Invisibly small carbon nanotubes aligned as fibers and sewn into fabrics become a thermoelectric generator that can turn heat from the sun or other sources into energy. The Rice University lab of physicist Junichiro Kono led an effort with scientists at Tokyo Metropolitan University and the Rice-based Carbon Hub to make custom nanotube fibers and test their potential for large-scale applications.
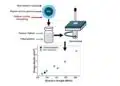
Their small-scale experiments led to a fiber-enhanced, flexible cotton fabric that turned heat into enough energy to power an LED. With further development, they say such materials could become building blocks for fiber and textile electronics and energy harvesting.
The same nanotube fibers could also be used as heat sinks to actively cool sensitive electronics with high efficiency. A paper about the project appears in Nature Communications.
The effect seems simple: If one side of a thermoelectric material is hotter than the other, it produces energy. The heat can come from the sun or other devices like the hotplates used in the fabric experiment. Conversely, adding energy can prompt the material to cool the hotter side.
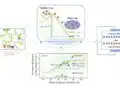
Until now, no macroscopic assemblies of nanomaterials have displayed the necessary “giant power factor,” about 14 milliwatts per meter kelvin squared, that the Rice researchers measured in carbon nanotube fibers.
“The power factor tells you how much power density you can get out of a material upon certain temperature difference and temperature gradient,” said Rice graduate student Natsumi Komatsu, lead author of the paper. She noted a material’s power factor is a combined effect from its electrical conductivity and what’s known as the Seebeck coefficient, a measure of its ability to translate thermal differences into electricity.
“The ultrahigh electrical conductivity of this fiber was one of the key attributes,” Komatsu said.
The source of this superpower also relates to tuning the nanotubes’ inherent Fermi energy, a property that determines electrochemical potential. The researchers were able to control the Fermi energy by chemically doping the nanotubes made into fibers by the Rice lab of co-author and chemical and biomolecular engineer Matteo Pasquali, allowing them to tune the fibers’ electronic properties.
While the fibers they tested were cut into centimeter lengths, Komatsu said there’s no reason devices can’t make use of the excellent nanotube fibers from the Pasquali lab that are spooled in continuous lengths. “No matter where you measure them, they have the same very high electrical conductivity,” she said. “The piece I measured was small only because my setup isn’t capable of measuring 50 meters of fiber.”
Pasquali is director of the Carbon Hub, which promotes expanding the development of carbon materials and hydrogen in a way that also fundamentally changes how the world uses fossil hydrocarbons.
“Carbon nanotube fibers have been on a steady growth path and are proving advantageous in more and more applications,” he said. “Rather than wasting carbon by burning it into carbon dioxide, we can fix it as useful materials that have further environmental benefits in electricity generation and transportation.”
Whether the new research leads to a solar panel you can throw in the washing machine remains to be seen, but Kono agreed the technology has great and varied potential.
“Nanotubes have been around for 30 years, and scientifically, a lot is known,” he said. “But in order to make real-world devices, we need macroscopically ordered or crystalline assemblies. Those are the types of nanotube samples that Matteo’s group and my group can make, and there are many, many possibilities for applications.”
Co-authors of the paper are Rice graduate students Oliver Dewey, Lauren Taylor and Mitchell Trafford and Geoff Wehmeyer, an assistant professor of mechanical engineering; and Yota Ichinose, Professor Yohei Yomogida, and Professor Kazuhiro Yanagi of Tokyo Metropolitan University.
Kono is the Karl F. Hasselmann Professor in Engineering and a professor of electrical and computer engineering, of physics and astronomy and of materials science and nanoengineering. Pasquali is the A.J. Hartsook Professor of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering and a professor of chemistry and of materials science and nanoengineering.
The Department of Energy Basic Energy Science program, the National Science Foundation, the Robert A. Welch Foundation, the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, the U.S. Air Force and the Department of Defense supported the research.