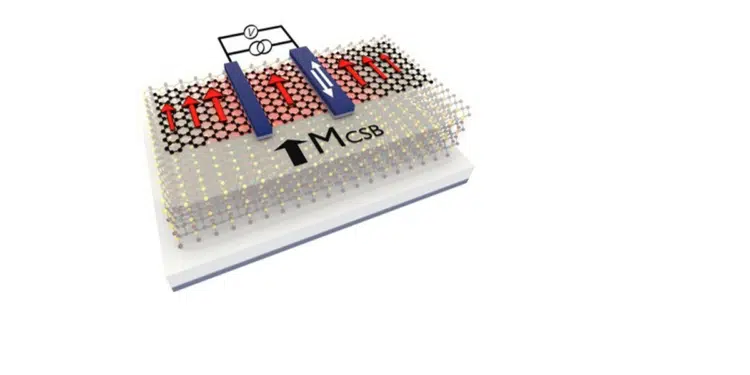
For over a decade, graphene has been the most favourable 2D material for the transport of the spin information. However, graphene cannot generate spin current by itself unless its properties are appropriately modified. One way to achieve this is to make it act as a magnetic material.
The magnetism would favour the passage of one type of spin and thus create an imbalance in the number of electrons with spin-up versus spin-down. In magnetic graphene this would result in a highly spin-polarized current.
This idea had now been experimentally confirmed by the scientists in the Physics of Nanodevices group led by prof. Bart van Wees at the University of Groningen, Zernike institute for advanced materials. When they brought graphene in close proximity to a 2D layered antiferromagnet, CrSBr, they could directly measure a large spin-polarization of current, generated by the magnetic graphene.
Spin-logic
In spintronics, the magnetic moment of electrons (spin) is used to transfer and manipulate information. An ultra-compact 2D spin-logic circuitry could be built from 2D materials that can transport the spin information over long distances and also provide strong spin-polarization of charge current. Experiments by physicists at the University of Groningen (The Netherlands) and Colombia University (USA) suggest that magnetic graphene can be the ultimate choice for these 2D spin-logic devices as it efficiently converts charge to spin current and can transfer this strong spin-polarization over long distances. This discovery was published on 6 May in Nature Nanotechnology.
In the conventional graphene-based spintronic devices, ferromagnetic (cobalt) electrodes are used for injecting and detecting the spin signal into graphene. In contrast, in circuits built from magnetic graphene, the injection, transport and detection of the spins all can be done by the graphene itself, explains Talieh Ghiasi, first author of the paper.
‘We detect an exceptionally large spin-polarization of conductivity of 14% in the magnetic graphene that is also expected to be efficiently tuneable by a transverse electric field.’ This, together with the outstanding charge and spin transport properties of graphene allows for realization of all-graphene 2D spin-logic circuitries where the magnetic graphene alone can inject, transport and detect the spin information.
Moreover, the unavoidable heat dissipation that happens in any electronic circuitry is turned to an advantage in these spintronic devices. ‘We observe that the temperature gradient in the magnetic graphene due to the Joule heating is converted to spin current. This happens by the spin-dependent Seebeck effect that is also observed in graphene for the first time in our experiments,’ says Ghiasi. The efficient electrical and thermal generation of spin currents by the magnetic graphene promises substantial advances both for the 2D spintronic and spin-caloritronic technologies.
Magnets Without Metals: Magnetic Graphene
Discovery of magnetic graphene has been already made by scientists in 2017 at the Regional Centre of Advanced Technologies and Materials (RCPTM) at the Palacky University in Olomouc.
By using graphene, an ultrathin form of carbon, these scientists prepared the first non-metallic magnet that retains its magnetic properties up to room temperature. In doing so, they disproved the old belief that all materials with room temperature magnetism are based on metals or their compounds. Chemically modified magnetic graphene has a vast range of potential applications, particularly in the fields of biomedicine and electronics.
“For several years, we have suspected that the path to magnetic carbon could involve graphene –a single two-dimensional layer of carbon atoms. Amazingly, by treating it with other non-metallic elements such as fluorine, hydrogen, and oxygen, we were able to create a new source of magnetic moments that communicate with each other even at room temperature. This discovery is seen as a huge advancement in the capabilities of organic magnets,” says Radek Zbořil, a leading author of the project and director of RCPTM
The idea and study arose solely from the work of the Olomouc scientists, who also developed a theoretical model to explain the origin of magnetism in these carbon materials. “In metallic systems, magnetic phenomena result from the behavior of electrons in the atomic structure of metals. In the organic magnets that we have developed, the magnetic features emerge from the behavior of non-metallic chemical radicals that carry free electrons,” says Michal Otyepka, a co-creator of the theoretical model whose work on the project was conducted within the framework of a prestigious European Research Council (ERC) grant.