This paper Towards W-Band Self-Biased Circulators For Next Generation Of Vhts Payload Was presented by Evan Roue, Univ Brest, France during the 5th Space Passive Component Days (SPCD), an International Symposium held from October 15th to 18th, 2024, at ESA/ESTEC in Noordwijk, the Netherlands. Published under permission from ESA SPCD organizers.
Introduction:
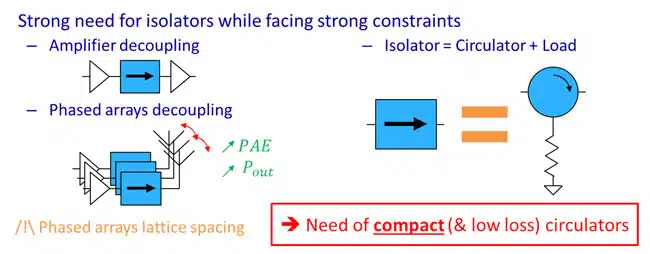
Circulators and isolators are pivotal non-reciprocal devices in satellite communication systems, primarily used to protect amplifiers from impedance mismatches and to maintain low reflection levels in electronically steerable antennas.
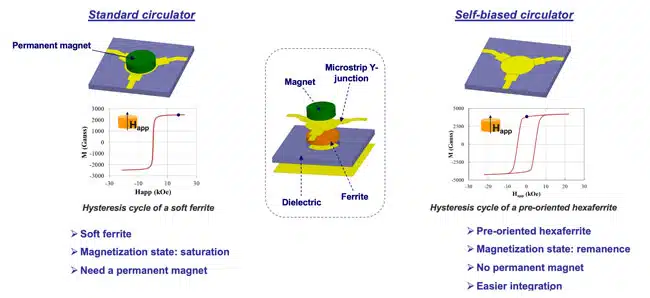
Conventional devices rely on soft ferrites and permanent magnets, which become bulky and inefficient at higher frequencies. This poses a challenge for future Very High Throughput Satellites (VHTS) utilizing W-band frequencies (71–76 GHz) to achieve higher data rates.
The study explores the fabrication and performance of compact, self-biased circulators and isolators using pre-oriented hexaferrites, eliminating the need for external magnets.
Key Points:
- Non-reciprocal Devices: Traditional circulators require bulky magnets, limiting their application at W-band frequencies.
- Self-biased Circulators: Utilizing pre-oriented hexaferrites allows the development of compact, magnetless circulators.
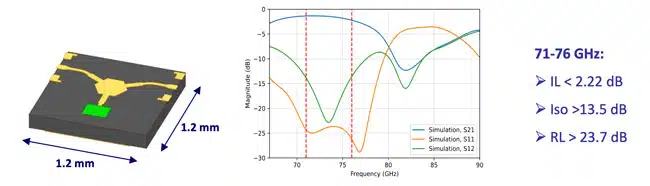
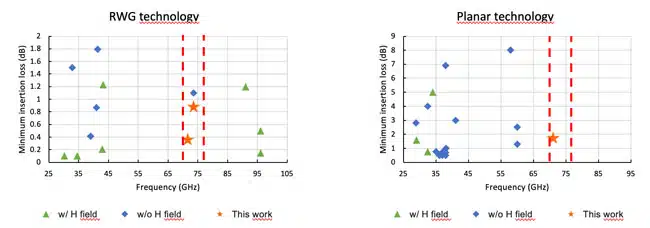
- W-band Performance: The study demonstrates promising results with insertion losses lower than 1.06 dB and isolation above 14.5 dB for waveguide circulators, and planar isolators achieving up to 25.1 dB isolation.
- Material Advantage: Strontium hexaferrites offer high anisotropy, robust performance against temperature and external magnetic fields.
Extended Summary:
The study investigates the feasibility of self-biased W-band circulators and isolators for next-generation VHTS payloads. Traditional soft ferrites, though effective, demand large permanent magnets that grow bulkier as operating frequencies increase. This issue is addressed by replacing soft ferrites with pre-oriented hexaferrites, specifically strontium hexagonal ferrites, which possess high anisotropy fields (18–20 kOe) and robustness against temperature variations and stray magnetic fields.
In the first phase, the researchers designed and fabricated WR-10 rectangular waveguide circulators optimized for 71–76 GHz. The circulators demonstrated insertion losses as low as 1.06 dB and isolation levels exceeding 14.5 dB. The performance indicates strong potential, especially as assembly and calibration processes are further refined.
Subsequently, ultra-compact planar microstrip isolators were developed within the same frequency range. These devices, measuring just 2 mm × 2 mm, incorporate coplanar waveguide-to-microstrip transitions to facilitate probe station measurements. Despite a slight frequency shift, the planar isolator achieved insertion losses below 2.29 dB and isolation levels peaking at 25.1 dB at 72.7 GHz, remaining above 11 dB across the operational band.
The study details the material properties of substituted hexaferrites used, emphasizing their high remanence-to-saturation ratio and coercive field, which eliminate the need for external magnetic biasing. The waveguide circulators employed a split-block aluminum design with silver-plated interiors to minimize metallic loss. Measurements conducted with Rohde & Schwarz network analyzers revealed results closely aligned with simulations, though minor discrepancies were noted due to technological tolerances and ferrite placement variations.
For planar technology, Y-junction circulators were adapted into isolators by terminating one port with a matched load. Fabrication involved standard ceramics-based microwave processing, including photolithography and selective etching. The devices were magnetized using a vibrating sample magnetometer at 23 kOe. Measurement data confirmed the feasibility of compact, efficient W-band self-biased isolators suitable for satellite applications.
Conclusion:
This research successfully demonstrates state-of-the-art performance for self-biased circulators and isolators operating in the W-band. Both rectangular waveguide and planar technologies achieved competitive insertion loss and isolation metrics compared to traditional magnet-based designs. Notably, the planar isolator represents the first of its kind in W-band, highlighting significant potential for integration into future VHTS payloads. The promising results pave the way for further development of compact, lightweight, and efficient non-reciprocal devices critical to next-generation satellite communication systems.
Read the full paper: