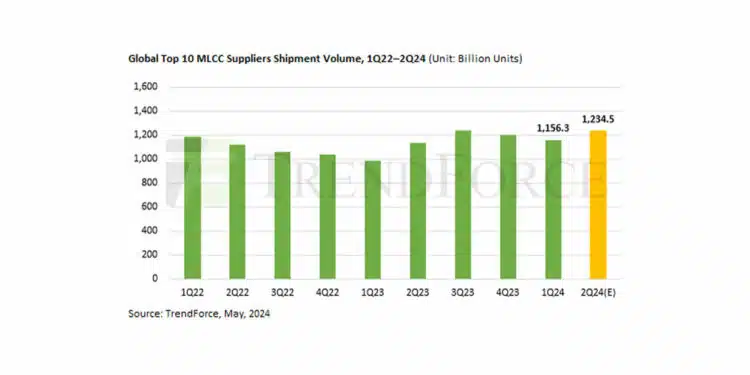
TrendForce projected MLCC ceramic capacitors shipments to increase by 6.8% in the second quarter to reach 1.2345 trillion units, which will also drive slight revenue growth in the same period.
TrendForce says that MLCC shipments in 1Q24 are expected to reach a three-quarter low. In the second quarter, demand for AI servers continued to grow steadily, while orders for other consumer electronics have fallen short of expectations due to traditional seasonal demand and preparations for China’s May Day holiday and the 618 shopping festival.
Overall, AI server orders and stable ICT product demand—despite not seeing high seasonal growth—are helping stabilize production capacity utilization.
Smartphone, PC/notebook, and general server inventory remain steady; MLCC BB Ratio for Q2 is estimated to be around 0.92.
Consumer interest in AI-related products has not met expectations due to pricing and lack of applications. For example, US commercial notebook brands currently have ODM orders for Meteor Lake models averaging only 200,000 to 240,000 units per month for the second quarter—a significant drop from the usual 500,000 units per month for new platforms in the same period. Additionally, in the Chinese smartphone market, only Huawei has maintained stable inventory due to strong sales of the new Pura 70 series, while other brands have slowed their inventory, leading to a 5–7% QoQ decline in MLCC orders.
Due to steady demand from the ICT industry in the second quarter, OEMs and ODMs are planning their MLCC orders conservatively. As a result, MLCC suppliers are cautiously managing capacity and inventory, focusing primarily on urgent, short-term, and reallocation orders. TrendForce believes that if ODMs maintain their current stocking pace, the MLCC suppliers’ average BB Ratio for the second quarter is expected to increase slightly to 0.92—a QoQ growth of 2.2%.
Consumer-grade MLCC prices remain stable or see reduced price declines; Automotive-grade MLCCs face a price war
As market demand growth remains sluggish in the first half of the year, suppliers are becoming more cautious about traditional peak season demand in the second half. In late May, MLCC suppliers began price negotiations with ODMs for the third quarter. Due to the OEMs’ conservative approach to peak season order planning, with an average quarterly increase of only 8–10%, which is below past peak season levels, consumer-grade product prices have either remained stable or slightly declined. MLCC suppliers are only adjusting prices for certain high-capacity or special specification products to prioritize the demand growth from sectors like AI servers.
In contrast, the Chinese automotive market is seeing a price war for automotive-grade MLCC products due to aggressive expansion by Chinese automakers into domestic and European markets. This competition persists despite the recent significant increase in tariffs on Chinese EV imports by the US. The Chinese government’s active promotion of industries like EVs, batteries, and solar panels continues to attract European automakers to collaborate with Chinese companies for development and production. Examples include partnerships between Volkswagen and Xpeng, Stellantis and Leapmotor, and Mercedes-Benz and Geely. Consequently, MLCC suppliers are likely to continue adjusting prices each quarter to meet customer demands, keeping prices under pressure. Given the growing significance of the Chinese market, MLCC suppliers face mounting pressure to maintain their market positions there.