Researchers from China published scientific article in Chemical Engineering Journal on Superior dielectric energy storage performance for high-temperature film capacitors through molecular structure design.
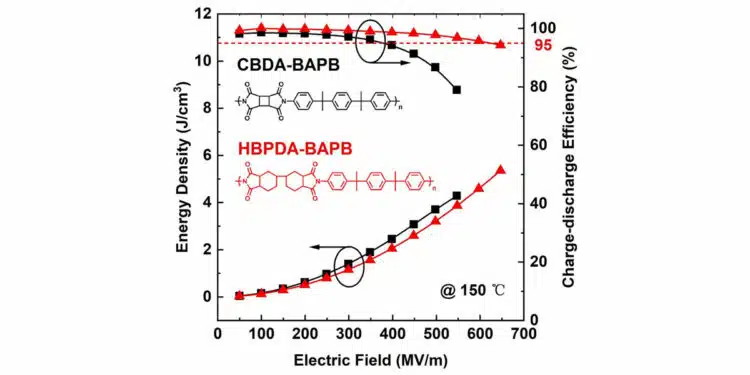
The elongated non-coplanar alicyclic structures reduce dielectric conduction loss of film capacitor dielectrics and allow to achieve a record-high energy density of ∼4.9 J/cm3 with η > 95 % at 150 °C. Stable cyclability over 100,000 cycles under 400 MV/m at 150 °C is achieved.
Abstract
Film capacitors based on polymer dielectrics face substantial challenges in meeting the requirements of developing harsh environment (≥150 °C) applications. Polyimides have garnered attention as promising dielectric materials for high-temperature film capacitors due to their exceptional heat resistance.
However, conventional polyimides with narrow bandgaps suffer from significant conduction loss at high temperatures and high electric fields. Here, we design and synthesize a series of modified polyimides featuring different saturated alicyclic structures on their main chains. Among these, the HBPDA-BAPB polyimide exhibits a superior discharged energy density of 4.9 J/cm3 with a high efficiency exceeding 95 % at 150 °C, outperforming other reported dielectric polymers and composites.
The mechanism is attributed to the incorporation of elongated noncoplanar dicyclohexyl units into the backbones, which significantly reduces molecular conjugation, enhances the bandgap and suppresses leakage current. Our findings demonstrate the potential of modified polyimides with alicyclic structures as high-temperature dielectric materials for practical applications.
Technical Background
Polymer-based materials are widely used as dielectrics in electrostatic capacitors due to their high voltage resistance, flexibility and cost-effectiveness. Biaxially oriented polypropylene (BOPP) is the most commonly used dielectric polymer in industry. However, it has a serious limitation of being unable to withstand high temperatures above 105°C. In some emerging fields, such as the power inverter of hybrid electric vehicles, the ambient temperature can reach 150 °C. In this case, BOPP capacitors need to be equipped with a cooling device to ensure normal functionality, which leads to an increase in the overall system’s weight, size, cost, and energy consumption. Thus, developing new polymer dielectrics that maintain low leakage current and stable energy storage performance over a wide temperature range is essential for practical applications in harsh operating environments.
Numerous studies have been conducted to develop high-temperature polymer dielectrics, which can be mainly categorized into three types as follows.
- Constructing multilayer or heterojunction structures to suppress carrier injection or inhibit carrier transport has been proven to be an effective method. For example, depositing wide bandgap inorganic layers (e.g., SiO2, and Al2O3) onto the surface of a polymer film can introduce a high interfacial barrier and reduce charge injection.
- Introducing deep traps into the matrix to capture carriers is also beneficial for reducing the leakage current and improving the energy storage performance of polymer dielectrics at high temperatures. Adding wide bandgap inorganic nanofillers (e.g., SiO2, Al2O3, BN, etc.) to polymer dielectrics can introduce traps, but this often results in filler aggregation, hindering scale-up production. Hence, it may be more appropriate to construct all-organic polymer dielectrics with deep traps by blending, cross-linking or doping high-electron-affinity organic semiconductors.
- Synthesizing new polymers through structural design can fundamentally and significantly regulate the glass transition temperature (Tg) and bandgap, thereby directly improving their dielectric performance under high temperatures and high electric fields. For instance, a series of polyoxafluoronorbornenes (POFNBs) composed of rigid fused bicyclic structures were reported to maintain high Tgs ranging from 186 to 244 °C and wide bandgaps of approximately 4.9 eV, which has allowed POFNBs to discharge a high energy density of 8.3 J/cm3 at 150 °C with an efficiency of 80 %.
Polyimides are the most commonly used high-temperature polymers for insulating and packaging materials in the electronics industry. The conventional all-aromatic polyimide, consisting of an alternating combination of aromatic dianhydride and diamine, offers excellent mechanical and thermal properties (Tg higher than 200 °C). However, conventional all-aromatic polyimides often suffer from a small bandgap (∼3.0 eV) and large leakage current under high temperatures and high electric fields due to the formation of intra- and inter-molecular charge-transfer complexes in highly conjugated molecular structures.
To overcome this limitation, inserting alicyclic links into the main chains of polyimides to disrupt this conjugation is considered an effective method for increasing the bandgaps of polyimides. The large optical bandgap (∼4.6 eV) and high Tg (∼277 °C) enable the alicyclic polyimide film to deliver a discharged energy density of ∼1.8 J/cm3 at 150 °C with an efficiency of 95 %. These findings suggest the critical role of alicyclic groups, and thus careful design of polyimides with suitable alicyclic groups is important. However, the cyclobutyl in the earlier report is more planar and smaller in size than other alicyclic structures, which leads to a relatively high tunneling probability of delocalized π electrons. It will be interesting to introduce an alicyclic structure with less planarity and a larger size, which will principally improve the dielectric performance of polyimide even further.
Here, we designed and fabricated a series of new polyimides with different alicyclic structures in the main chain, among which HBPDA-BAPB discharges a record-high energy density of 4.9 J/cm3 with a high efficiency above 95 % at 620 MV/m at 150 °C. Significantly, the charge–discharge test demonstrated a remarkably stable cyclability over 100,000 cycles at 150 °C under a high electric field of 400 MV/m, thereby highlighting the exceptional potential of the modified polyimides for high-temperature film capacitor applications.
Conclusion
In summary, we designed and synthesized polyimides with different alicyclic units inserted between imide groups and investigated their dielectric energy storage performance. The monomers of CBDA, HPMDA, and HBPDA with different spatial structures of cyclobutyl, cyclohexyl and dicyclohexyl linkers were selected to construct new types of polyimides. Among reported dielectric polymers, the polyimide of HBPDA-BAPB with dicyclohexyl units on the backbone delivers the highest discharged energy of 4.9 J/cm3 with a high efficiency above 95 % at 620 MV/m at 150°C.
The full article reference:
Ding, S., Jia, J., Dai, Z., Wang, Y., Shen, S., Yin, Y., & Li, X. (2024). Superior dielectric energy storage performance for high-temperature film capacitors through molecular structure design. Chemical Engineering Journal, 493, 152623. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2024.152623