Source: Alter Technology article
by Francisco Javier Aparicio Rebollo
The Fluorescence Microscopy + dye penetrant test is a technique that combines two inspection methods commonly used for the detection of surface anomalies such as cracks, porosity, laps, delaminations, and other discontinuities.
This joint approach is intended to highlight and resolve surface anomalies thanks to the irreversible infiltration with a fluorescent marker. Hence, fluorescent-based inspection methods are mandatory or highly recommended by different international regulations and reference books for space materials in the case of non-porous surfaces: ASTM international (ASTM E1417), MIL-STD standards MIL-STD-750 and MIL-STD-833 (USA Defense and Logistics Agency) and “Materials and Processes for Spacecraft and High Reliability Applications” (Barrie Dunn, Springer 2015).
Other characteristics of the technique are:
- Non-destructive character.
- Cost effective.
- Requires sample preparation.
- Higher sensitivity than conventional optical-microscopy methods.
Practical examples.
Main advantages of the technique lie on the dual specificity of the fluorescence phenomena which is exclusively activated under specific illumination wavelength (excitation light colour) and provides wavelength-specific light emission (specific emission colour). This allows us to unambiguously identify surface anomalies difficult to be resolved by naked-eye inspection. Due to the simplicity, the non-destructive character and the high sensitivity both conventional dye penetration test and the fluorescent microscopy dye-penetration test are commonly used not only in the space and aerospace sectors but also in other fields requiring of completely crack free materials such as oil and gas industry and power generation.
In Alter Technology dye penetrant testes are routinely used to verify the hermeticity of EEE parts by visual fluorescence inspection.
To improve the quality of our inspections processes they are also included within the verification protocol of high reliability surface mounted devices and other PCB systems. The figure shows one representative example of the latter application. Pictures at the left correspond to the cross-section of a soldered SMD leaded-device. In the figure on the top it is evident the presence of a crack at the solder however this optical image does not reveal the actual crack length. In this case fluorescence microscopy is used to disclose how the crack extend along the solder lead interface and determine the length of the crack which is a critical rejection/acceptance criteria.
Optical Image
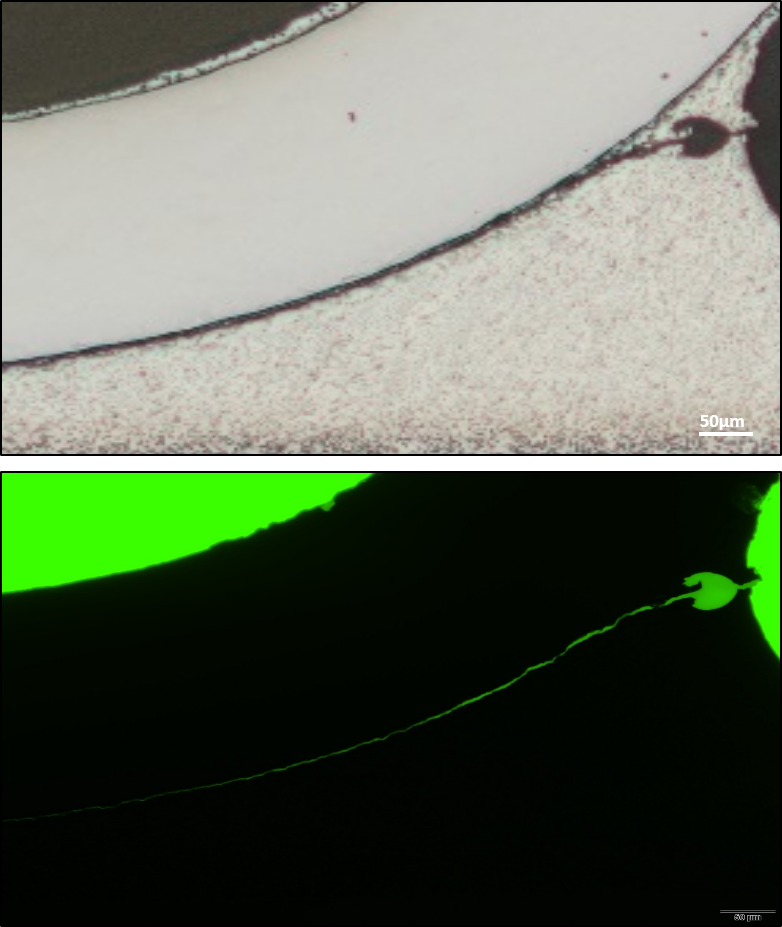

Fluorescence microscopy after dye infiltration
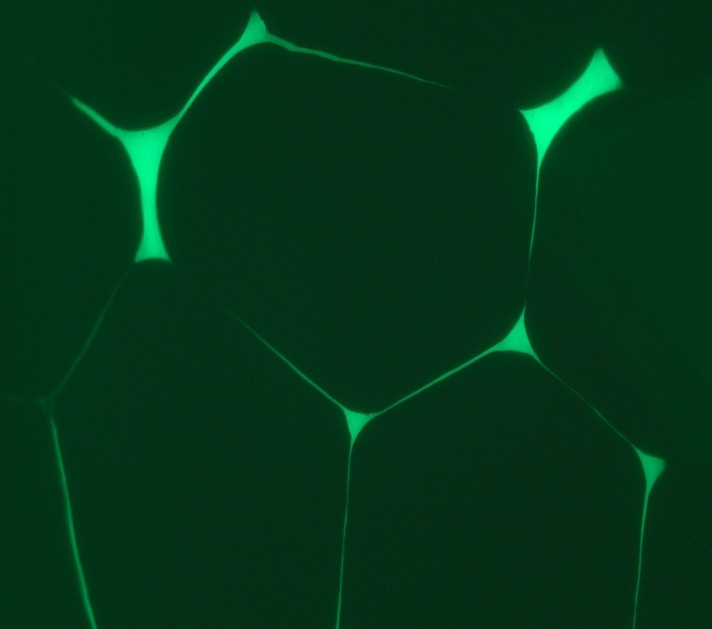
As an additional advantage related to this example, since dye infiltration is conducted before microsection only those crack present before cutting are outlined. Therefore, fluorescent inspection allows us to discard other features that eventually might be produced during microsection. This and other characterises makes it a valuable tool for failure analyses. In other application (picture beside) the technique is used to analyse wire separation in crimped connectors.
Figure: Wire separation in crimped connectors
Due to the fluorescent mechanism (see next section) proper fluorescence inspection requires the suitable selection of the fluorescent tag and the optical systems adapted to the fluorescence characteristics of the fluorophore (excitation lamps, fluorescence filters, and others). With this concerns Alter Technology team consist of experienced researchers in materials science and fluorescence techniques.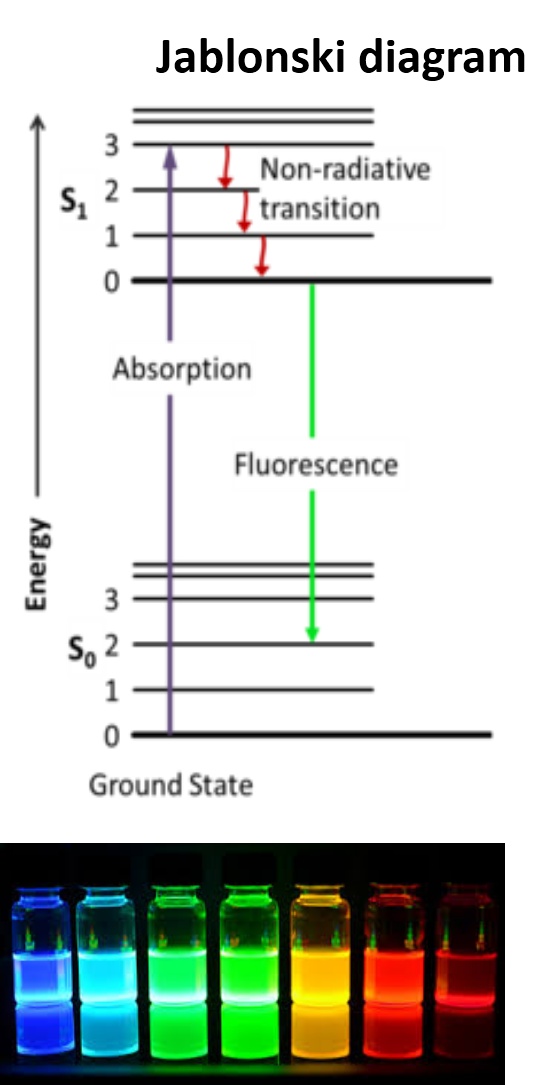
How it works
Fluorescence is the emission of light observed when some chemical elements (rare earths) organic compounds (organics dyes) and other confined materials (Quantum dots) are irradiated, typically with short-wavelength (UV) light. Taking as example an organic fluorophore, fluorescence emission is excited when a photon is absorbed by substance. Subsequent to this excitation process the fluorophore is promoted to a high electronic level as illustrated by the Jablosnki diagram (picture beside). In the excited state the molecule undergoes very fast non-emitting dissipation processes and transition toward the lower sub-vibration level of the exited state. In fluorescent compounds, the remaining excess of energy is released in form of light at wavelengths characteristic the used fluorophore. In general, fluorescence emission the is less energetic (longer wavelength) that the excitation beam as consequences of the previously mentioned excited-state dissipation processes. The wavelength difference between the excitation and emission wavelength is denominated stokes shift. This is an important factor for the de selection of the suitable fluorophore depending on the intending application. For marking proposes large stokes shift is very recommended to filter out the reflection of the excitation beam from the emission signal.
Featured image: crack extending along the base on a SMD device, image credit: Alter Technology






























