This article based on Modelithics blog article “taking advantage of discrete optimization” explains hot to optimize discrete components in RF circuit design using Keysight ADS and Modelithics Microwave Global Models that automatically selects real-world component values during simulation.
This bridges the gap between idealized designs and manufacturable circuits, improving accuracy and streamlining the design process.
Introduction: The Hidden Gap in RF Circuit Optimization
In the world of RF and microwave circuit design, optimization is not just a luxury—it’s a necessity. Whether you’re crafting a high-performance filter or fine-tuning an amplifier, the ability to adjust component values to meet stringent performance goals is central to success. Yet, a persistent challenge lurks beneath the surface of traditional optimization workflows: the disconnect between idealized component values and the real-world parts available from manufacturers.
Imagine designing a lowpass filter using surface-mount RLC components. You run a simulation, perform an optimization, and arrive at values that look perfect on paper. But when you go to source those components, you realize that the values—say, 5.569 nH for an inductor or 2.076 pF for a capacitor—don’t exist in any catalog. The result? A frustrating and time-consuming process of manually mapping ideal values to the closest available parts, often compromising performance in the process.
This is where discrete optimization enters the picture—not as a workaround, but as a transformative solution.
Discrete Optimization: Bridging Simulation and Reality
Discrete optimization is a feature available in Keysight’s Advanced Design System (ADS) when paired with Modelithics Microwave Global Models™. Unlike traditional optimization, which treats component values as continuous variables, discrete optimization constrains those values to actual, manufacturer-specified part numbers. This means that the output of your simulation isn’t just theoretically optimal—it’s physically realizable.
Modelithics offers comprehensive model libraries for RLC components from leading vendors such as Coilcraft and KYOCERA AVX. Each Microwave Global Model spans an entire part series, enabling designers to simulate, tune, and optimize across a wide range of real-world values. These models include parameters like L_Discrete, C_Discrete, and R_Discrete, which allow you to select specific part values or activate discrete optimization mode directly within ADS.
A Practical Example: Designing a Lowpass Filter
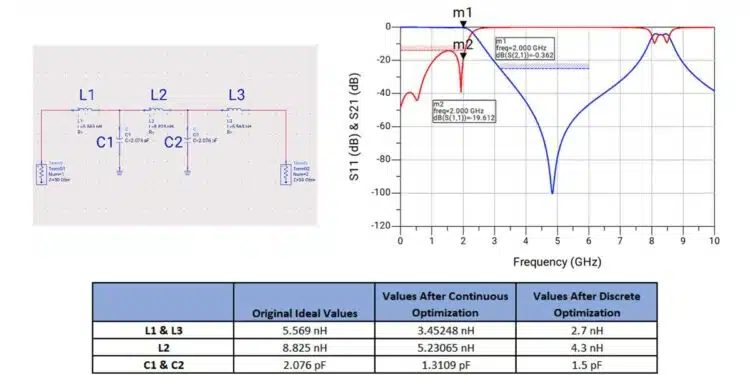
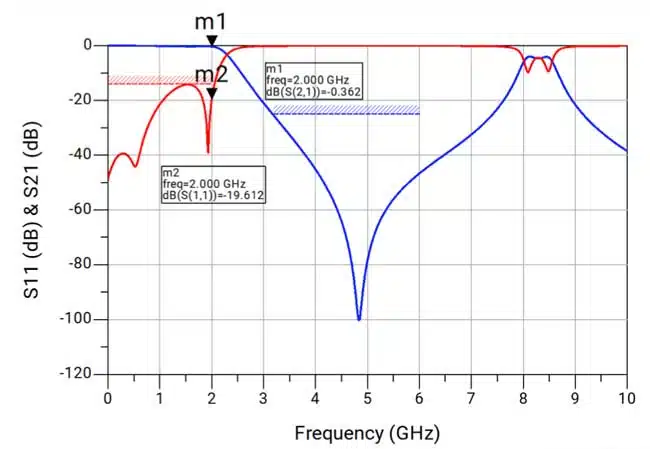
To illustrate the power of discrete optimization, consider a simple lowpass filter designed to pass signals up to 2 GHz. Using a synthesis tool, the initial design specifies ideal component values: inductors L1 and L3 at 5.569 nH, L2 at 8.825 nH, and capacitors C1 and C2 at 2.076 pF. These values serve as a theoretical starting point. See Figure 1. schematic and its frequency response.
When these ideal models are replaced with real components—specifically, Coilcraft’s 0402CS series inductors and KYOCERA AVX’s 600L series capacitors—the frequency response shifts downward by approximately 630 MHz. This deviation underscores the impact of parasitics and layout effects, which are captured by the Modelithics models but absent in ideal simulations.
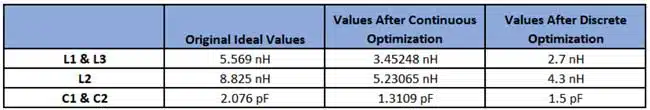
To correct this, the design undergoes a two-step optimization process. First, a continuous optimization is performed to identify the general range of values that meet the desired performance goals: S11 below −14 dB from DC to 2 GHz, and S21 below −25 dB from 3.2 to 6 GHz. This yields new component values—L1 and L3 at 3.45248 nH, L2 at 5.23065 nH, and C1 and C2 at 1.3109 pF—but again, these are not real parts.
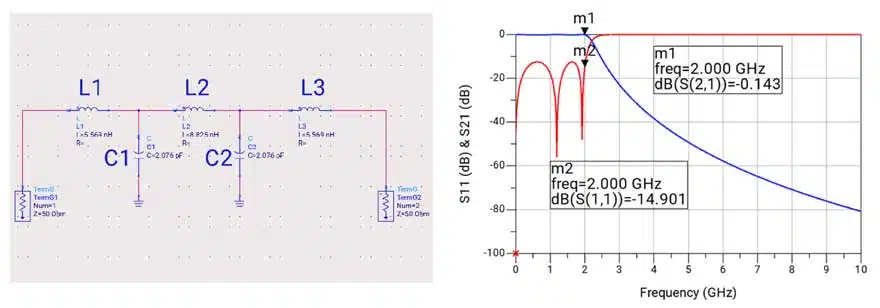
Armed with this insight, the designer then performs a discrete optimization. By setting nominal, minimum, and maximum values based on the results of the continuous optimization, the tool automatically selects the best available components. The final design uses L1 and L3 at 2.7 nH, L2 at 4.3 nH, and C1 and C2 at 1.5 pF—values that exist in manufacturer catalogs and deliver the desired frequency response. See Table 2. of the parameters optimization and frequency response of real parts in the Figure 2.
Strategic Impact: Why Discrete Optimization Matters
The implications of this approach extend far beyond a single filter design. Discrete optimization streamlines the entire design workflow, eliminating the guesswork and manual adjustments that often plague RF projects. It ensures that simulation results translate directly into manufacturable designs, reducing time-to-market and improving reliability.
Moreover, by leveraging vendor-validated models, designers gain a deeper understanding of how components behave in real-world conditions. This leads to more accurate simulations, better performance, and fewer surprises during prototyping and testing.
Conclusion: A Smarter Way to Design
Discrete optimization is more than a feature—it’s a philosophy. It represents a shift toward realism, precision, and efficiency in RF design. By integrating Modelithics Microwave Global Models with Keysight ADS, engineers can move confidently from concept to implementation, knowing that their designs are grounded in the realities of component availability and performance.
If you’re ready to elevate your design process, discrete optimization is the tool you’ve been waiting for.