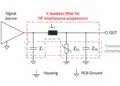
This article based on Knowles Precision Devices blog introduces bias filter networks and self-bias networks – the two types of biasing components developed by Knowles Precision Devices for use in high-frequency microwave and RF applications.
What Are Bias Filter Networks?
Bias filter networks in RF amplifiers refer to specific arrangements of passive components like resistors, capacitors, and inductors that provide a stable DC bias voltage or current to the active devices in the amplifier.
They have three main functions:
- Biasing: Providing the required DC voltage/current to the transistors to keep them operating in their optimal region.
- Filtering: Using capacitors and inductors to prevent RF signals from flowing back into the DC supply or other circuit sections, avoiding interference and instability.
- Decoupling: Isolating different amplifier stages to prevent their performances from impacting each other, which is important in multi-stage amplifiers
Bias filter networks play a crucial role in ensuring RF amplifiers operate efficiently, maintain linearity, and minimize noise/interference.
What Are Self-Bias Networks?
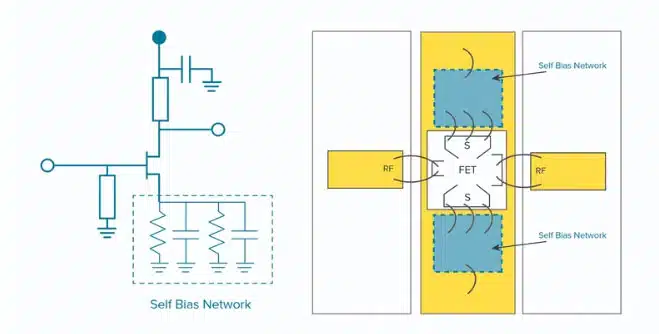
Self-bias networks in RF/microwave circuits are configurations designed to automatically set the DC bias point of active devices like transistors without requiring an external bias supply. They consist of resistors and capacitors connected to the device’s terminals in a voltage divider configuration to provide the bias voltage, while blocking DC signals.
The main advantage of self-bias networks is they automatically adjust the bias point based on factors like device characteristics and temperature to maintain consistent circuit performance. They simplify design and reduce components needed.
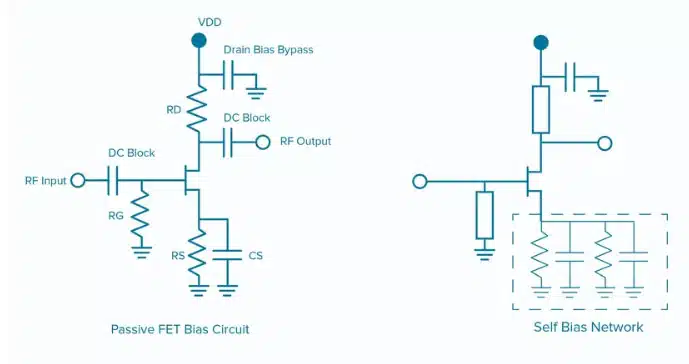
How Bias Filter Networks and Self-Bias Networks Work
Bias filter networks filter noise from DC supplies and reduce RF feedback in high-frequency applications like wireless communications. They combine high-permittivity dielectrics and thin-film processing to filter noise when transmitting DC voltage from point A to B in a circuit.
Bias filter networks should be used in applications that require filtering of noise and isolation of RF signals from DC bias lines, such as:
- Gate biasing for FETs and MMICs
- Varactor control lines in VCOs, frequency synthesizers, and PLLs
- Mixed signal modules with both analog and high-speed digital signals
- Cascaded high-gain amplifier modules sharing a common gate bias
Self-bias networks integrate decoupling capacitors and user-selectable bias resistors to optimize bias currents for amplifiers, such as GaAs and GaN FET amplifiers. They use high-permittivity ceramics and thin-film resistors to provide adjustable bias resistance and improve gain flatness/stability in FETs.
Integrating Bias Filter Networks and Self-Bias Networks from Knowles Precision Devices
Knowles leverages specialized expertise with high-permittivity materials and thin-film processing o develop customized bias filter and self-bias networks that provide critical biasing, filtering and isolation functions in high-frequency microwave and RF applications. With a broad range of solutions, Knowles bias filter networks are designed to filter RF signals from bias and control lines from 10 MHz to 40 GHz.
With bias filter and self-bias networks from Knowles, engineers:
- Simplify assembly by integrating multiple discreet components into one surface-mountable package
- Reduce size, weight and power consumption
- Effectively filter noise and optimize biasing
- Maximize isolation when mounting directly on a ground plane