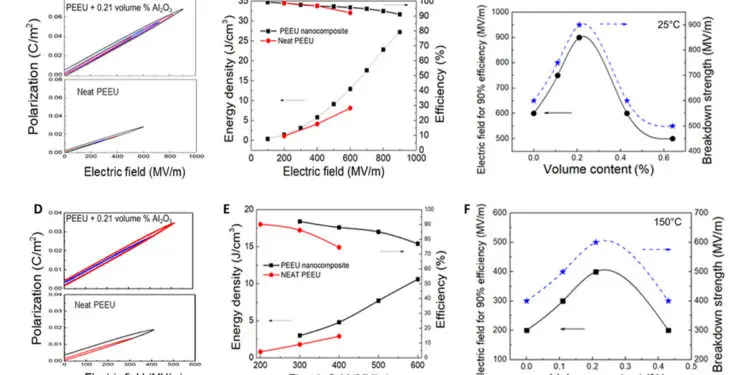
Researchers from The Pennsylvania State University, USA published an article in Science Advances on highly scalable polymer dielectric metamaterial with superior capacitor performance over a broad temperature.
Although many polymers exhibit excellent dielectric performance including high energy density with high efficiency at room temperature, their electric and dielectric performance deteriorates at high temperatures (~150°C). Here, we show that nanofillers at very low volume content in a high-temperature (high–glass transition temperature) semicrystalline dipolar polymer, poly(arylene ether urea), can generate local structural changes, leading to a marked increase in both dielectric constant and breakdown field, and substantially reduce conduction losses at high electric fields and over a broad temperature range. Consequently, the polymer with a low nanofiller loading (0.2 volume %) generates a high discharged energy density of ca. 5 J/cm3 with high efficiency at 150°C. The experimental data reveal microstructure changes in the nanocomposites, which, at 0.2 volume % nanofiller loading, reduce constraints on dipole motions locally in the glassy state of the polymer, reduce the mean free path for the mobile charges, and enhance the deep trap level.
The current paper reports development of a highly scalable and low-cost dielectric metamaterial approach, in which nanoparticles at very low volume loading (~0.2 volume %) substantially enhance the energy density, C/D efficiency, and breakdown field of high-temperature semicrystalline dipolar polymers. Specifically, the researches show that in poly(arylene ether urea) (PEEU), which is a high-Tg (>250°C) semicrystalline dipolar polymer, ca. 0.2 volume % of 20-nm-sized alumina nanofiller increases both the dielectric constant K and breakdown field E over a broad temperature range to >150°C. The dielectric constant K is raised from K = 4.7 of the base PEEU to 7.4. At 150°C, the nanocomposite films exhibit a breakdown field of 600 MV/m, increased from 400 MV/m of the base PEEU films. Moreover, the nanofiller at such a low loading also substantially reduces the high-field conduction loss. As a result, the PEEU films deliver a discharged Ue of 5 J/cm3 with a high C/D efficiency (>90%) at 150°C. The study chose PEEU because its urea unit has a high dipole moment of 4.56 D, which can serve as deep traps and reduce the conduction loss. In addition, the crystalline phase in PEEU is sensitive to processing conditions, which may be exploited for tuning the dielectric properties in dielectric metamaterials. Alumina (Al2O3) nanoparticles (K = 9.1; size, 20 nm; gamma phase), which have been widely used in nanocomposites, are chosen as the nanofiller.
The full detailed article is available at the link below