Effects at the interface between magnetic and non-magnetic layers have been exploited for data storage for three decades. This has led to a steady increase in hard drive storage capacity and is one reason why researchers see potential for ushering data processing into a new era. One way these interfaces can be produced is using ion beams. Scientists led by Dr. Alina Maria Deac from the Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf (HZDR) have now shown the exact processes taking place. Their results, published in the journal Applied Materials and Interfaces, could advance the development of powerful neuromorphic computers.
Spintronics is considered a promising field of research for smaller, more powerful and economical hardware. While the electric charge is the main focus in conventional semiconductor electronics, the magnetic moment of the electrons is of decisive importance in spintronics. It has been known for several years that such nanostructures, which consist of magnetic and non-magnetic layers, can be produced using ion beams.
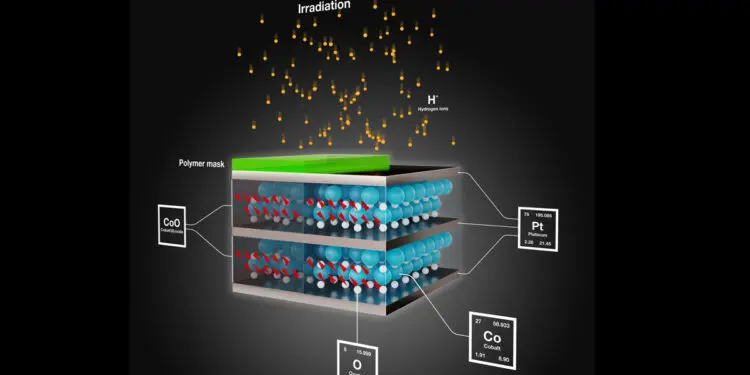
Non-magnetic cobalt oxide, for example, when bombarded with ions, converts to ferromagnetic cobalt. Thus, by introducing multilayers of non-magnetic cobalt oxide and platinum, ion irradiation yields structures where magnetic and non-magnetic layers alternate. Various effects occur at the interfaces between these layers, which are only a few nanometers thick. These effects are essential for magnetic data storage and transmission and could considerably improve these aspects.
Not chemically bound, but physically removed
“What precisely occurs when an ion beam converts a non-magnetic oxide into magnetic metal has already been studied by a South Korean research group in 2012,” says Deac. At the time, the scientists used proton beams – the nuclei of ordinary hydrogen. According to the prior assumption, these could chemically fuse with the oxygen in the cobalt oxide. What would remain is the magnetic cobalt and water.
“We didn’t want to pursue this explanation,” Deac says. “Because no one has yet been able to detect the water in the material, which would also be entirely out of place for an electronic component.” The researchers believed that if no water could be detected, it would either need to disappear from the material in some unknown manner, or another effect would be responsible for the conversion of cobalt oxide to cobalt.
Deac and her team then carried out their own experiments using different particle beams and were able to show that no chemical reaction occurs. “The oxygen atoms do not react chemically. The irradiating ions simply push them mechanically out of the way,” the scientist explains. The team used different masks for the tests to cover portions of the starting material. The researchers were thus able to show that the effect occurs only at the points where the beam directly hits the cobalt oxide. “So the oxygen atoms are either pushed into the neighboring, non-irradiated areas of the same layer, or into the layers beneath,” summarizes Deac the results.
Blazing a trail for entirely new hardware
Understanding these processes is vital for the future production of component nanostructures using ion beams. While such structures have traditionally been two-dimensional, Deac and her research group have added a third dimension to the manufacturing processes by irradiating the multiple layers of cobalt oxide and platinum with ions only at selected points. “This forms two different types of interfaces,” Deac says, describing the result. “On the one hand, there is a horizontal interface between cobalt and platinum that forces the magnetization of the cobalt in a preferred direction; and on the other, there is a vertical interface between cobalt oxide and cobalt, where the magnetic moment is blocked to a specific direction at low temperatures.”
These three-dimensional structures open up a great deal of potential for further miniaturization. After all, manufacturing extremely small, economical and powerful components is the basic prerequisite for a whole new generation of computers. The Dresden researchers mainly have neuromorphic hardware in mind. This new type of computer is at the very early stage of development. They are modelled on the human brain and combine highly networked parallel synthetic neurons and synapses on the chips. They not only outperform today’s computers in terms of computing power, but are also considerably smaller and more energy-efficient. This makes them an ideal hardware for applications in the field of artificial intelligence, such as for use in autonomous vehicles.