Source: TTI MarketEye article
05/02/2018 // by Dennis M. Zogbi This unique Paumanok comparison shows how the number of vendors that were able to move the technology of stacking high capacitance multilayered ceramic chip capacitors in the X5R and X7R product markets became limited after 2005 as the ability to increase capacitance in specific operating parameters ground to a halt and many customers began to rely on a smaller number of vendors to support key capacitance values in the lucrative 1 to 470 chip capacitor microfarad marketplace.
This case study for TTI MarketEYE also reveals that consolidation of technology through acquisition also played a role in limiting the number of viable competitors in the space today.
Technology Assessment of the High Capacitance X5R MLCC Market Segment: 2005, 2013, 2018 Comparisons of the Roadmap:
The key competitive area with respect to (1) maximum capacitance per MLCC, (2) coupled with “change in capacitance with temperature” is the X5R dielectric MLCC, which is not as stable as true X7R, but is acceptable in applications where the shelf life of the product is not more than three years. However, as far as we can tell from our primary research with customers who purchase and design in these components, they have proliferated over the years into more end-markets such as lighting ballasts and drivers, high voltage power supplies, high temperature engine electronics and high frequency backbone infrastructure where they had not been used during past iterations of this report. X5R type high capacitance MLCC would also be the location where we would find the most vendors of the lucrative 100 microfarad MLCC, a market which is now being designed into handset modules for the smartest of phones.
When we review the technology comparisons that Paumanok IMR conducted between 2005 and 2013 and 2018, we see how the X5R MLCC technology remains the most valuable portion of the market to date as well as the fastest growing as it has successfully extended the capacitance value of the MLCC into the 100 microfarad, 220 microfarad, 330 microfarad and 470 microfarad range, which is remarkable because it moves deep into the heart of the electrolytic capacitor market, which has been historically quite large and lucrative. This is a much more attractive and potentially lucrative segment with one of the greatest potential returns on investment over the next five years, primarily because it has proven itself to be so on numerous occasions over the past quarter century.
X5R MLCC are all considered by Paumanok to be “high capacitance BME (Base Metal Electrode), or in effect covering the market from 2.2 to 470 microfarad and therefore where the parameters of performance and production have extended the technology very far into the electrolytic range employing the relatievly stable performance guidelines associated with the X5R ceramic dielectric formulation, but not quite achieving the +/- 10% stability found in true X7R MLCC, or the +/- 5% stability found in molded tantalum chip capacitors that employ a tantalum pentoxide dielectric.
X5R MLCC Market Impacted by Acquisitions and Slow Adoption of Technology: 2005-2013-2018
The chart below illustrates the sample of vendors and their respective MLCC portfolios in X5R dielectric in the years 2005, 2013, and 2018. The reader should note that in 2005 the sample of vendors producing this technology was twelve (12). Between 2005 and 2013 three of the vendors were consolidated through acquisitions (and these were very smart purchases in hindsight of the current shortages); and included (1) Murata’s purchase of Panasonic’s MLCC operations and (2) Murata’s purchase of Rohm Company Limited’s MLCC operations; and these two purchases propelled Murata into significant market positioning in X5R MLCC. Likewise, (3) TDK also purchased EPCOS which inlcuded the EPCOS MLCC factory in Austria. The EPCOS auto MLCC plant in Austria for example catered largely to automotive “Under-The-Hood” customers in Germany, further consolidating the supply chain.
So in 2005 we see that four companies lead the field in terms of their ability to produce MLCC in the X5R dielectric to 100 microfarad (and beyod to 470 µF) and these are Murata, TDK, Taiyo Yuden and Kyocera Corporation. However, by 2013, we see other MLCC manufacturers increase their technology base at a much faster rate through thoughtful and applied investment and we see Murata, Taiyo Yuden, Yageo, Samsung EMCO and Walsin emerging as technology leaders. By advancing their X5R technology base toward the next levels of volumetric efficiency and maximum capacitance, these vendors located almost exclusively in Asia, now have a competitive advantage over the entire supply chain for high-tech goods. It is also clear at this point that some of the manufacturers got consolidated through acquisition or through private label agreements, thus further narrowing those who are actually contributing to maintain the technology roadmap.
Once again, by 2018 we see that there are eight manufacturers supplying the market and four manufacturers emerging as still moving the technology forward, with Taiyo Yuden, Murata, Samsung and Walsin working hard to promote the advancement of X5R technology in 2018, but with the clear milestones of the Taiyo Yuden 470 microfarad X5R MLCC and the Murata 330 Microfarad MLCC showing us the pathway to where the next level of investment is required, but also revealing during that process that the technology is challenging to master and not easy for others, even those involved in the market to emulate further suggesting that the current shortage will last as long as the vendors in the table below do not expand beyond the ability for the market to absorb their output.
SUMMARY TABLE: Competitive Environment In X5R High Capacitance MLCC Markets By Maximum µF: 2005-2013-2018
Source: Paumanok Publications, Inc. “Capacity Expansion In The Global MLCC Industry”: 2005, 2013 and 2018 Editions; ©2018 Paumanok Publications, Inc.
Technology Assessment of the High Capacitance X7R MLCC Market Segment: 2005, 2013, 2018 Comparisons of the Roadmap
An even more challenging area for technology has been in the high capacitance X7R MLCC market segment. X7R is a demanding dielectric and difficult to master and work with according to primary sources who engage in ceramic dielectric chemistry. Over the years, certain problems have arisen that are specific to the X7R dielectric chemistry when applied to extremely thin MLCC layers with emphasis on adverse interaction of the dielectric layer and the fine nickel electrode. This makes the extension of MLCC with true X7R performance into increasingly higher capacitance levels a very difficult proposition and a true hurdle in moving the high capacitance MLCC market forward. The surprising aspect once again is that in true X7R high capacitance MLCC, the number of vendors who have mastered the BME MLCC technology remains limited.
So in the 2013 market analysis, it became clear that Taiyo Yuden, Samsung and Murata were the only vendors that had invested the research and development dollars into capturing the X7R high capacitance MLCC market to 47 microfarad, and we see no evidence of movement at all in advancing the technology after that time period (between 2013 and 2018).
X7R MLCC Market Impacted by Lack of Investment in High Capacitance Variations: 2005-2013-2018
The following chart illustrates that by 2005, the number of vendors of high capacitance X7R MLCC included ten manufacturers, with two vendors who competed in X5R selecting not to compete here in the high capacitance X7R dielectric MLCC markets; with two remaining vendors using a ceramic variation and not actually achieving X7R. We also note that by 2013, that Rohm Company MLCC business has been acquired by Murata, and Murata emerged as the market leader and advanced the technology to 47 microfarad, as did Taiyo Yuden and Samsung EMCO.
Please note however that between 2013 and 2018 there are no movements in advancing the X7R MLCC technology, and the number of vendors who can produce a true X7R 47 µF MLCC remain at only three. And this shows us the leading edge of the shortage, the tip of the technology limitation spear.
SUMMARY TABLE: Competitive Environment In X7R High Capacitance MLCC Markets By Maximum µF: 2005-2013-2018
Source: Paumanok Publications, Inc. “Capacity Expansion In The Global MLCC Industry”: 2005, 2013 and 2018 Editions; ©2018 Paumanok Publications, Inc.
High Capacitance MLCC Lead Times in April 2018:
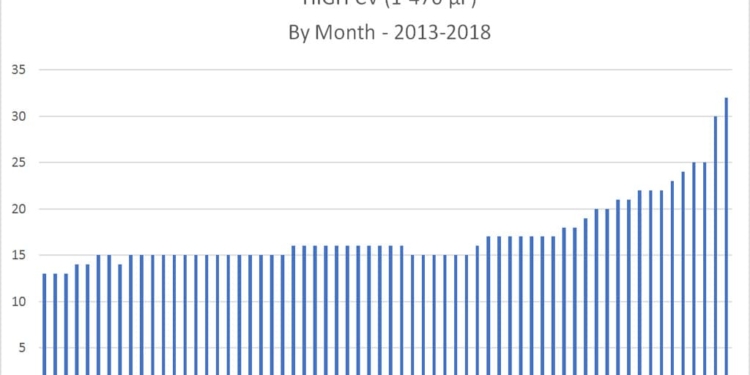
The following chart illustrates the latest data on collective lead times for high capacitance BME MLCC for the month of April 2018. The data supports an increasingly longer lead time for high capacitance BME MLCC consumption. The chart shows approximately five years of monthly data that graphically illustrates the lengthening lead times and MLCC shortages evident in the supply chain in 2017 and 2018.
High Capacitance MLCC Lead Time Trends: January 2013- April 2018
see featured image, source: Paumanok Publications, Inc. Monthly Market Research Report on Passive Electr0nic Components April 2018 Edition PPI ANALYSIS: CERAMIC CAPACITOR LEAD TIMES Ceramic capacitor lead times continued to rise in April 2018. Major ceramic capacitor vendors include Murata, TDK, Taiyo Yuden, Kyocera/AVX, Walsin, Yageo and KEMET.
Summary and Conclusions
Advances in high capacitance MLCC in the X5R and X7R dielectric have been slow to develop between 2005 and 2018 as this MarketEYE article discusses. Most emphasis has been placed on expanding the “easier to master” X5R dielectric for capacitance values to 100 microfarad and beyond, and also places some emphasis on the narrowing of the channel because of smart acquisitions and because of private label agreements. We expect that capacity expansion in the global MLCC markets will eventually cause lead times to come back down, but the added difficulties of achieving profitable capacity expansion in the much needed X7R dielectric seems slightly out of reach for some of the challengers to the competition.