Source: Tokyo Institute of Technology news
Scientists at Tokyo Institute of Technology and University of Tsukuba demonstrate that polymers could play a key role in the fabrication of single-molecule electronic devices, allowing us to push the boundaries of the nanoelectronics revolution.
One of the most striking aspects of the electronic devices we have today is their size and the size of their components. Pushing the limits of how small an electronic component can be made is one of the main topics of research in the field of electronics around the world, and for good reasons. For example, the accurate manipulation of incredibly small currents using nanoelectronics could allow us to not only improve the current limitations of electronics, but also grant them new functionalities.
So, how far down does the rabbit hole go in the field of miniaturization? A research team led by Tomoaki Nishino, Associate Professor of the School of Science at Tokyo Institute of Technology (Tokyo Tech) is exploring the depths of this; in other words, they are working on single-molecule devices. “Ultimate miniaturization is expected to be realized by molecular electronics, where a single molecule is utilized as a functional element,” explains Nishino.
However, as one would expect, creating electronic components from a single molecule is no easy task. Functional devices consisting of a single molecule are hard to fabricate. Furthermore, the junctions (points of “electric contact”) that involve them have short lifetimes which makes their application difficult. Based on previous works, the research team inferred that a long chain of monomers (single molecules) to form polymers would yield better results than smaller molecules.
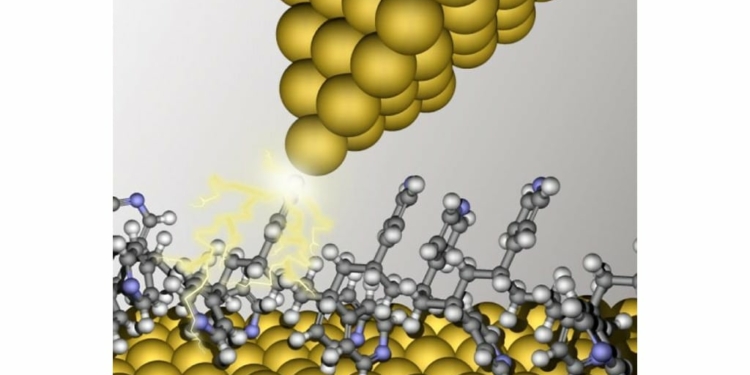
To demonstrate this idea, they employed a technique called scanning tunneling microscopy (STM), in which a metallic tip that ends in a single atom is used to measure extremely small currents and their fluctuations that occur when the tip creates a junction with an atom or atoms at the target surface (see featured image). Through STM, the team created junctions composed of the tip and either a polymer called poly(vinylpyridine) or its monomer counterpart, called 4,4′-trimethylenedipyridine, which can be regarded as one of components of the polymer. By measuring the conductive properties of these junctions, the researchers sought to prove that polymers could be useful for fabricating single-molecule devices.
However, to carry out their analyses, the team first had to devise an algorithm that allowed them to extract quantities that were of interest to them from the current signals measured by the STM. In short, their algorithm allowed them to automatically detect and count small plateaus in the current signal measured over time from the tip and the target surface; the plateaus indicated that a stable conducting junction was created between the tip and a single molecule on the surface.
Using this approach, the research team analyzed the results obtained for the junctions created with the polymer and its monomer counterpart. They found that the polymer yielded much better properties as an electronic component than the monomer. “Probability of junction formation, one of the most important properties for future practical applications, was much higher for the polymer junction,” states Nishino. In addition, the lifetimes of these junctions were found to be higher, and the current flowing through the polymer junctions was more stable and predictable (with less deviation) than that for the monomeric junctions.
The results presented by the research team reveal the potential of polymers as building blocks for electronics miniaturization in the future. Are they the key for pushing the boundaries of the achievable physical limits? Hopefully, time will soon tell.
Research co-authors
Doctoral student Takanori Harashima (right) and Associate professor Tomoaki Nishino (left) in the laboratory at Tokyo Tech.
Reference
Authors :
Takanori Harashima1, Yusuke Hasegawa1, Satoshi Kaneko1, Manabu Kiguchi1, Tomoya Ono2 and Tomoaki Nishino1
Title of original paper :
Highly reproducible formation of polymer single-molecule junction for well-defined current signal
Journal : Angewandte Chemie International Edition
DOI : 10.1002/anie.201903717
Affiliations :
1Department of Chemistry, School of Science, Tokyo Institute of Technology
2Center for Computational Sciences, University of Tsukuba
featured image: Single-molecule junctions composed of the STM tip and a polymer. The study of single-molecule devices using a scanning tunneling microscope (STM) involves creating a junction (electrical contact) between the metallic tip of the microscope and a single molecule on a target surface. The current that flows through the tip is analyzed to gauge the potential of the target molecule for functional applications in single-molecule electronics. Image credit: Tokyo Institute of Technology