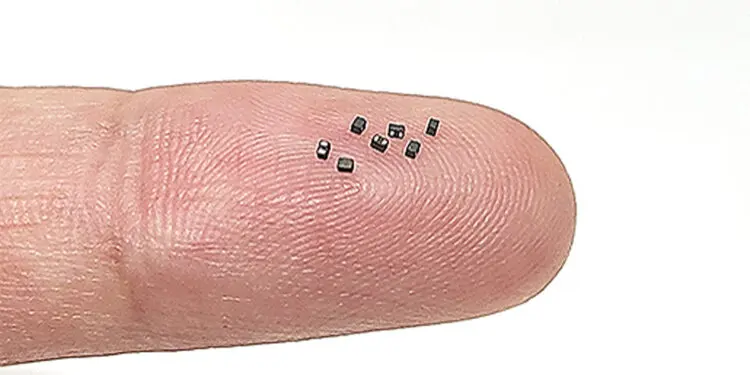
Samsung Electro-Mechanics revealed that it had developed the world’s smallest 0804 size power inductor.
The power inductor that was developed is of 0804 size (width 0.8mm, length 0.4mm), which is a significant decrease in area compared to the previously most smallest product of size 1210 (width 1.2mm, length 1.0mm), with a thickness of only 0.65mm. Samsung Electro-Mechanics is planning to supply this product global mobile companies.
The power inductor is a core component necessary to supply stable electricity (power) coming from the battery to the semiconductor, and it is a necessity used in smart phones, wearable devices, and electric vehicles. Recently, with the gradual trend towards light weight and size reduction of IT devices and increase in the number of multifunctional and high-performance components installed in 5G telecommunications and multi-cameras, the internal storage space for components has decreased, requiring miniature products. Moreover, with an improvement in component specs, power usage has increased, resulting in the need for power inductors that can withstand high currents.
The performance of the power inductor is generally determined based on the magnetic substance material (an object with magnetic characteristics) and the number of coils (copper wires) that can be internally winded. That is, in order to improve the performance of the power inductor, it is necessary to improve the magnetic substance characteristics and wrap more coils within a limited space.
Based on its material technology and semiconductor substrate manufacturing method accumulated through MLCC< Samsung Electro-Mechanics was able to reduce the size by approx. 50% and improve electricity loss. Moreover, rather than generally processing the power inductor in individual units, Samsung Electro-Mechanics manufactured them in substrate units to improve productivity and develop a thin product.
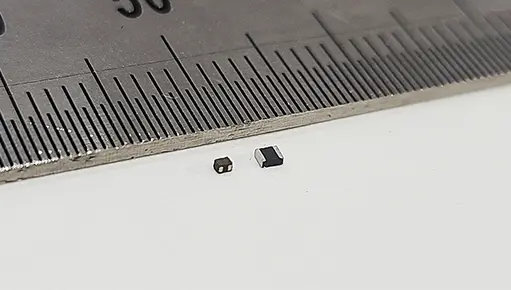
Samsung Electro-Mechanics developed materials that applied nano-grade, ultra-microscopic powder in-house and succeeded in realizing finely spaced coils by applying the dimming technology (manufacturing method using light to mark circuits) applied in semiconductor manufacturing.
Kang Heon Hur, Vice President and Head of the Central Research Institute at Samsung Electro-Mechanics, revealed, “As the performance for electronic products increase and functionalities diversify, the size of the internal components must decrease along with an improvement in performance and volume. To do this, differentiating technology is necessary. Samsung Electro-Mechanics has been enhancing its product competitiveness through conversion and integration of technologies as the only company that possesses both material technology and micro engineering technology.”
Since 1996, Samsung Electro-Mechanics has been developing and manufacturing inductors, and it has been recognized for its industry-leading technology in miniaturization. Samsung Electro-Mechanics plans to expand its product line-up and market share through material development and super-differential technology, such as ultrafine engineering method.
With the high-performance and multifunctionality of electronic devices, activation of 5G telecommunications, and growth of the wearable device market, the demand for super-small power inductors is expected to grow at a rapid pace, and its installment within electronic devices is forecasted to grow by at least 20% per year.
※ Reference
Both the MLCC and power inductors are passive components that control voltage/current to allow for smooth operation of electronic devices. Because each component has its own characteristics, they must both be installed in the electronic device. Generally, the capacitator serves a role in supplying voltage and the inductor serves a role in supplying stable energy to the semiconductor by preventing sudden changes in the current.