Source: Panasonic article
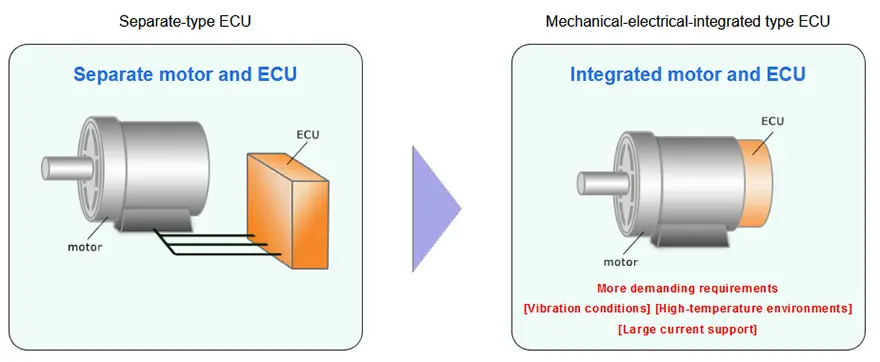
With the growing demand for energy efficiency of eco-friendly cars and the need to comply with environmental regulation, computerization of cars has been rapidly expanding, and ECUs are being incorporated, more frequently and on larger scales in cars. In addition, more ECUs are being placed within the engine itself, elevating integration of mechanical and electronic in-vehicle components. This trend has created a need for automotive ECUs that can be installed in high-temperature environments that have more severe vibration conditions and support large current.
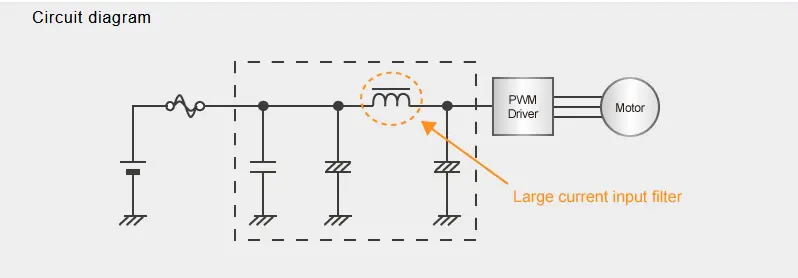
Choke coils with high resistance to vibration and heat as well as support for large current are essential for removing noise and smoothing the power supply of power circuits that constitute automotive ECUs. Panasonic is launching its surface-mounted type power choke coil for automotive use achieving resistivity of 50 G or higher vibration acceleration.
What is high vibration acceleration-resistant, power choke coil for automotive use
Excellent vibration resistance, heat resistance, and large current support allow customers to streamline their production process, and contribute to the placement of ECUs in the engine itself and integration of mechanical and electrical components.
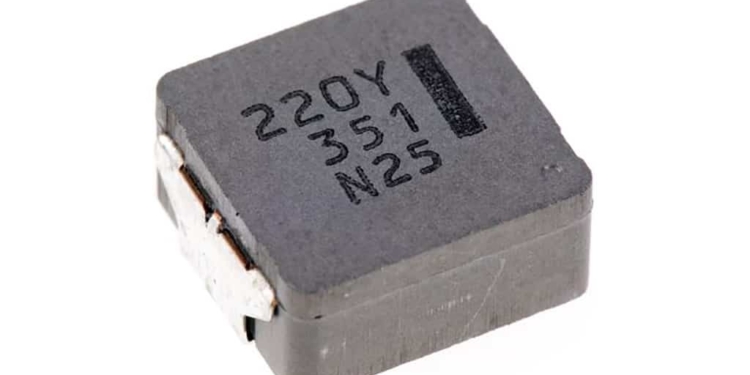
Features of high vibration acceleration-resistant, power choke coil for automotive use
- High resistance to vibration acceleration, enabling the automotive ECU to be more resistant to vibration.
- Remove the need for the anti-vibration reinforcement as part of the board mounting process, allowing the streamlining of the production process.
- Its excellent heat-resistance and support for large current, contributes to the ability to place of automotive ECUs in the engine itself.
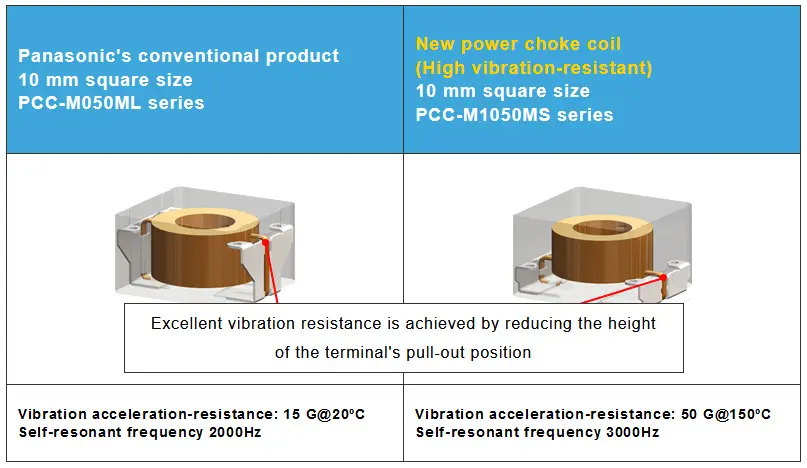
Product Features
1. The power choke coil has high resistance to vibration acceleration, enabling automotive ECUs to be more resistant to vibration.
The new power choke coil withstands vibration acceleration of 50 G or higher in 150ºC environments (490 m/s2). The conventional product only withstands vibration acceleration of 15 G (147 m/s2).
Conventional products structurally have a low self-resonant frequency around 2,000 Hz and have an issue with vibration resistance. By utilizing the company’s unique metal composite material using its unique metal magnetic material and unique winding and molding technologies, Panasonic created a coil with a high self-resonant frequency of 3,000 Hz or higher leading to high resistance to vibration acceleration of 50 G or higher, contributing to more vibration-resistant automotive ECUs.
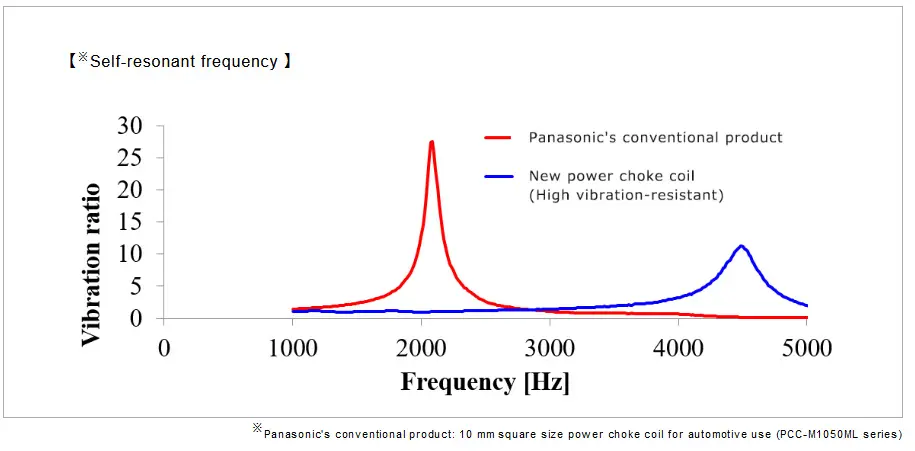
Self-resonant frequency:
An inductor has a natural frequency, and this frequency is referred to as self-resonant frequency. When the frequency of vibration conditions externally applied is in vicinity of the self-resonant frequency, stress several to several tens of times of applied acceleration is applied on the inductor, significantly deteriorating the vibration resistance.
2. The new power choke coil removes the need for anti-vibration reinforcement as part of the board mounting process, allowing the streamlining of the production process
The conventional automotive ECU board mounting process requires anti-vibration measures, such as anchoring components with bonding agents (adhesives), to make the ECU resistant to vibration. The height of the developed power choke coil’s terminal pull-out position is reduced to half that of the company’s conventional product through the adoption of the company’s unique winding and molding technologies, allowing its placement near the mounting board and achieving excellent vibration resistance. This has made conventional anti-vibration measures unnecessary, and allowing the streamlining of the production process.
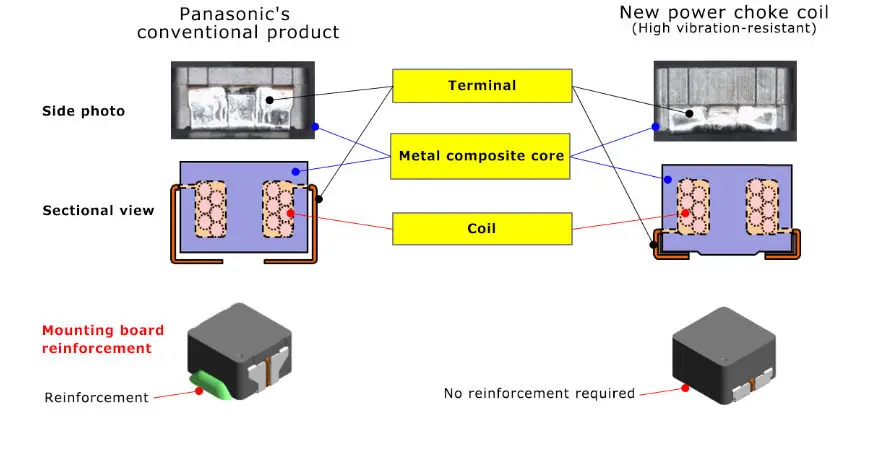
3.The power choke coil, with their excellent heat-resistance and support for large current, contributes to the placement of automotive ECUs within the engine itself
Coils used in automotive ECUs are required to be heat-resistant and support high current, in addition to being highly resistant to vibration. Previously, coils with high resistance to vibration acceleration of 30 G or higher had an issue of not being able to support large current due to their low profile and small size. The developed power choke coil achieves a vibration acceleration resistance of 50 G or higher while also having excellent heat resistance and supporting large current, through the adoption of the company’s unique metal composite material, thereby contributing to the placement of automotive ECUs in the engine itself.
【Vibration durability conditions】
| Vibration acceleration | 50G(490 m/s2) |
|---|---|
| Frequency | 5~2000Hz |
| Amplitude | 5mm max. |
| Vibration directions, number of times (Time) | X, Y, Z directions, 108 times (equivalent to 100 h) |
| Temperature | 150°C (including product’s self-heating when energized) |
【Lineup】
| Series | Part No. | Case size (L×W)㎜ |
Inductance(※1) | DC resistance (at 20℃)(※2) |
Rated current (※3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCC-M1050MS | ETQP5MR68YSC | 10.9 x 10.0 | 0.68 µH | 1.66 mΩ | 27.0 A |
| PCC-M0854MS | ETQP5M2R5YSK | 8.5 x 8.0 | 2.45 µH | 7.40 mΩ | 12.0 A |
- (※1) Measured at 100 kHz.
- (※2) Typical value
- (※3) DC current which causes temperature rise of 40 K. Parts are soldered by reflow on four-layer PWB (1.6 mm FR4) and measured at room temperature.
Application
Applications that require high vibration resistance, high heat resistance, and large current support
- ELECTRIC PUMP INPUT FILTER
- ELECTRIC FAN MOTOR INPUT FILTER
- DIRECT INJECTION INPUT FILTER / BOOST CHOKE
- BREAKING SYSTEM INPUT FILTER
- EGR INPUT FILTER
- ELECTRIC COMPRESSOR INPUT FILTER
- EPS INPUT FILTER
- START&STOP BUCK-BOOST & INPUT/OUTPUT FILTER
- BODY ELECTRIC SYSTEM INPUT FILTER