This article based on Knowles Precision Devices blog looks at three key trends impacting EV development that we are currently monitoring around shifting semiconductor development, in-vehicle system integration as a way to control costs, and the evolution of the EV charging ecosystem.
The market demands and technology trends that impact all aspects of electric vehicle (EV) development are constantly evolving. As trends change, so do the requirements for EV power systems, which impacts the demands placed on the components we supply.
Trend 1: Shifting to Wide Band Gap Semiconductors
Consumer demands for longer range per charge and faster charging times are leading to EV power systems that must operate at higher voltages and temperatures. But as this shift happens, power system efficiency can’t suffer. In fact, battery systems must actually become more efficient. To increase efficiency of these high-voltage systems, we are starting to see a shift from using conventional silicon-based (Si) semiconductors to using wide-bandgap (WBG) semiconductors built with silicon carbide (SiC) or gallium nitride (GaN).
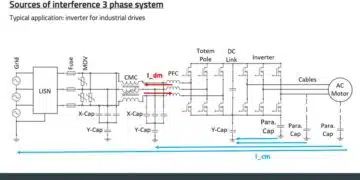
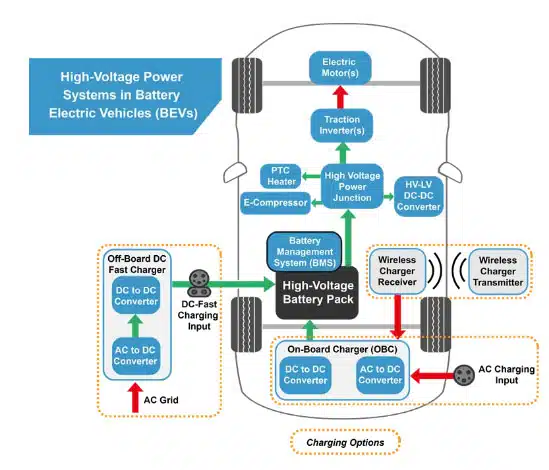
Currently, SiC-based WBG semiconductors are being used in applications such as inverters in 800V systems since these components enable higher switching frequencies and can help reduce the size and weight of the system. We are also seeing GaN-based semiconductors start to emerge as an option for lower-power systems such as the DC-DC converters that manage the auxiliary systems in the vehicle. If you look at this from the functional block diagram level (Figure 1), the table below shows how we see the device technology to WBG trend shaping up:
| Functional Block | From | To |
| OBC | IGBT | SiC MOSFET, GaN HEMT |
| Inverter | IGBT | SiC MOSFET |
| DC-DC | IGBT | SiC MOSFET, GaN HEMT |
While this shift is happening, researchers are of course already trying to further push limits as they work on developing ultra-WBG semiconductors. These semiconductors are poised to operate at even higher voltages and temperatures while being built using innovative materials that make them even smaller and lighter. It will be exciting to keep an eye on these developments and what will be possible in the near future with these components!
Trend 2: Integrating In-Vehicle Systems
Like most industries, EV manufacturers feel the pressure to reduce costs, even as they push the limits of what vehicles are capable of. Integration, or the combining of individual subsystems (functions from the EV block diagram in Figure 1) together into multi-function modules, is now a growing trend to help curb costs. Below are three in-vehicle systems where integration is starting to (or will likely start to) play a key role:
- Configuring bidirectional charging, which enables vehicle-to-home (V2H) and vehicle-to-grid (V2G) charging (discussed more below)
- Combining the onboard charger (OBC) and the DC-DC converter into a single unit that is smaller and lighter while offering increased power density
- Incorporating all-in-one power systems such as an 8-in-1 power system that combines many key components of the electric drive train into a single module
Looking back at the first trend we discussed around WBG semiconductors, you can see how we feel these two trends tie together in the table below:
| Theme | From | To |
| Device Technology | IGBT | SiC MOSFET, GaN HEMT |
| Voltage Level | 650 (for 400V Systems) | 1200V (for 800V systems) |
| Integration | Individual Subsystems | Highly Integrated Systems |
Trend 3: Boosting the EV Charging Ecosystem
As we all know, charging is a key part of the EV ecosystem – without sufficient charging, EVs simply don’t work. But charging is no longer as simple as having a means to plug in the vehicle and get it juiced up. There are a lot of market and societal demands EV engineers must also consider that range from rapid charging, especially when people are on the go, to the desire to use the energy generated from charging more efficiently. As a result, we are seeing several in-vehicle changes starting with the big shift from 400V to 800V systems, which is necessary for rapid charging to become a reality.
Looking at ways to use the energy generated from vehicle charging more efficiently, especially excess energy, there are a few key parts of this trend. As mentioned above, V2H and V2G are bidirectional charging methods that can further proliferate the sustainability benefits of EVs beyond the vehicle. In a V2H application, the EV battery acts as a mobile power bank that can supply a person’s home with electricity during peak hours. A V2G scenario is similar except the energy can be fed back to the grid to help balance energy fluctuations and promote grid sustainability. And similarly, there is also a demand from consumers around the concept of “green mobility,” where the EV, the EV charger, and renewable energy sources are all integrated on the grid to avoid using electricity generated from coal to charge vehicles.