Additive layer-by-layer fabrication of a fully screen printed monolithic supercapacitor exhibiting performance comparable with supercapacitors prepared using lamination is reported by researchers from Tampere University in Finland in article published by Journal of Applied Electrochemistry.
A novel separator material improves the performance of the monolithic supercapacitor, is easily applicable using scalable processes such as screen and stencil printing, and is based on sustainable biomaterials. The additive monolithic manufacturing offers advantages for system integration and avoids the need of an additional alignment step as needed in the fabrication of laminated supercapacitors.
Previously, the monolithically fabricated supercapacitors showed higher equivalent series resistance (ESR) and leakage current than the laminated ones. By using microfibrillated cellulose (MFC) and chitosan as separator materials ESR and leakage current were decreased. These disposable and non-toxic aqueous electrolyte supercapacitors are optimized for autonomous sensor systems, for example in Internet-of-Things (IoT) applications, with capacitance of 200–300 mF and ESR of about 10 Ω. The new composite separator material consisting of MFC and chitosan has good adhesion on the electrodes and the substrate, is easy to apply using printing and coating processes, and does not diffuse into the porous electrode.
In the near future, it is expected that there will be billions of devices which should all integrate and connect smoothly with the “Internet of Things” (IoT) in different services, for example smart homes, healthcare and industry automation. IoT devices and sensor networks need non-toxic and inexpensive ways to store energy. Supercapacitors are in many cases a better choice than batteries for managing the energy storage due to their safety, disposability and higher cycle life.
Supercapacitors store energy into the electrochemical double-layer at a highly porous electrode surface. The key elements of a supercapacitor are current collectors, electrodes, separator and electrolyte. Printed supercapacitors are usually manufactured by applying two electrodes on the current collectors separately, laminating the electrodes face-to-face while sandwiching the separator between them and applying the electrolyte before encapsulation.
We report here the monolithic fabrication of supercapacitors, by applying the films layer by layer on top of each other on the substrate. Monolithic fabrication can have advantages over the conventional lamination approach, both for system integration and for fabrication of series connected modules when higher voltage is needed. Previously reported monolithically fabricated aqueous supercapacitors showed higher equivalent series resistance (ESR) and higher leakage current to capacitance ratio than laminated ones. We have improved the performance by using a novel, bio-derived composite material as a separator, consisting of microfibrillated cellulose (MFC), also known as nanocellulose, and the polysaccharide chitosan.
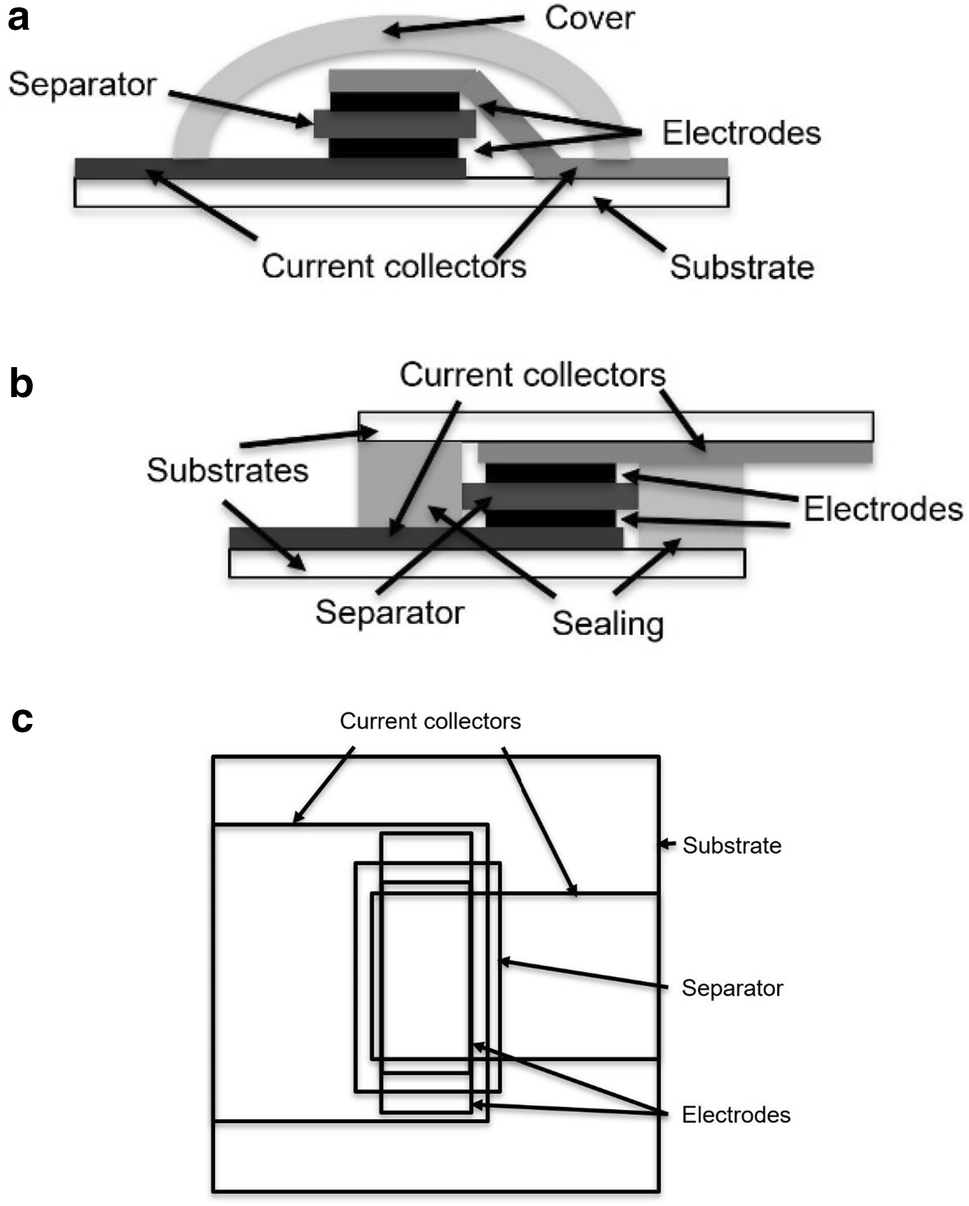
The use of MFC in supercapacitors has been reported previously. However, most of these reports are concerned with the use of MFC-based conductive materials for electrodes and current collectors. Other reports on MFC materials do not describe their application in supercapacitors but instead report the chemical properties of the material. MFC-based cellulose papers have also been used as separators in supercapacitors, but these devices were assembled using lamination. A monolithically fabricated supercapacitor has also been reported previously, although the size and the materials of the supercapacitors were different from the ones reported here.
The separator of the supercapacitors must be thin and electrochemically stable. It must have high ionic conductivity. On the other hand, the separator must prevent short circuit between the electrodes. The use of MFC as a separator material was previously reported by Tuukkanen et al.. This work is motivated by the previous work and extends it to easier and more consistent manufacturing and performance by forming a composite with the biopolymer chitosan.
Achievements and Conclusions
Monolithic supercapacitors have potential advantages for manufacturing and system integration, but have previously showed higher ESR and leakage current per capacitance than laminated devices. A novel bio-derived composite material made from chitosan and MFC was used as a printable separator in monolithic aqueous supercapacitors and was found to improve the electrical performance of the devices to a level comparable with laminated supercapacitors.
The ESR s is the same as measured for laminated components and the leakage current per capacitance is improved. The new material, CM5050, is easier to apply than chitosan and is thus advantageous from a manufacturing point of view. The correlation between leakage current and capacitance of the monolithic supercapacitors follows trends generally observed in supercapacitors.
We also fabricated a supercapacitor in which both electrodes and current collectors were manufactured by screen printing to further enhance the possibility of potential industrial fabrication.
Read the full paper at the link below