source: EDN article
Martin Rowe -October 02, 2016
Early in my editorial career, I wrote an article about thermocouples in Test & Measurement World where I incorrectly said that a voltage proportional to the junction temperature develops across the junction of two dissimilar metals. A reader wrote me a detailed letter (on paper, no e-mail then) explaining the Seebeck effect. Ever since, whenever I see anything about thermocouples using the incorrect description, I realize that yet another author is perpetuating the same old error.
When Gordon Lee sent me his article Thermocouples: Basic principles and design essentials, I immediately looked for how he described thermocouple physics. He got it right. Jim Williams, however, made the same mistake I made.
While skimming through some EDN print issues, I ran across a letter to the editor written by Bill Dubé in the September 1, 1988 issue (Signals and noise, p.32). Dubé pointed out that Jim Williams made the same mistake in an article on thermocouple circuits from the May 26, 1988 issue, Clever techniques improve thermocouple measurements. EDN’s editors notified Williams of the letter. Jim did his homework and replied that he indeed got it wrong. See the text of the letter below, reprinted from the September 1 issue.
Some 20+ years after I made the same mistake, I feel exonerated, even though two wrongs don’t make a right (except in digital logic).
Thermocouple misconceptions are common
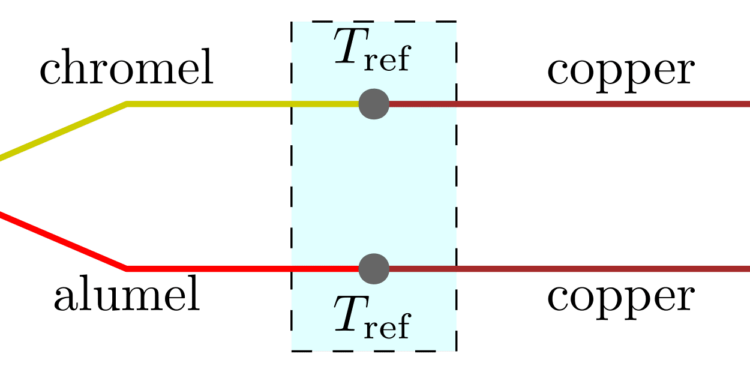
Jim Williams’s fine article “Clever techniques improve thermocouple measurements” (EDN, May 26, 1988, pg 145) is sadly flawed by a basic misunderstanding of the physics of thermocouples. It is a common misconception that the voltage of a thermocouple is generated across the junction. This is simply not true. The voltage is generated along the wires and is driven by the temperature difference between the sensing junction and the reference (“cold”) junction. For a given temperature difference, the two dissimilar wires generate unequal voltages. The voltage appearing across the thermocouple circuit at the reference junction is the difference between these unequal voltages.
The more technical explanation is that for a given temperature gradient dT/dx, an electric field dV/dx is generated. This electric field is a function of both dT/dx and absolute temperature. The local value of the difference dV/dT for a given alloy pair at a particular temperature is called the Seebeck coefficient. If the integral of the Seebeck coefficient is evaluated between-the sensing junction and the reference junction, the thermoelectric voltage results.
Thermal voltages in thermocouple circuits are always the result of thermal gradients. If a section of a thermocouple circuit has an unknown or undesirable Seebeck coefficient, then its influence can be diminished by suppressing thermal gradients in that section. For example, when you make a connection in a thermocouple circuit, it’s best to thermally anchor each of the wires to a common temperature before they reach the electrical connection point. The connection point should also be thermally anchored to this temperature. This procedure tends to suppress thermal gradients across the oxides, unknown alloys, etc, that make up the connection. If the thermal gradients are sup pressed, spurious thermal voltages will be reduced.
I hope this explanation will help clear up some of the misconceptions about the physics of thermocouples. Jim Williams is not alone in his misunderstanding—I have seen a remarkably similar treatment of thermocouples in a high-school physics text that is currently being used by the Denver School Dept.
Bill Dubé
Mechanical Engineer Denver, CO
Jim Williams responds:
Some friends and I have reviewed Bill Dubé’s comments and found them to be quite correct. As such, I find myself corrected, educated, and apologizing for any confusion I may have caused EDN’s readers. Although Bill’s distinctions are subtle, they are still the more correct interpretation, and I appreciate his remarks.