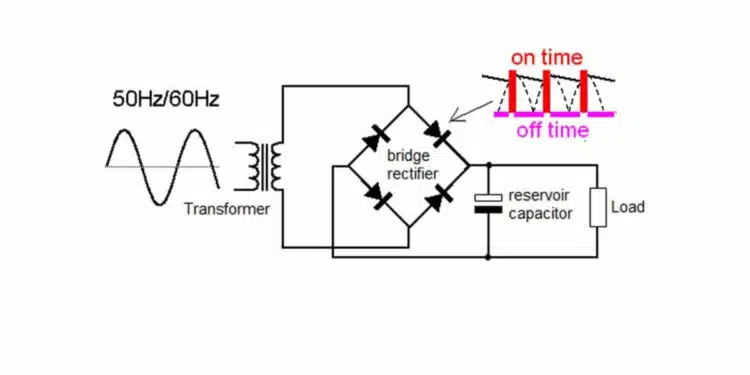
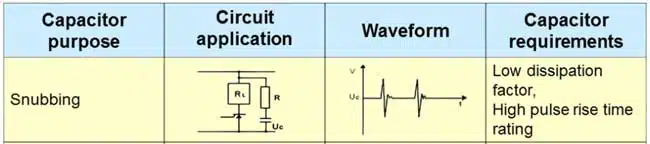
Large voltage spikes are common in power circuits, especially during switching. Switching devices are exposed to large spikes during turn-off, and voltage suppression circuits are required to protect them.
Key Takeaways
- Snubber capacitors protect switching devices from harmful voltage spikes during operation, improving reliability and efficiency.
- RC and RCD snubbers are the two most common designs; RC snubbers help minimize voltage spikes, while RCD snubbers reduce losses and improve load lines.
- Polypropylene film capacitors are preferred for snubber applications due to their stability and ability to withstand high voltage transients.
- Ceramic and mica capacitors are suitable for low-power applications, while polypropylene capacitors perform well in both low and high-power circuits.
- Implementing snubber capacitors efficiently reduces EMI and protects components, making them essential in various power circuits.
Circuits for protecting FETs, IGBTs and other switching devices from large voltage spikes produced during switching operations are commonly referred to as snubbers and snubber capacitors.
Snubber Circuits
A snubber is an essential part of a power conversion circuit. Snubbers are used in power circuits for a broad array of applications including reducing or eliminating voltage or current spikes, limiting dV/dt, or dI/dt, reducing electromagnetic interference (EMI), reducing losses caused by switching operations, shaping load lines, and transferring power dissipation to resistors or useful loads.
A “hard switching” operation subjects a switch to voltage and current stress and causes high switching loss. Presence of parasitic capacitance and parasitic inductance increases this stress further. The total parasitic capacitance comprises of stray capacitance and junction capacitance while the total parasitic inductance comprises of lead inductance and inductance due to circuit layout. Using good circuit layout practices helps to minimize parasitic inductance.
Although the electronic circuits of motor drives, lamp ballasts, power converters, and other power devices may be different, most have common switch-diode-inductor networks and waveforms. The most common circuits are buck, boost, buck-boost, and inverter pole networks. Power electronic circuits that share a common switch-diode-inductor network have same snubber requirements since the behavior of the fundamental network is identical.
There are many types of snubber designs but the resistor-capacitor (RC) and the resistor-capacitor-diode (RCD) snubbers are the most common. A resistor-capacitor snubber helps to suppress peak voltage and minimize ringing. Compared to RC snubbers, RCD snubbers have additional advantages. Apart from limiting peak voltage, this snubber also helps to reduce circuit loss and yields better load lines. On the flip side, the presence of a diode across the resistor causes the effective value of resistance to be zero when the capacitor is charging.
Most of today’s high voltage inverter circuits use IGBTs as the switching devices. IGBTs have lower conduction losses and occupy a smaller die area compared to MOSFETS, and this makes them a better choice for hard switching applications. A significant increase in switching losses at high frequencies makes IGBT modules unsuitable for applications exceeding 20 KHz. Since IGBTs can switch high currents within short time frames, they are exposed to potentially harmful voltage transients and therefore require protection circuits. Adding a snubber capacitor across the IGBT diverts the inductive current thus protecting the switch.
RC snubbers are mostly used in low power and medium power applications. In high power applications, these snubbers exhibit excessive power losses making them unsuitable for such applications. In comparison, RCD snubbers are suitable for medium current and high current applications. They are commonly used for protecting various switching devices including IGBT modules. In high current applications, RC snubbers are mostly used for secondary damping. See also article RC snubber design for SMPS protection.
Snubber capacitors
Snubber circuits are exposed to high stress, so it is important to select components that can withstand such conditions. The types of capacitors that are widely used for snubber applications include film and ceramic capacitors. Whereas plastic film capacitors can be used for both high power and low power circuits, ceramic capacitors are mostly used for low power applications.
A snubber capacitor is a capacitor connected to a high-current switching node. It’s designed to protect electronics from voltage spikes and transients that can occur during switching.
It’s common for the actions of a switch (i.e., opening or closing) to induce a high voltage across a device. Those voltage spikes cause failures if they exceed component ratings.
Snubber capacitors offer an alternate path for excess energy to be absorbed and dissipated, ultimately reducing voltage spikes and ringing effects. Implementing snubber capacitors improves efficiency, reduces EMI and protects components.
While there are many snubber designs, resistor-capacitor (RC) and resistor-capacitor-diode (RCD) are the most common. RC snubbers suppress peak voltage and minimize ringing; RCD snubbers have the additional benefit of reducing circuit loss, but the diode across the resistor causes resistance to reduce to zero while the capacitor is charging. Worth noting!
Snubber capacitors are powerful tools for improving circuit reliability and efficiency. They allow aps to leverage the benefits of switching without the potentially harmful effects of voltage spikes.
Capacitors used in snubber circuits are subjected to high dV/dt and extremely high values of peak and rms current. These circuits demand capacitors that can withstand current spikes with high peak and rms values. The characteristics of polypropylene film capacitors make them suitable for snubber applications.
Film capacitors for snubber applications
Most snubber capacitors are designed with polypropylene material. The performance characteristics of this low-loss dielectric material make it suitable for designing capacitors for use in both low and high pulse applications. The properties of a film capacitor are significantly dependent on the construction technology used.
Metallized film capacitors, also commonly known as metallized electrode capacitors, have self-healing properties while discrete foil electrode capacitors do not have them. Polypropylene film/foil capacitors are commonly used as snubber capacitors in low pulse applications. In comparison, polypropylene metallized film capacitors and double sided metallized film capacitors have self-healing property, and they are suitable for use in low pulse and medium pulse applications. These two types of capacitors are suitable for protecting various switching devices including thyristors, FETs, and IGBT modules. Some polypropylene metallized film capacitors are specially designed for direct mounting on IGBT modules.
A hybrid electrode capacitor is a combination of metallized electrode and discrete foil technologies. These capacitors are used in applications that expose capacitors to extremely high in-rush currents, voltage stress, and dV/dt. Hybrid electrode capacitors have self-healing property, and they are commonly used as snubber capacitors in high pulse applications.
Polypropylene capacitors offer high tolerance and stability. Changes in temperature or applied voltage have minimal effects on the performance characteristics of these components. Furthermore, polypropylene capacitors have low and virtually linear temperature coefficient. The high stability of capacitance of polypropylene capacitors makes them a suitable option for snubber applications.
Snubber circuits subject components to extremely high voltage transients and demand components that can withstand high voltages. Polypropylene capacitors can withstand high voltages, and components with operating voltage ratings of 1 kV, 2kV, 3kVand above are commonly available. Furthermore, snubber applications demand components with low equivalent series resistance (ESR) and equivalent series inductance (ESL). Polypropylene capacitors have low ESR and ESL.
Apart from applications in circuits with extremely high peak current levels, polypropylene capacitors are also suitable for switching power supplies, precision timing circuits, high pulse discharge circuits, sample and hold circuits, and high frequency resonant circuits. These capacitors are usually available as leaded components.
Ceramic capacitors for snubber applications
Multilayer ceramic (MLCC) capacitors have many applications in today’s electronic circuits. These passive components are broadly classified into three classes: Class I, Class II, and Class III. Class I capacitors are designed with low-K materials such as calcium zirconate (CaZrO3) while Class II and III capacitors are based on high-K materials such as barium titanate (BaTiO3).
Since calcium zirconate (CaZrO3) and titanium oxide (TiO3) have low relative permittivity, they yield capacitors with low capacitance. These temperature compensating capacitors have high stability of capacitance and are suitable for snubber applications. Class I capacitors have fairly linear temperature characteristics. Changes in voltage have minimal effects on the characteristics of these capacitors. Furthermore, Class I capacitors are not susceptible to aging.
Unlike polypropylene film capacitors, MLC capacitors are mostly used in low power applications. Apart from MLC capacitors and film capacitors, mica capacitors are also used as snubber capacitors. These capacitors have high stability and low inductive and resistive losses. Mica capacitors are suitable for low pulse applications.
Conclusion
Switchers produce potentially harmful voltage spikes that can damage electronic components. Snubbers are used in power circuits to suppress harmful voltage transient spikes. Apart from limiting voltage transients, snubbers are also used for shaping load lines, limiting dV/dt, reducing switching losses, transferring power dissipation from switches, and reducing voltage and current ringing. The performance characteristics of polypropylene capacitors make them a suitable choice for snubber circuits, AC filtering, and DC-link applications. Polypropylene film capacitors are suitable for both low power and high power applications. In comparison, ceramic and mica snubber capacitors are mostly used in low power equipment. Snubber capacitors are common in inverter/converter, welding equipment, uninterruptible power supply (UPS), and motor controls circuits.
FAQ – Snubber Capacitors: User’s Guide
A snubber capacitor is a capacitor connected across a high-current switching node, designed to protect electronic circuits from voltage spikes and transients during switching events. It provides a path to absorb and dissipate excess energy, reducing voltage spikes and increasing circuit reliability.
Snubber capacitors are used to suppress potentially damaging voltage and current spikes, reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI), limit dV/dt and dI/dt, shape load lines, and improve the overall efficiency and safety of switching devices like FETs and IGBTs.
Polypropylene film capacitors are most commonly recommended for both low and high power applications due to their low-loss, high-stability, and excellent voltage endurance. Ceramic capacitors (especially multilayer ceramic/MLCC) and mica capacitors are also suitable, particularly for low power and high-frequency use.
RC snubber circuits (resistor-capacitor) suppress peak voltage and minimize ringing, commonly used in low and medium power applications. RCD snubber circuits (resistor-capacitor-diode) add a diode to further reduce losses and improve efficiency but change the current path when the capacitor is charging, making them ideal for medium to high current scenarios.
They are frequently found in inverter/converter circuits, welding equipment, UPS systems, motor controls, and high-frequency resonant circuits—anywhere switching devices need protection from voltage transients.
How-to Use and Select Snubber Capacitors
- Assess Circuit Requirements
Identify if your application involves switching devices (e.g., FETs, IGBTs) prone to voltage transients and spikes. Determine the voltage and current stress levels.
- Choose the Snubber Type
Select an appropriate snubber circuit design, such as RC for lower power and RCD for higher power or more demanding applications.
- Select the Capacitor Type
For high reliability and stability, use polypropylene film capacitors for both high- and low-power applications. Use MLCC (ceramic) or mica capacitors for low-power or high-frequency designs.
- Calculate Key Parameters
Determine required capacitance, voltage, and current ratings, ensuring the chosen component can withstand high dV/dt, peak and RMS currents. Factor in ESR and ESL requirements for efficiency and reduced losses.
- Implement in the Circuit
Install the snubber capacitor at the high-current switching node. Ensure proper layout to minimize parasitic inductance and optimize performance.
- Verify Functionality
Test for reduced voltage spikes and improved waveform quality. Check component temperature and operation integrity under load.
Continue reading: