This article is based on a blog post by Samtec that explores the concept of tolerance stack-up and the mating of multi-connectors in various board to board connectors applications.
Mating a daughtercard (also known as a daughterboard) to a motherboard using two or more high-density array connectors or multiple fine-pitch connectors is quite common in today’s complex system designs.
To ensure proper end-system functionality, it’s advisable to conduct a tolerance stack-up analysis well before manufacturing commences.
The significance of Tolerance Stack-up Analysis
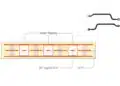
Let’s delve into a single connector mezzanine application. In such an application, the daughtercard is assumed to be free-floating, with alignment features integrated within the connectors. This ensures perfect alignment, making it unaffected by PCB fabrication and assembly process tolerances.
However, in multi-connector applications involving two or more connectors, mechanical tolerances accumulate in various directions and distances. Tolerances from the board house for the motherboard and daughtercard, the equipment, and the final assembly process all contribute to cumulative tolerance stacking, which can impact connector functionality.
To ensure the reliability of the final system, predictive analysis should be conducted early in the design stages.
Considerations and Recommendations
From an interconnect perspective, the best starting point for analyzing tolerance stacking is to confirm the final placement of connectors relative to each other on the same board by establishing a connector center of guidance.
Once a center of guidance is established, you can determine misalignment. Misalignment values influence the acceptance limits for tolerance analysis. Even slight misalignment can significantly increase tolerance stack and final assembly pin registration.
In addition to connectors, other elements must also be considered when evaluating alignment, such as:
- Solder pad size and location
- Connector placement onto the solder pad before reflow
- Connector movement during processing
- Whether the connector self-levels or self-centers
- Mating/unmating forces
- If alignment pins or standoffs are used
It can be recommended using standoffs to negate angular and z-axis misalignment effects. However, for optimal results, place standoffs as close to the connector system as possible to localize stress and reduce unsupported PCB span. It’s also advisable to leave standoffs and similar items loose-fitted until post-connector mating, then tighten them to the final torque specifications.
Alignment pins are excellent for guiding connector placement during hand assembly and polarizing the connector to the PCB. However, they can contribute to tolerance stack. Therefore, it is recommended using a product without alignment pins for machine placement or in multi-connector applications. If alignment pins are necessary for machine placement due to polarization, oversizing the drill hole on the PCB is recommended.
Tolerance analysis methods can be performed using an Arithmetic Worst-Case study or a Root Sum of Squares study, depending on the application requirements. For instance, some applications require analyzing zero failure targets, while others allow for a less conservative approach to reach dimensional goals, potentially resulting in lower costs.
Root Sum of Squares (RSS) study: This statistical approach simulates the expected outcomes for all parts used in a multi-connector application, providing a comprehensive analysis of tolerance stack-up.
Arithmetic Worst-Case (AWC) study: This traditional approach calculates the cumulative measurements of all part tolerances at their limits, resulting in the largest or smallest cumulative measurements.
The role of a connector manufacturer involves ensuring that these recommendations are met to achieve high-quality connectors and minimize the risk of failures.
All components used in system creation and manufacturing have their own tolerances that must be considered in a tolerance stack-up analysis. The combination of these tolerances creates stacking. Included but not limited to are tolerances from the board house, contract equipment manufacturer, and final assembly process. All of these factors impact connector function, so it is important to follow manufacturers’ general guidance to ensure end system reliability.
Connector manufacturer can only control the tolerances of its own connectors. Samtec aims to clearly define connector tolerances, maximum allowable misalignment, footprint and stencil designs, and processing recommendations. Connector print and footprint information is located at the bottom of each product Series tech spec page (for example, samtec.com?SEAM).