This article based on Knowles Precision Devices blog discusses bootsrap capacitors its function and benefits of using ceramic capacitors.
Power electronics play a critical role in converting and managing electrical energy efficiently. As electric vehicles (EVs), renewable energy systems, and consumer electronics quickly become more powerful, the demand for high-voltage power electronics is quickly increasing.
This means the importance of components like bootstrap capacitors has grown significantly.
Key Takeaways
- Bootstrap capacitors are vital for driving high-side MOSFETs in power electronics, especially in EVs and renewable energy systems.
- They maintain the required gate voltage for efficient switching, ensuring proper power conversion.
- Multilayer ceramic capacitors (MLCCs) can effectively serve as bootstrap capacitors due to their compact size and high capacitance.
- Using MLCCs improves reliability, temperature stability, and energy efficiency while reducing PCB space requirements.
- Overall, MLCCs offer benefits like low failure rates, wide voltage range, and low ESR for better performance in power electronics applications.
Bootstrap Capacitors
In power electronics, a bootstrap capacitor is a specific type of capacitor used to drive high-side MOSFETs efficiently.
The bootstrap capacitor plays a critical role in maintaining the gate voltage required to turn on the high-side MOSFET in a half-bridge or full-bridge configuration. By using the charge stored in the bootstrap capacitor, the high-side MOSFET’s gate voltage can be boosted above the supply voltage, ensuring proper switching operation and enabling efficient power conversion (Figure 1).
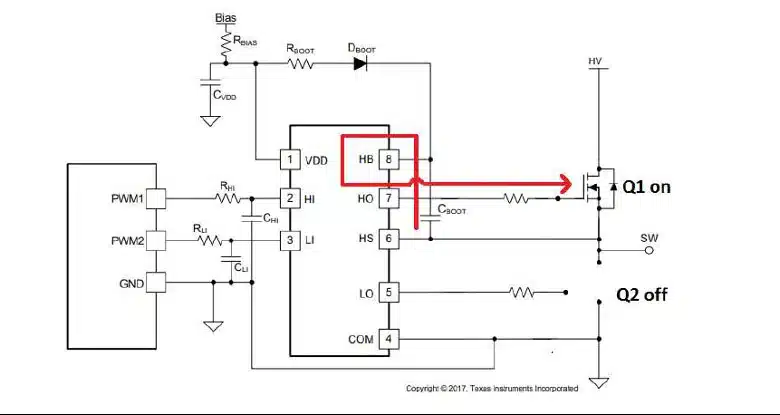
How MLCCs Fill the Role of the Bootstrap Capacitor
Now that it’s clear the role a bootstrap capacitor plays in a circuit, let’s look at how multilayer ceramic capacitors (MLCCs) can fulfill the bootstrap capacitor role and help you design more efficient and reliable power circuits. Since MLCCs are compact and have high capacitance and low equivalent series resistance (ESR), these components are generally well-suited for using as bootstrap capacitors.
Integrating MLCCs in the capacitor role within bootstrap circuits can improve system performance, reduce the PCB space required, and enhance overall energy efficiency.
Using an MLCC as a bootstrap capacitor brings the following additional benefits for your power electronics applications:
- Reliability: MLCCs have low failure rates and stable performance over extended operating periods, enhancing the longevity of power electronics systems.
- Compact Form Factor: The small footprint of MLCCs allows for space-saving designs, making them ideal for modern, miniaturized power electronics applications.
- Temperature Stability: MLCCs maintain their capacitance and performance across a wide range of operating temperatures, ensuring consistent functionality in diverse environments.
- Wide Voltage Range: MLCCs are available in a wide range of voltage ratings, providing flexibility in design for various power electronics systems.
- Low ESR: The low ESR of MLCCs ensures minimal power loss during switching, contributing to higher overall efficiency in power electronics circuits.
FAQ: Benefits of Ceramic Capacitors as Bootstrap Capacitors
A bootstrap capacitor is used to drive high-side MOSFETs in half-bridge or full-bridge circuits. It stores charge to boost the gate voltage above the supply voltage, ensuring efficient switching.
Multilayer ceramic capacitors (MLCCs) are compact, have high capacitance, low ESR, and excellent reliability, making them ideal for bootstrap roles in modern power circuits.
They improve efficiency, save PCB space, provide temperature stability, support a wide voltage range, and reduce power loss during switching.
They are essential in EV inverters, renewable energy systems, and consumer electronics where efficient high-voltage switching is required.
How-to: Implement Ceramic Capacitors as Bootstrap Capacitors
- Identify the switching circuit
Determine if your design uses half-bridge or full-bridge MOSFET configurations that require a bootstrap capacitor.
- Select an MLCC with proper rating
Choose an MLCC with the correct capacitance, voltage rating, and low ESR to handle the switching frequency and load.
- Place the capacitor close to the MOSFET
Minimize parasitic inductance by positioning the MLCC near the high-side MOSFET gate driver.
- Validate performance
Test the circuit for stable gate drive voltage, efficient switching, and thermal stability across operating conditions.
- Optimize for reliability
Ensure long-term stability by monitoring ESR, temperature behavior, and cycle endurance of the MLCC in the application.































