This article based on Knowles Precision Devices blog explains RF Inductors via their key characteristics and applications.
Inductors are a fundamental component in electronic circuits, but not all inductors perform equally across different frequency ranges.
At high frequencies, standard power inductors suffer from increased losses, reduced efficiency, and undesirable parasitic effects.
RF inductors, specifically designed for radio frequency and microwave applications, address these challenges by minimizing resistive losses, optimizing self-resonant frequency, and maintaining signal integrity.
Here, we examine the distinguishing characteristics of RF inductors, highlighting how they differ from other inductor types and why they are essential in high-frequency applications.
How Are RF Inductors Different from Other Inductors?
An RF inductor is a specialized passive electronic component designed to operate efficiently at radio frequencies and microwave frequencies. Unlike power inductors, which manage energy transfer and filtering in power supply applications, RF inductors are optimized for minimal energy loss and high signal integrity at high frequencies.
The primary difference between RF inductors and other inductors lies in:
- Frequency Range: RF inductors function in the megahertz to gigahertz range while power inductors typically operate at lower frequencies.
- Core Material: RF inductors often feature ceramic or air cores to minimize energy losses and ensure stability at high frequencies. Power inductors use ferrite cores to achieve higher inductance values.
- Current Handling: Power inductors are designed to handle significant current loads whereas RF inductors prioritize maintaining signal integrity with minimal distortion.
Key Electrical Properties for Selecting RF Inductors
Selecting the right RF inductor requires an understanding of its key electrical properties, which includes:
- Inductance Value: Determines the inductor’s ability to oppose changes in current
- Self-Resonant Frequency (SRF): The point where the inductor’s parasitic capacitance cancels out its inductance defining the maximum effective operating frequency
- Q-Factor: A measure of efficiency; higher values indicate lower energy losses and improved performance in filtering and tuning applications
- DC Resistance (DCR): Lower DCR reduces power loss, which is critical in high frequency circuits
| Application | Inductance | Maximum DC Current (IDC) | Self-Resonant Frequency (SRF) | Quality Factor (Q) | DC Resistance (RDC) |
| High-frequency resonance circuits (RF) | Low | Low | Very High | Very High | Low |
| EM coupling (Power) | High | – | High | Low | Very Low |
| Filter circuits (Power) | High | High | High | Low | Very Low |
| Switch-mode power supplies, DC/DC converters (Power) | – | High | Medium | Low | Very Low |
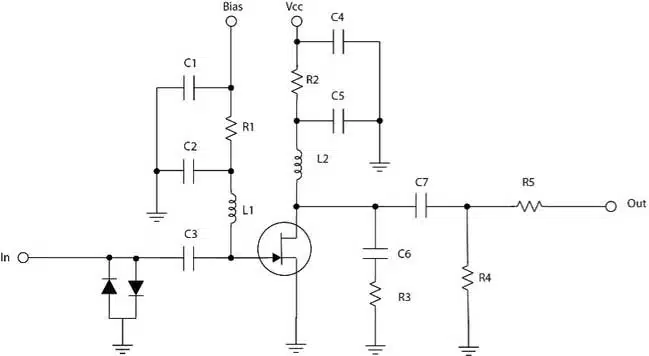
RF inductors are essential in high-frequency applications, enabling critical functions in communication, medical, and defense systems. They are used in RF filters and oscillators to control frequency bands, amplifier biasing circuits for impedance matching, and MRI preamplifiers (Figure 1) to ensure low-noise signal processing. Additionally, they support radar and communication systems across VHF, UHF, and S-band frequencies and maintain signal integrity in RF test equipment.