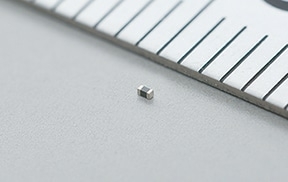
source: Murata news
Murata Manufacturing Co., Ltd., will start mass production in August of high-frequency inductors, the world’s smallest at 008004 size (0.25 × 0.125 mm). The LQP01HQ series consumes half mounting area of the smallest previous product (01005 size) and retains the same Q characteristics as the 01005 size LQP02TN series.
Background
As mobile devices such as smartphones gain more functions and improved performance, there is a need for more compact components in order to fit more of them on internal circuit boards. At the same time, wearable devices are becoming more popular, and this creates increased demand for more compact and high-performance high-frequency inductors for use in impedance matching in the high-frequency circuits required to implement wireless communication functionality.
Murata is establishing itself as a leader in this area by commercializing high-frequency inductors that achieve the industry’s highest Q*1 characteristics in a compact 01005 size device (the LQP02HQ series). Going further, Murata has now developed the LQP01HQ series, the world’s smallest at 008004 size, which will contribute to the realization of more compact mobile devices with even better performance.
The LQP01HQ series is based on the design expertise used to achieve high Q characteristics in previous products, and incorporates advances in ultrafine material and processing technology to enable the formation of extremely compact coils. Mass production is made possible through the creation of manufacturing technology that allows fabrication of these devices at the world’s smallest size. The lineup includes 25 versions with inductance ratings ranging from 0.3 nH to 2.7 nH. A 10 nH version is scheduled to be added at the end of 2016. Moving forward, Murata plans to continue to expand its lineup of high-frequency inductors to meet demand in the automotive market for expanded communication functionality and more reliable vehicles.
*1: Q = This is the reciprocal of the dielectric dissipation factor (DF). The higher the Q value, the lower the loss and also the more efficient the inductor.
Features
World’s first high-frequency inductors at the industry’s smallest size (008004 size: 0.25 × 0.125 mm)
The mounting area is approximately half that of the smallest previous product (01005 size).
- Retains the same Q characteristics as the one-size-larger LQP02TN series.
Applications
- Smartphones, mobile phones (WCDMA, GSM, LTE, etc.)
- High-frequency modules for mobile communication devices (PA, ANT, SAW, GPS, etc.)
- Wireless modules such as W-LAN and Bluetooth® modules
- Wearable devices
Part numbers
LQP01HQ0N3B02 to LQP01HQ2N7B02
External size
0.25 × 0.125 × 0.20 mm
Production
Mass production scheduled to begin in August 2016 at the Miyazaki Plant of Fukui Murata Manufacturing Co., Ltd.
Sample price
¥5/piece