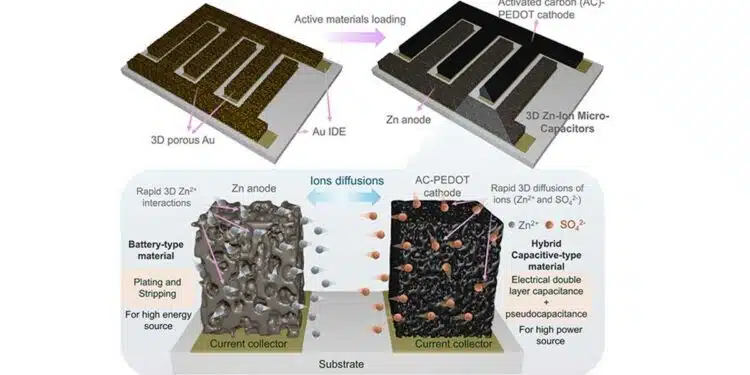
The study published in ACS Nano Journal (DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.5c00917) presents the design and fabrication of high-performance zinc-ion microcapacitors hybrid supercapacitors (ZIMCs) using 3D gold (Au) interdigitated electrodes (IDEs) as porous current collectors.
The 3D Au IDEs, fabricated using a dynamic bubbling electrodeposition technique, are loaded with zinc (Zn) as the anode and a hybrid activated carbon (AC) coated with PEDOT (AC-PEDOT) as the cathode.
The resulting ZIMCs exhibit enhanced charge storage performance, with the 3D Au Zn//AC-PEDOT configuration demonstrating a significant increase in CV area compared to planar counterparts.
The ongoing evolution of wearable and implantable technologies has heightened the demand for compact, high-performance energy storage devices. Zinc-ion microcapacitors (ZIMCs) have emerged as promising candidates by merging battery-type and capacitor-type charge storage mechanisms.
Despite their potential, challenges in electrode material optimization and device architecture have hindered their widespread adoption. This article explores an innovative approach leveraging porous 3D interdigitated current collectors and hybrid microcathodes to enhance ZIMC performance.
Key Points
- Advanced Electrode Architecture: Introduction of 3D gold interdigitated electrodes (3D Au IDEs) as porous current collectors.
- Hybrid Microcathodes: Utilization of zinc (Zn) anodes coupled with activated carbon coated with PEDOT (AC-PEDOT) cathodes.
- Fabrication Technique: Application of a microplotter technique for precise material deposition.
- Performance Metrics: Achieved areal capacity of 1.3 μAh/cm², peak areal energy of 1.11 μWh/cm², and peak areal power of 640 μW/cm².
- Enhanced Device Stability: Improved long-term cycling stability and superior charge storage capabilities.
Extended Summary
Zinc-ion microcapacitors (ZIMCs) are pivotal for powering next-generation compact electronics due to their hybrid energy storage mechanism, combining the benefits of high energy density from batteries and high power density from capacitors. Traditional planar electrode structures limit performance due to restricted ion transport pathways and suboptimal material utilization.
This study introduces a novel design employing 3D Au IDEs as porous current collectors. These collectors are fabricated using an advanced microplotter technique that allows precise layering and patterning on a ceramic substrate. The Zn anode and AC-PEDOT cathode are sequentially deposited onto these porous structures, enhancing the electrode-electrolyte interface and facilitating faster ion diffusion.
Electrochemical analyses, including cyclic voltammetry (CV) and galvanostatic charge-discharge (GCD) tests, reveal that the 3D Au IDE-based ZIMCs significantly outperform traditional planar designs. The devices exhibit a marked increase in both capacitive-controlled and diffusion-controlled charge storage contributions. Notably, the 3D Au Zn//AC-PEDOT ZIMCs demonstrate superior rate capability and energy density, attributed to the synergistic effects of the porous structure and hybrid electrode materials.
Long-term cycling tests confirm the device’s stability, with a capacity retention of up to 78% after 5000 cycles. The incorporation of PEDOT onto the AC cathode enhances pseudocapacitive behavior, further boosting overall performance. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) indicates reduced charge transfer resistance, affirming efficient charge transport within the 3D porous framework.
Conclusion
The integration of 3D porous Au IDEs with hybrid AC-PEDOT cathodes presents a transformative approach in micro-scale energy storage. This architecture not only optimizes charge storage capacity and cycling stability but also sets a new benchmark in the performance of ZIMCs. This work paves the way for the development of high-performance, compact energy storage solutions critical for future wearable and implantable electronic devices.
Read the full article:
Design of Porous 3D Interdigitated Current Collectors and Hybrid Microcathodes for Zn-Ion Microcapacitors, Yujia Fan, Nibagani Naresh, Yijia Zhu, Mingqing Wang, and Buddha Deka BoruahACS Nano 2025 19 (13), 13314-13324 DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.5c00917