Researchers from the Department of Physics and the Swiss Nanoscience Institute at the University of Basel, working in collaboration with the University of Bern, have now produced and studied kagome graphene for the first time, as they report in the journal Angewandte Chemie. The researchers’ measurements have delivered promising results that point to unusual electrical or magnetic properties.
Researchers around the world are searching for new synthetic materials with special properties like superconductivity—that is, the conduction of electric current without resistance. These new substances are an important step in the development of highly energy-efficient electronics. The starting material is often a single-layer honeycomb structure of carbon atoms (graphene).
Theoretical calculations predict that the compound known as kagome graphene should have completely different properties to graphene. Kagome graphene consists of a regular pattern of hexagons and equilateral triangles that surround one another. The name kagome comes from the old Japanese art of kagome weaving, in which baskets are woven in the same pattern.
Kagome lattice with new properties
To produce the kagome graphene, the team applied a precursor to a silver substrate by vapor deposition and then heated it to form an organometallic intermediate on the metal surface. Further heating produced kagome graphene, which is made up exclusively of carbon and nitrogen atoms and features the same regular pattern of hexagons and triangles.
Strong interactions between electrons
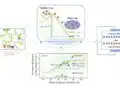
“We used scanning tunneling and atomic force microscopes to study the structural and electronic properties of the kagome lattice,” reports Dr. Rémy Pawlak, first author of the study. With microscopes of this kind, researchers can probe the structural and electrical properties of materials using a tiny tip—in this case, the tip was terminated with individual carbon monoxide molecules.
In doing so, the researchers observed that electrons of a defined energy, which is selected by applying an electrical voltage, are “trapped” between the triangles that appear in the crystal lattice of kagome graphene. This behavior clearly distinguishes the material from conventional graphene, where electrons are distributed across various energy states in the lattice—in other words, they are delocalized.
“The localization observed in kagome graphene is desirable and precisely what we were looking for,” explains Professor Ernst Meyer, who leads the group in which the projects were carried out. “It causes strong interactions between the electrons—and, in turn, these interactions provide the basis for unusual phenomena, such as conduction without resistance.”
Further investigations planned
The analyses also revealed that kagome graphene features semiconducting properties—in other words, its conducting properties can be switched on or off, as with a transistor. In this way, kagome graphene differs significantly from graphene, whose conductivity cannot be switched on and off as easily.
In subsequent investigations, the team will detach the kagome lattice from its metallic substrate and study its electronic properties further. “The flat band structure identified in the experiments supports the theoretical calculations, which predict that exciting electronic and magnetic phenomena could occur in kagome lattices. In the future, kagome graphene could act as a key building block in sustainable and efficient electronic components,” says Ernst Meyer.