Researchers from the ICN2 and the ICMM-CSIC have developed a new material able to cool another one by emitting infrared radiation. The results are published in Small and are expected to be used in devices where an increase in temperature has drastic effects on performance, like solar panels and computer systems, among other applications.
Refrigeration is a central issue in current societies: be it in a supermarket or on your personal computer, the regulation of temperature is necessary to keep human beings comfortable or just machines working reliably. Cooling systems account for 15% of the global energy consumption and are responsible for 10% of greenhouse gas emissions. One could say that the cure is worse than the disease, as greenhouse gases generate global warming, thus requiring even more refrigeration.
A way out of this loop has been found by researchers from the Catalan Institute of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology (ICN2) in collaboration with researchers from the Instituto de Ciencia de Materiales de Madrid (ICMM-CSIC). Members of the ICN2 Phononic and Photonic Nanostructures Group, led by ICREA Prof. Dr Clivia M. Sotomayor Torres, and the ICMM Photonic Crystals Group have reported a novel two-dimensional material able to remove heat, cooling down the surface in which it is placed without energy consumption or gas emissions of any kind. The work has been published in Small, with Dr Juliana Jaramillo-Fernández, who is a Marie Slodowska-Curie COFUND Postdoctoral Researcher at the ICN2, as its first author.
The material is inspired by the Earth’s efficient temperature-regulation mechanism, named radiative sky cooling. Although the Earth is heated by the Sun, it also emits infrared radiation to the outer space, as this kind of radiation is not captured by the atmosphere. The sand grains in deserts are among the major contributors to this phenomenon, which keeps the average temperature of our planet stable as long as we do not consider human activities.
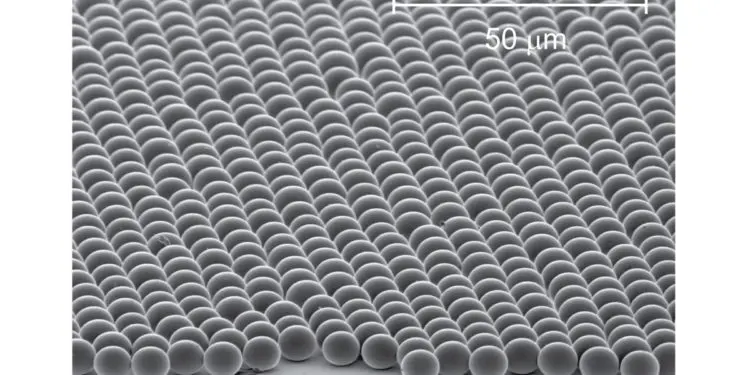
The proposed material takes advantage of the same principle. The researchers have shown that it is able to cool down a silicon wafer under direct sunlight irradiation by 14 ºC, whereas an ordinary soda-lime glass just lowers it by 5 ºC. The material is formed by a self-assembled array of 8 µm-diameter silica spheres, like sand grains a million times smaller in volume. This layer behaves almost as an ideal infrared emitter, providing a radiative cooling power of up to 350 W/m2 for a hot surface, such as a solar panel.
To put this into context, this would remove half of the heat accumulated in a typical solar panel in a regular clear day, which is enough to increase the relative efficiency of a solar cell by 8%. Considering the global solar energy production in 2017, such an efficiency increase represents enough energy to power the city of Paris during an entire year.
The researchers have unravelled the radiative sky cooling potential of self-assembled crystals, showing that only a single-layer of microspheres is necessary for achieving the best cooling performance, which is of great interest for future up-scaling and applicability. This is in sharp contrast to current state-of-the-art radiative cooling materials, since it is six times thinner than the existing glass-polymer films and it avoids the use of plastics.
The potential impact of this kind of technologies has not gone unnoticed. Dr Juliana Jaramillo, Dr Achille Francone and Dr Nikolaos Kehagias, from the aforementioned ICN2 group, have also developed another material that is easily up-scalable and is capable of providing both radiative cooling and self-cleaning. The Collider, a technology transfer programme promoted by Mobile World Capital Barcelona that connects scientific research with entrepreneurial initiative, has awarded this project The Collider Tech Award 2019, a prize that encourages further development of this research line on radiative cooling materials. A European patent protecting the intellectual property rights of this technology was filed on 31 July 2019 by the ICN2 and ICREA.
Aside from use on solar panels, other conceivable applications include refrigeration of thermoelectric modules —devices that convert temperature differences into electric current—, cooling computer systems in data centres or even smart windows that would refresh themselves and their surroundings, saving air conditioning costs.
Featured image source: ICN2
Article reference:
Juliana Jaramillo‐Fernandez, Guy L. Whitworth, Jose Angel Pariente, Alvaro Blanco, Pedro D. Garcia, Cefe Lopez, Clivia M. Sotomayor‐Torres. A Self‐Assembled 2D Thermofunctional Material for Radiative Cooling. Small, 2019; 1905290. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201905290