Common mode filter inductors are required in many power conversion applications and a choice of core material options can give an optimum trade-off between the operating temperature and filter effectiveness. This blog article describes a range of parts that give that flexibility.
The design of power electronics systems always comes with the need to consider EMI – the electrical interference that is generated by power switches operating at high frequency. A potential outlet for this noise is the supply line to a power converter, and filters are usually needed to bring conducted emissions down to an acceptable level.
Noise comes in two flavors; differential mode (DM), appearing between power lines, and common mode (CM), from each line to ground. CM noise limits are set by standards such as EN 55032. These standards can be challenging to meet, as filter components from the power line to the ground are often limited by other considerations such as high test voltages and AC leakage current.
For best effect, a CM filter includes a ‘common mode’ choke to block interference, as local to the source as possible, allowing shunt capacitors to divert noise to the ground. The filter choke consists of two coupled inductors, one in each power line, phased such that magnetic flux from normal running current cancels and common mode signals see the full impedance of the winding inductance. High inductance values can therefore be used without core saturation for good levels of noise attenuation.
Core Materials Get Closer to the Ideal
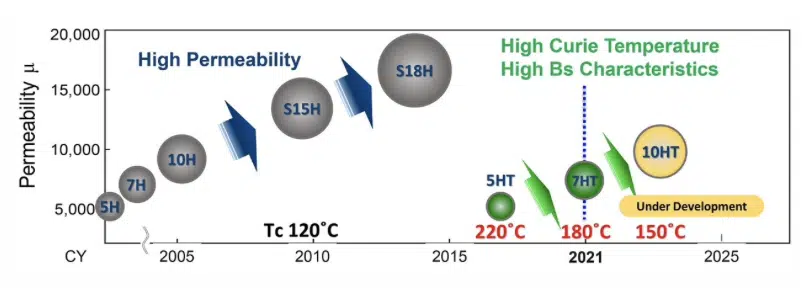
An ideal common mode choke is as small as possible and has a high permeability core for high inductance with a minimum number of turns. This core permeability gives high impedance while minimizing ohmic heating from the running current. The parts should also work over broad environmental conditions. Over the years, we have addressed the requirement and have developed core materials that get ever closer to the ideal. Figure 1 shows the progression, from a permeability of around 5,000 with our 5H material to more than 16,200 with S18H material.
As in all technology, there are trade-offs; very high permeability materials, typically Manganese-zinc ferrites, have a lower ‘Curie temperature,’ Tc, above which permeability and hence inductance and filtering effect fall substantially. For the KEMET xxH range this is 120°C. For operation at higher temperatures, a new xxHT range of materials has been developed with progressively increasing permeability, as shown in Figure 1. This range includes the 7HT ferrite with a permeability of approximately 7,000 and a Tc of 180°C. 10HT material is under development, promising around 10,000 permeability and a Tc of 150°C.
Another difference between the materials is their high-frequency performance. The higher permeability S15H is effective up to approximately 2 MHz and the 7HT is a little higher – to around 5 MHz. Both provide very good attenuation of the high-energy fundamental and first few harmonics of typical switching power supply operating frequencies of around 100 kHz.
Common Mode Chokes Are Available with Improved Performance
These materials have been designed into the KEMET SCR-XV and SCT-XV common mode chokes, available in a wide variety of horizontal and vertical through-hole formats.
The parts are available in three different core dimensions, 15 / 25 / 29 mm diameter. The SCR-XV and SCT-XV are rated from 5 A / 11.8 mH to 35 A / 110 µH with 144 parts filling in the current and inductance combinations. For a given current rating, parts can be specified in either of the two materials: the SCT-XV range uses the high-temperature 7HT material, and the SCR-XV range uses S15H for environments where the temperature is controlled to be lower. In this way, an optimum part can be selected for the application conditions.
Both ranges are rated at 1,000 Vac/Vdc between windings, with a test voltage of 2,400 Vac/2 seconds, guaranteed by an insulated, molded UL 94 V-0 rated cover around the core and integral spacers for a minimum creepage and clearance between the windings. Additionally, the SCR-XV and SCT-XV series are AEC-Q200 automotive-qualified with an IATF 16949 managed production process. These qualifications guarantee that the parts are suitable for the harsh automotive environment, with typical applications like power line filters for onboard chargers, wireless charging systems, medium power traction drives for 48 V mild hybrids, and motor drives for auxiliary equipment such as steering and air conditioning. The high voltage withstand rating makes the parts suitable for high voltage battery systems up to the specified current ratings.
Of course, the parts’ high performance and qualification level also make them suitable for demanding industrial applications as power line filters in all types of power conversion equipment.