Wearable sensors are evolving from watches and electrodes to bendable devices that provide far more precise biometric measurements and comfort for users. Now, an international team of researchers has taken the evolution one step further by printing sensors directly on human skin without the use of heat.
Led by Huanyu “Larry” Cheng, Dorothy Quiggle Career Development Professor in the Penn State Department of Engineering Science and Mechanics, the team published their results in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces.
“In this article, we report a simple yet universally applicable fabrication technique with the use of a novel sintering aid layer to enable direct printing for on-body sensors,” said first author Ling Zhang, a researcher in the Harbin Institute of Technology in China and in Cheng’s laboratory.
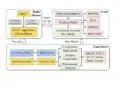
Cheng and his colleagues previously developed flexible printed circuit boards for use in wearable sensors, but printing directly on skin has been hindered by the bonding process for the metallic components in the sensor. Called sintering, this process typically requires temperatures of around 572 degrees Fahrenheit (300 degrees Celsius) to bond the sensor’s silver nanoparticles together.
“The skin surface cannot withstand such a high temperature, obviously,” Cheng said. “To get around this limitation, we proposed a sintering aid layer — something that would not hurt the skin and could help the material sinter together at a lower temperature.”
By adding a nanoparticle to the mix, the silver particles sinter at a lower temperature of about 212 F (100 C).
“That can be used to print sensors on clothing and paper, which is useful, but it’s still higher than we can stand at skin temperature,” Cheng said, who noted that about 104 F (40 C) could still burn skin tissue. “We changed the formula of the aid layer, changed the printing material and found that we could sinter at room temperature.”
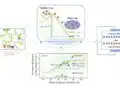
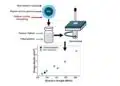
The room temperature sintering aid layer consists of polyvinyl alcohol paste — the main ingredient in peelable face masks — and calcium carbonate — which comprises eggshells. The layer reduces printing surface roughness and allows for an ultrathin layer of metal patterns that can bend and fold while maintaining electromechanical capabilities. When the sensor is printed, the researchers use an air blower, such as a hair dryer set on cool, to remove the water that is used as a solvent in the ink.
“The outcome is profound,” Cheng said. “We don’t need to rely on heat to sinter.”
The sensors are capable of precisely and continuously capturing temperature, humidity, blood oxygen levels and heart performance signals, according to Cheng. The researchers also linked the on-body sensors into a network with wireless transmission capabilities to monitor the combination of signals as they progress.
The process is also environmentally friendly, Cheng said. The sensor remains robust in tepid water for a few days, but a hot shower will easily remove it.
“It could be recycled, since removal doesn’t damage the device,” Cheng said. “And, importantly, removal doesn’t damage the skin, either. That’s especially important for people with sensitive skin, like the elderly and babies. The device can be useful without being an extra burden to the person using it or to the environment.”
Next, the researchers plan to alter the technology to target specific applications as needed, such as a precise on-body sensor network placed to monitor the particular symptoms associated with COVID-19.
Other contributors include Hongjun Ji, Senpei Xie, Yaoyin Li, Ziheng Ye, Tiesong Lin, Xiangli Liu, Xuesong Leng, Mingyu Li, Pengdong Feng, Jiaheng Zhang and Xing Ma, all of whom are affiliated with the Harbin Institute of Technology; Houbing Huang and Xiaoming Shi, both with the Beijing Institute of Technology; and Ning Yi, with the Penn State Department of Materials Science and Engineering.
This work was supported by Penn State, the National Science Foundation, the American Chemical Society Petroleum Research Fund, the Shenzhen Science and Technology Program, the Bureau of Industry and Information Technology of Shenzhen and the National Science Foundation of China.