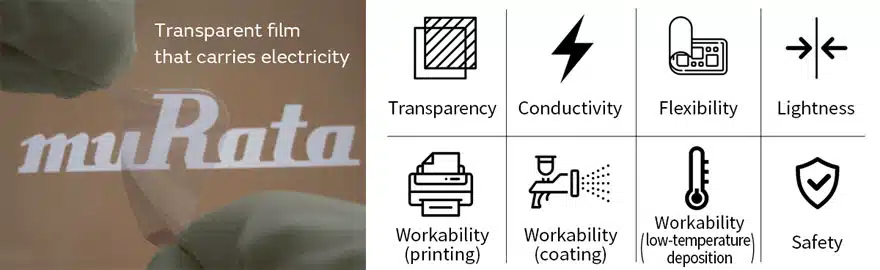
Murata is seeking partners to develop applications for a new transparent and bendable conductive film which combines transparency, flexibility and high conductivity.
Murata Manufacturing is now developing a new material with unprecedented strong points. This new material combines transparency, flexibility, conductivity, and safety.
Furthermore, it realizes high workability to be able to easily draw circuit patterns and other elements with diverse methods.
It is possible that we will be able to create new value with approaches different from conventional technologies for electrical and electronic devices by applying this new material. Murata is seeking partners to discuss the application of new ideas using this new material regardless of your business or industry.
There are broadly two strong points to Transparent and Bendable Conductive Film: it enhances the functions and performance in applications and it produces usage benefits to user companies that develop and produce products to which this material is applied (Fig. 1).
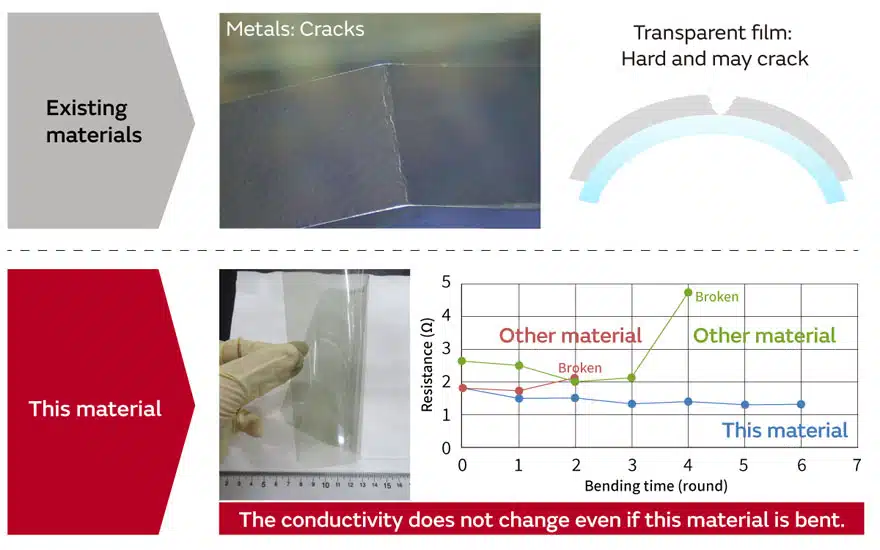
The film combines conductivity while being transparent even when it is bent. Films of indium tin oxide (ITO)-based materials used in touch-panel electrodes, wiring, and other components and conductive films using graphene composite material ink also serve as transparent and bendable conductive films. (Fig.2).
Looking only at transparency, flexibility, and conductivity, there are many materials that display even better characteristics and there are materials that combine two out of three of these strong points. However, it is not easy to find materials that combine these three strong points at a high level like with Transparent and Bendable Conductive Film.
The Film is a hydrophilic material. Accordingly, it can be easily and uniformly dispersed in solvents. Therefore, it is possible to produce inks according to the processing method and to use existing coating and printing techniques to form films with stable characteristics.
Specifically, it is possible to draw patterns under normal temperatures and pressures with inkjet printers, stamp and screen printing, spray coating, pen drawing, and other methods. Of course, it will also be possible to open up unknown applications by developing new never-before-seen ground-breaking coating systems and optimizing the ink. The ability to draw patterns using such diverse processing methods is a strong point that will support expansion of applications. For example, it is possible to draw wiring with fine line widths of several hundred microns by using an inkjet printer. Using such processing methods allows patterns to be drawn as desired without a removal process like masks or etching.
In addition, it is possible to draw just the parts that function as conducting wire. Therefore, it also realizes the effective use of materials and a reduction in the environmental burden. On the other hand, adopting a method of coating with a spray means it is even possible to cover substrates with three-dimensional curved surfaces by using the same method as that of coating the body of an automobile.
That enables the formation of conductive film on the surface of large and complex objects. Furthermore, it is also possible to easily add electrical functions to the surface of tools and devices for which the shape itself has meaning.
ITO-based electrodes require some kind of high-temperature treatment to form wiring patterns and similar to exhibit conductivity. For instance, it is necessary to attach film to the substrate with a vacuum deposition process that is performed under a high-temperature and vacuum environment for ITO-based materials.
As a result, it has been impossible to avoid an increase in the processing workload and a deterioration of the substrates to be coated. That led to drawbacks including limited applications and increased costs. Transparent and Bendable Conductive Film does not have such factors hindering an expansion in applications.
Another major advantage is the fact that post-processing after the pattern formation is simple (Fig.3.). It is necessary to add a firing process at 150 to 200°C for Ag ink that is one of the conventional materials to form transparent conductive film.
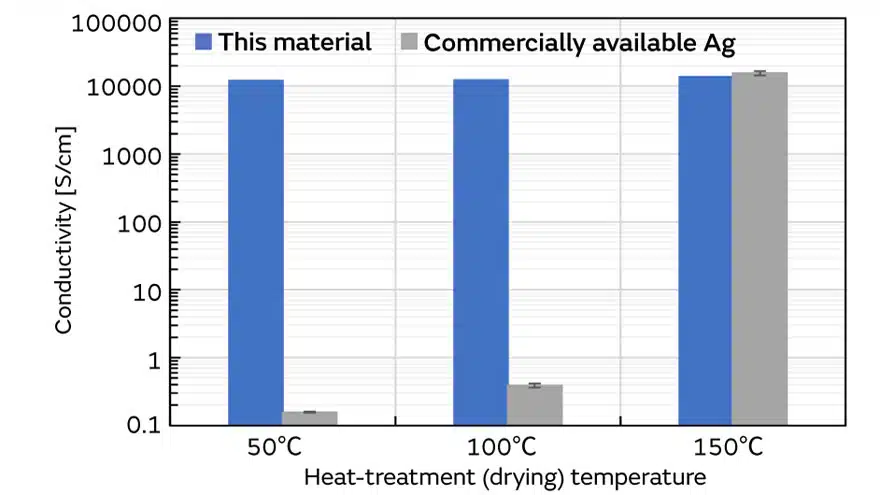
This is to ensure conductivity by connecting fine Ag particles to each other after drawing the pattern. Transparent and Bendable Conductive Film can demonstrate conductivity just by drying water at 50 to 100°C. Therefore, it is also possible to form it on substrates vulnerable to heat damage. You can even use it with natural drying if you don’t mind waiting for some time.
Transparent and Bendable Conductive Film is made from micro-ceramics at the nanometer level with the property to carry electricity. The shape of these micro-ceramics is flat. Accordingly, due to the microscopic size and shape of these ceramics, this material exhibits characteristics halfway between metal and ceramics to obtain transparency and conductivity.
Its workability is also due to this size and shape. The film after coating and drying the ink in which this material is dispersed enters a state in which the entire pattern drawn is energized because the micro-ceramics lie on top of each other. Substances have been emerging in recent years that exhibit unique characteristics due to their nano-sized micro-structure and size instead of the composition of their materials like graphene, which demonstrates high conductivity by connecting carbon (C) atoms.
No rare metals or earths are used. Accordingly, the raw materials are inexpensive and can be stably procured.
In addition, there is room for further adjustments to improve the new material’s characteristics and to enhance its suitability for specific applications by optimizing the composition, structure, and size of the micro-ceramics.