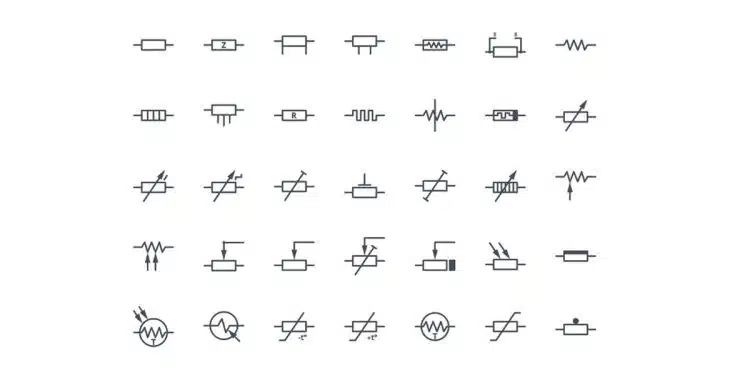
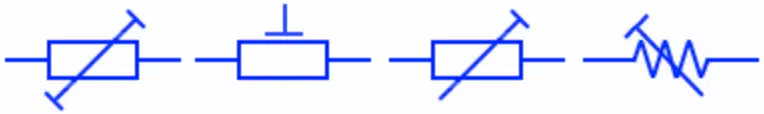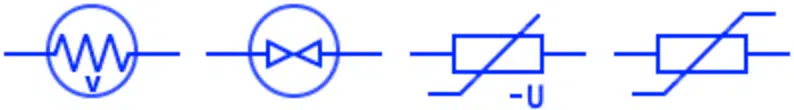There are number of resistor components and symbols. Here we are providing overview of standard but also some unusual symbols related to resistive products.
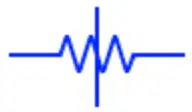
There are two symbols standards used in USA/Japan (NEMA) “zig-zag” style and IEC “new boxed” style used in Europe.
This document provides a comprehensive comparison of resistor symbols across the major international standards used in electrical and electronics circuit diagrams. The three primary standards are IEC 60617 (International Electrotechnical Commission), ANSI Y32.2/IEEE 315 (American National Standards Institute/Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers), and ISO 14617 (International Organization for Standardization) [1][2][3].
Understanding these symbol variations is essential for engineers, technicians, and electronics professionals who work with international schematics or collaborate across different regions. While IEC symbols are predominantly used in Europe and internationally, ANSI/IEEE symbols remain common in the United States and parts of Asia [2][3].
Standard Resistor Symbols
Resistor (NEMA & IEC Systems)
It is the symbol of a fixed resistor. Both of these symbols represent a fixed resistor in NEMA (left) & IEC (right) standards systems.
Attenuator
An attenuator works opposite to the amplifier. It reduces the power of the signal without distorting it. It dissipates the signal’s power within its own resistor network. The symbol of attenuator is given above.
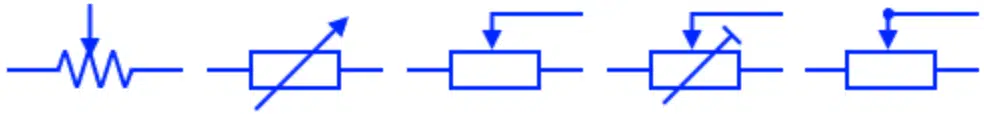
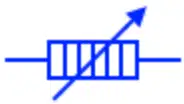
Preset Resistor
It is a variable resistor whose resistance is adjusted during manufacturing or designing of the circuit. It is not changed during normal use of the circuit. The resistance of preset resistor is changed using a screwdriver.
Non Reactive Resistor
These resistors, also known as non-inductive resistors, have pure resistance. A common wire wound resistor has inductance due to the magnetic field produced by the winding. Non-reactive resistors have special winding designs to cancel each other’s magnetic fields.
Impedance
The impedance is a complex quantity made of real & imaginary part. The real part represent the resistance & the imaginary part represents the reactance.
Heating Element
This component converts the electrical energy into heat energy. The current flow through the heating element generates heat energy due to its resistance.
Protective Resistor
These both symbols represent a protection resistor. It operates like a resistor that limits the current flow & if the current exceeds its certain limit then it blow out opening the circuit.
Memristor
Memristor or also known as memory resistor is a hypothetical non-volatile memory component whose resistance depends on the current that has been passed through it in the past. It remembers its last known resistance when it is Powered OFF/ON.
Shunt Resistor
A shunt resistor (also known as current shunt) is a resistor with low & precise resistance used to measure the current through it. The current is measured by the voltage drop across it. Thus it acts as a current sensor.
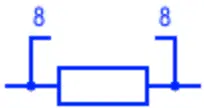
Resistor Array
Resistor array is a combination of multiple resistors in a single packaging. It contains multiple individual resistors denoted by the number in the symbols e.g 8 in this case. The resistors are not connected together except for its one side which is connected with VCC for pull up & GND for pull down. They are used for saving space & cost of placing.
Variable & Adjustable Resistor Symbols
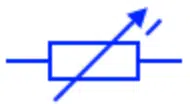
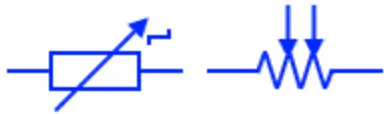
Variable Resistor
A variable resistor also known as potentiometer or rheostate has a variable resistance. It has three terminals. The two of them have fixed resistance while the third terminal move over the resistive trace or wire to increase or decrease the resistance. They are used for increasing or decreasing the current flow in a circuit during its normal operation.
Continuous Variable Resistor
Such type of variable resistor has a continuous resistance i.e. the sliding or rotating the contact gives out a continuous value of resistance. It can achieve infinite numbers of resistance values ranging from min to max.
Step Variable Resistor
This type of variable resistor’s resistance increase or decreases in steps . The contacts does not slide smoothly but jumps from steps . Each step movement increase or decrease a fixed amount of resistance.
Carbon Pile Variable resistor
This type of variable resistor is made up of carbon discs clamped together between two metal plates. Increasing or decreasing the pressure between these metal plates increases the resistance of the device.
Variable Resistor with ON/OFF switch
This type of variable resistor has a built-in switch that breaks or make the contact between the two terminals.
Preset Resistor
Preset resistor is a variable resistor that is only operated during manufacturing and tuning a circuit. they are not operated during the normal use of a circuit. there design are not as rigid as a variable resitors (Potentiometer etc).
Special Resistor Symbols
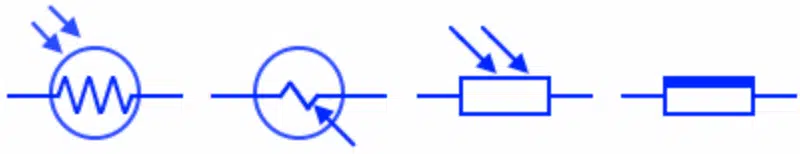
Photo resistor Light Dependent Resistor LDR
It is a light dependent resistor i.e. its resistance depends on the intensity of the light. The resistance of LDR decreases with increase in the light intensity.
Thermistor
Thermistor or thermal resistor is a type of resistor whose resitance depends on its surrounding temperature. It either decrease or increase with the temperature depnding on the type of thermistor.
NTC & PTC Thermistor
NTC stands for negative temperature coefficient & PTC stands for positive temperature coefficient. The NTC Thermistor resistance decrease with increase in the temperature & denoted by –t° sign. The PTC thermistor resistance increase with increase in temperature & denoted by +t° sign.
Varistor VDR
Varistor or VDR (voltage dependent resistor) is a type of resistor whose resistance depends on the voltage applied. Its resistance varies with the change in the applied voltage. These symbols (some of them are old & new) represent varistor.
Iron Hydrogen Resistor
It is positive temperature coefficient resistor made of iron wire inside hydrogen filled bulb. Its resistance increase with temperature which is due to the increase in the current flow. The increasing resistance opposes the increase in current. Thus they are used in stabilizing circuit.
Magneto Resistor
Magneto resistor or MDR (Magnetic dependent resistor) is a type of resistor whose resistance depends on the external magnetic field. It resistance changes with change in magnetic field intensity & It is a used as a magnetic sensor for sensing magnetic field.
Resistance thermometer or RTD
Resistance temperature detector (RTD) is a temperature sensor whose electrical resistance changes with the temperature. The material used in RTD’s has very accurate relation between the resistance & temperature. It can be measured by supply of constant current & the voltage drop across the resistor.
Regional and Historical Variants
1 DIN 40900 (Germany – Obsolete)
The German DIN 40900 standard, now superseded by IEC 60617, used symbols very similar to modern IEC standards, with rectangular representations for fixed resistors and similar arrow indicators for variable types [2].
2. AS 1102 (Australia – Obsolete)
The Australian AS 1102 standard has been replaced by adoption of IEC 60617. Historical Australian schematics may show minor variations in symbol proportions and arrow styles [2].
3 JIS (Japanese Industrial Standards)
Japanese standards generally follow IEC 60617 conventions but with occasional local variations. Some older Japanese schematics may use ANSI-style zig-zag symbols due to historical US inuence[2][3].
Symbol Selection Guidelines
Choosing Between IEC and ANSI
International Projects: Use IEC 60617 symbols (rectangular style) for broader international compatibility[2][3]. US-Based Projects: ANSI/IEEE 315 symbols (zig-zag style) remain common in American industry and education[2][3]. Consistency: Never mix IEC and ANSI symbols within a single schematic diagram[2].
Documentation: Always specify which standard is used, typically in the drawing title block [2].
Modern Trends
Current trends show increasing adoption of IEC 60617 symbols globally, even in traditionally ANSI-dominated regions[2][3]. Most modern EDA (Electronic Design Automation) software packages support both standards and allow users to select their preferred symbol set.
Reference Designations and Value Notation
Regardless of the symbol standard used, resistor reference designations follow consistent conventions:
- Reference Designator: Always begins with “R” followed by a sequential number (R1,R2, R3, etc.) [3]
- Value Notation: Expressed in ohms (Ω), kilohms (kΩ), or megohms (MΩ) [3]
- Tolerance: Often indicated as a percentage (±1%, ±5%, etc.) [3]
- Power Rating: Specified in watts (W) when critical to design [3]
Example Reference Designation
- R15
- 4.7kΩ ±5%
- 0.25 watts.
Standards Comparison Summary
| Standard | Region | Status | Symbol Style |
|---|---|---|---|
| IEC 60617 | International | Active | Rectangle-based |
| ANSI Y32.2 / IEEE 315 | United States | Active (revised periodically) | Zig-zag based |
| ISO 14617 | International | Active | Similar to IEC |
| DIN 40900 | Germany | Obsolete | Rectangle-based |
| AS 1102 | Australia | Obsolete | Replaced by IEC |
| JIS C 0617 | Japan | Active | Generally follows IEC |
Understanding resistor symbol variations across IEC, ANSI/IEEE, and other standards is essential for eective communication in international electronics engineering. While the fundamental concepts remain consistent—xed resistors, variable resistors, and specialized types—the graphical representation diers primarily between the rectangular IEC style and the zig-zag ANSI style[2][3].
Modern engineering practice increasingly favors IEC 60617 symbols for international compatibility, though ANSI/IEEE 315 remains prevalent in US-based work[2][3]. The most critical practice is maintaining consistency within any single schematic and clearly documenting which standard is employed.
References
- [1] IEC 60617 Symbols Documentation. Available at: https://qelectrotech.org/forum/misc.php?action=punattachment&item=2124
- [2] EEPower. (2024). Resistor Symbols | Resistor Standards and Codes. https://eepower.com/resistor-guide/resistor-standards-and-codes/resistor-symbols/
- [3] Utmel. (2025). Resistor Symbols: From Circuit Diagrams to PCB Design. https://www.utmel.com/blog/categories/resistor/resistor-symbols-from-circuit-diagrams-to-pcb-design
- [4] Passive Components EU. (2026). Resistor Symbols. https://passive-components.eu/resistor-symbols/
- [5] ASUTPP. Resistor Symbols: Complete List. https://www.asutpp.com/resistor-symbols.html
- [6] AiChipLink. (2025). Decoding Potentiometer Symbols in Circuit Diagrams. https://aichiplink.com/blog/Decoding-Potentiometer-Symbols-in-Circuit-Diagrams
- [7] Wikipedia. (2005). Electronic symbol. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electronic