source: Energy Harvesting Journal article
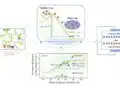
Engineers at Oregon State University have made a fundamental breakthrough in understanding the physics of photonic “sintering,” which could lead to many new advances in solar cells, flexible electronics, various types of sensors and other high-tech products printed onto something as simple as a sheet of paper or plastic.
Sintering is the fusing of nanoparticles to form a solid, functional thin-film that can be used for many purposes, and the process could have considerable value for new technologies.
Photonic sintering has the possible advantage of higher speed and lower cost, compared to other technologies for nanoparticle sintering.
In the new research, OSU experts discovered that previous approaches to understand and control photonic sintering had been based on a flawed view of the basic physics involved, which had led to a gross overestimation of product quality and process efficiency.
Based on the new perspective of this process, which has been outlined in Nature Scientific Reports, researchers now believe they can create high quality products at much lower temperatures, at least twice as fast and with 10 times more energy efficiency.
Removing constraints on production temperatures, speed and cost, the researchers say, should allow the creation of many new high-tech products printed onto substrates as cheap as paper or plastic wrap.
“Photonic sintering is one way to deposit nanoparticles in a controlled way and then join them together, and it’s been of significant interest,” said Rajiv Malhotra, an assistant professor of mechanical engineering in the OSU College of Engineering. “Until now, however, we didn’t really understand the underlying physics of what was going on. It was thought, for instance, that temperature change and the degree of fusion weren’t related – but in fact that matters a lot.”
With the concepts outlined in the new study, the door is open to precise control of temperature with smaller nanoparticle sizes. This allows increased speed of the process and high quality production at temperatures at least two times lower than before. An inherent “self-damping” effect was identified that has a major impact on obtaining the desired quality of the finished film.
“Lower temperature is a real key,” Malhotra said. “To lower costs, we want to print these nanotech products on things like paper and plastic, which would burn or melt at higher temperatures. We now know that is possible, and how to do it. We should be able to create production processes that are both fast and cheap, without a loss of quality.”
Products that could evolve from the research, Malhotra said, include solar cells, gas sensors, radiofrequency identification tags, and a wide range of flexible electronics. Wearable biomedical sensors could emerge, along with new sensing devices for environmental applications.
In this technology, light from a xenon lamp can be broadcast over comparatively large areas to fuse nanoparticles into functional thin films, much faster than with conventional thermal methods. It should be possible to scale up the process to large manufacturing levels for industrial use.
This advance was made possible by a four-year, $1.5 million National Science Foundation Scalable Nanomanufacturing Grant, which focuses on transcending the scientific barriers to industry-level production of nanomaterials. Collaborators at OSU include Chih-hung Chang, Alan Wang and Greg Herman.
OSU researchers will work with two manufacturers in private industry to create a proof-of-concept facility in the laboratory, as the next step in bringing this technology toward commercial production.
Source and top image: Oregon State University