Source: Newswise article
Newswise — For the first time, researchers have created a nanocomposite of ceramics with a two-dimensional material that opens the door to new designs of nanocomposites with a variety of applications, such as solid-state batteries thermoelectrics, varistors, catalysts, chemical sensors and much more.
Sintering is a method that uses high heat to compact powder materials into a solid form. Widely used in industry, ceramic powders are typically compacted at temperatures of 800 degrees Celsius or higher. Many low-dimensional materials cannot survive at those temperatures.
But a sintering process developed by a team of researchers at Penn State, called the cold sintering process (CSP), can sinter ceramics at much lower temperatures, less than 300 degrees C, saving energy and enabling a new form of material with high commercial potential.
“We have industry people who are already very interested in this work,” said Jing Guo, a post-doctoral scholar working in the group of Clive Randall, professor of materials science and engineering, Penn State. Guo is first coauthor on a paper appearing online today in the journal Advanced Materials. “They are interested in developing some new material applications with this system and, in general, using CSP to sinter nanocomposites.”
The idea of trying to develop a ceramic-2D composite system was the result of a National Science Foundation workshop on the future of ceramics, organized by Dr. Lynnette Madsen, that drew 50 of the top ceramic scientists in the U.S. Yury Gogotsi, a Charles T. and Ruth M. Bach Distinguished University Professor and Director of the A.J. Drexel Nanomaterials Institute, at Drexel University, heard Randall’s presentation on cold sintering and proposed a collaboration to develop a ceramic composite using a new class of two-dimensional materials, called MXenes, discovered by him and his collaborators at Drexel University. MXenes, which are carbide and nitride sheets a few atoms thin, possess extreme strength and many of them are excellent metallic conductors.
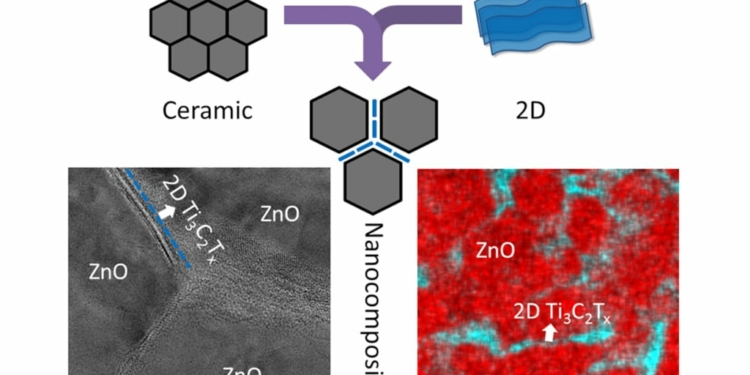
While it has been known that mixing even a very small amount of 2D materials, such as graphene, into a ceramic can dramatically change its properties, MXene has never been used in ceramic composites. In this work, Guo and Benjamin Legum, Gogotsi’s doctoral student, mixed 0.5-5 percent MXene into a well-known ceramic system called zinc oxide. The metallic MXene coated the ceramic powder and formed continuous two-dimensional grain boundaries, which prevented grain growth, increased the conductivity by two orders of magnitude, transforming semiconducting zinc oxide into a metallic ceramic, and doubled hardness of the final product. The addition of MXene also improved the ability of zinc oxide to transform heat to electricity.
“Ben came here quite frequently to work with Jing, and over time they overcame all of the problems involved with dispersing the 2D MXenes into the zinc oxide and then sintering it,” said Randall. “This opens a whole new world incorporating 2D materials into ceramics.”
Gogotsi added, “This is the first ceramic composite containing MXene. Taking into account that about thirty MXenes with diverse properties are already available, we are opening a new chapter in research on ceramic matrix composites, with potential applications ranging from electronics to batteries and thermoelectrics.”
Guo and Legum are co-first authors on the paper “Cold Sintered Ceramic Nanocomposites of 2D MXene and Zinc Oxide.” Gogotsi and Randall are corresponding authors. Other contributors are Dr. Babak Anasori and undergraduate student Pavel Lelukh from Drexel, and Ke Wang, staff scientist in Penn State’s Materials Research Institute.
The work was supported by the Air Force Research Laboratory and the National Science Foundation.
Featured image: The schematic illustration showing the co-sintering of ceramics and 2D materials using cold sintering processing, and TEM image and energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) map of cold sintered 99ZnO-1Ti3C2Tx nanocomposite. The MXene nanosheets are distributed homogeneously along the ZnO grain boundaries, as seen in the TEM image and EDS map. Image credit: MRI/Penn State