottom) will eliminate the need for complex assembly processes. This compatibility will also simplify the integration of the component into existing manufacturing lines, allowing manufacturers to use their expertise while benefiting from the increased efficiency provided by the RC Snubber.
By overcoming the issues that can be faced by Wide-Bandgap components, the Silicon RC Snubber enables to fully harness the benefits of these technologies.
REFERENCES
[1] Yole Power Electronics for Automotive – Focus Passenger and Light Commercial Vehicles | Report 2022